Embed presentation
Download to read offline

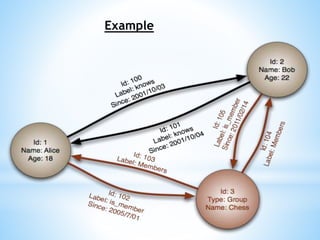






A graph database uses nodes and edges to store, map, and query relationships between data in a way that is optimized for highly connected information. It allows for schema-less and efficient storage of semi-structured data connected by rich relationships. Example applications include graph compute engines, recommendation systems, search engines, and social networks. While graph databases are well-suited for exploring connected data, they may not support data partitioning or use the single relational concept that traditional databases use.








