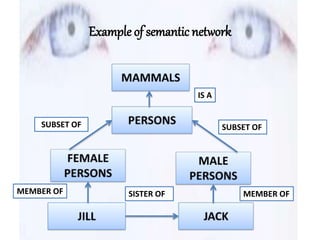
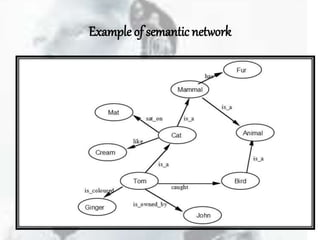
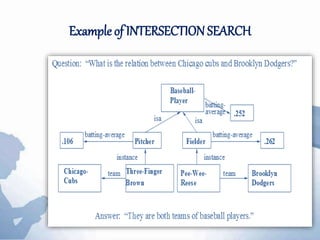
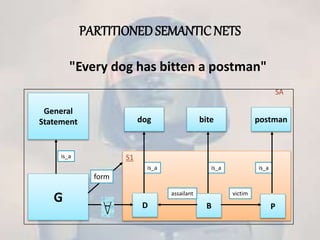
Semantic nets were originally proposed in the 1960s as a way to represent the meaning of English words using nodes, links, and link labels. Nodes represent concepts, objects, or situations, links express relationships between nodes, and link labels specify particular relations. Semantic nets can represent data through examples, perform intersection searches to find relationships between objects, partition networks to distinguish individual from general statements, and represent non-binary predicates. While semantic nets provide a visual way to organize knowledge, they can have issues with inheritance and placing facts appropriately.