The document defines and explains three key concepts in dynamics of machines:
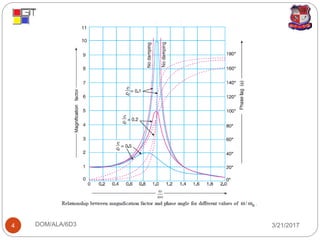
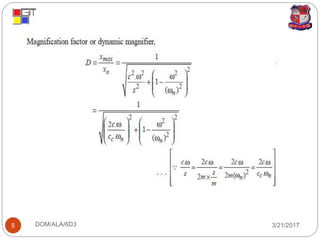
1. Magnification factor is the ratio of maximum displacement during forced vibration to static deflection.
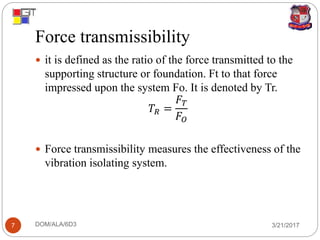
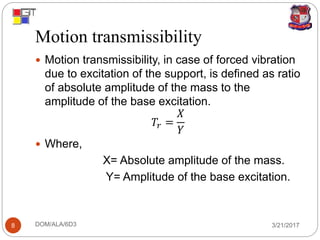
2. Vibration transmissibility measures how well a system isolates vibration, defined as the ratio of transmitted to input force (force transmissibility) or of mass to base amplitudes (motion transmissibility).
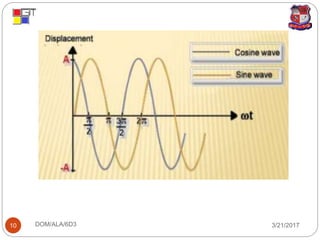
3. Phase difference is the difference in oscillation phases between two points over time, which can be any multiple of pi but 0 or 2pi indicate oscillations are in phase.