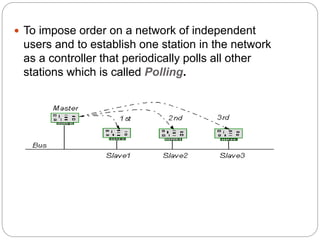
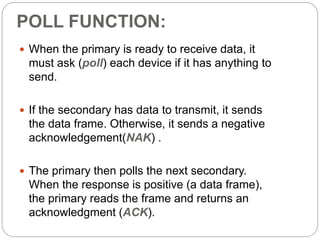
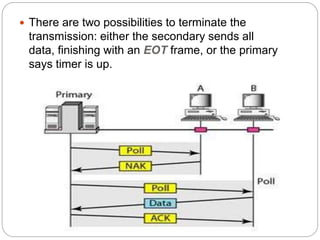
Polling is a method for controlling access to a shared medium where a primary station periodically polls or queries secondary stations on the network to see if they have any data to transmit. The primary station controls the link and knows when the medium is idle, but does not know the status of the receivers. It alerts receivers when it is ready to transmit and waits for an acknowledgement before sending data. The primary station must also poll each secondary station in turn when it is ready to receive data to see if any station has data to transmit. Polling allows for predictable access times but has drawbacks such as high dependence on the reliability of the primary station and reduced throughput under low loads.