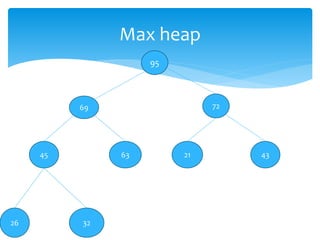
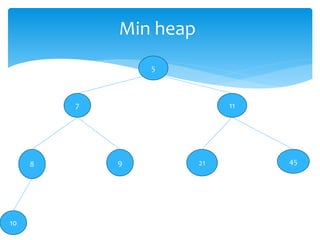
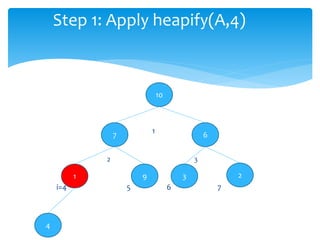
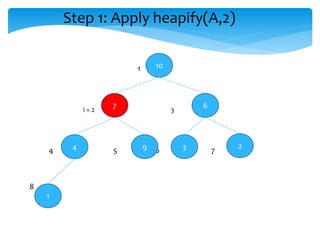
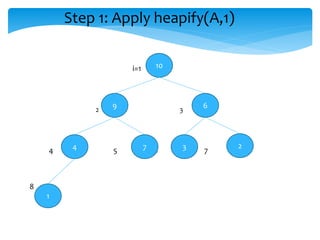
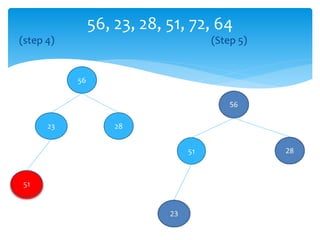
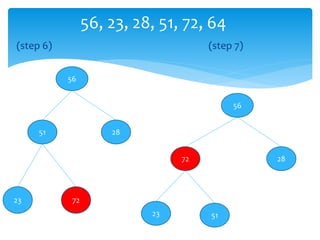
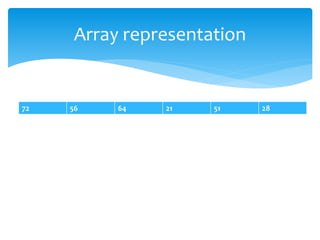
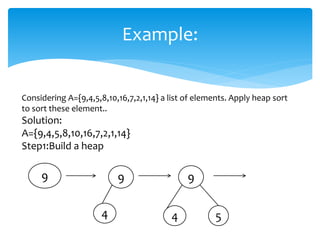
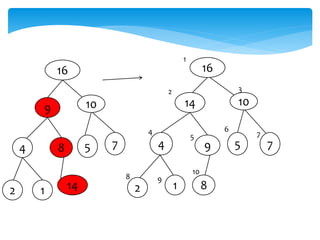
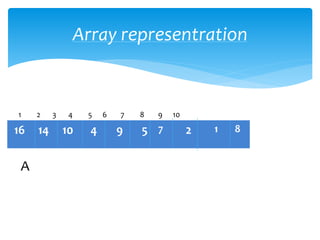
This document describes heap data structures and algorithms like heap sort. It defines a max heap and min heap. It explains the build heap, heapify, insertion and deletion algorithms. Build heap transforms an array into a max heap by applying heapify to each node from bottom to top. Heapify maintains the heap property when a node is added or removed. Heap sort works by building a max heap from the input array and then extracting elements from the root to sort the array in descending order.









![ Heapify is nothing but the procedures of heap.
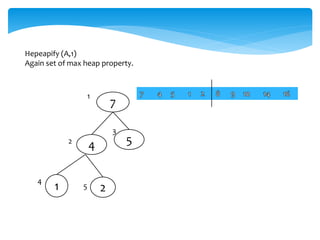
Heapify is a procedure for manipulating heap data
structures.
It is given an array A and index i into the array. The sub tree
rooted at the children of A[i] are heap but node A[i] itself
may possibly violate the heap property i.e., A[i] < A[2i] or
A[i] < A[2i +1]. The procedure 'Heapify' manipulates the
tree rooted at A[i] so it becomes a heap. In other words,
'Heapify' is let the value at A[i] "float down" in a heap so
that sub tree rooted at index i becomes a heap.
What is heapify ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-15-320.jpg)









![HEAPSORT ALGORITHM
HEAPSORT(A)
1. BUILD‐MAX‐HEAP(A)
2. for i ← length[A] downto 2
3. do exchange A[1] A[i]
4. heap‐size[A] ← heap‐size[A] −1
5. MAX‐HEAPIFY(A, 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-29-320.jpg)

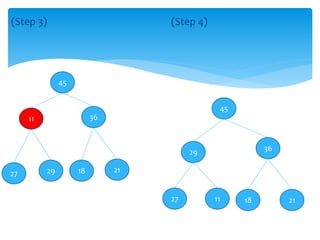
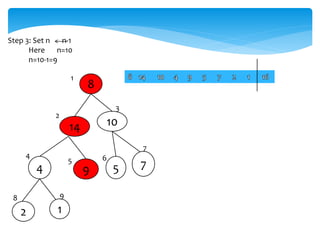
![Step 2: for i = n to 1 do
Swap( A[1],A[i])
8
14 10
4 9 5 7
2 1 16
Swap(A[1],A[10])
Swap(16,8)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-34-320.jpg)
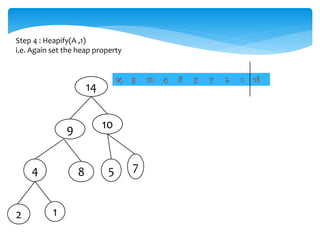
![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],A[9])
1
9 10
4 8 5 7
2 14
1
2
3
4
5
6 7
8
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-37-320.jpg)

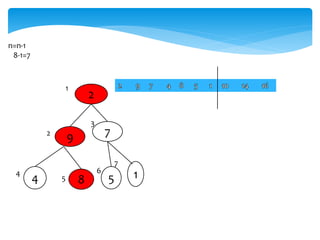
![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],A[8])
2
9 7
4 8 5 1
10
1
2
3
4
5
6 7
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-39-320.jpg)
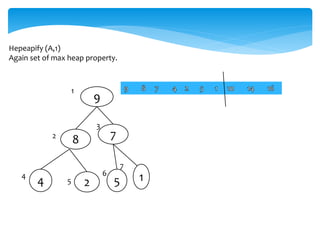
![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],A[7])
8 7
4 2 5
1
2
3
5
6
7
9
1
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-42-320.jpg)
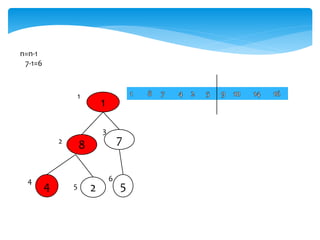

![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],A[6])
4 7
1 2 8
1
2
3
6
5
4
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-45-320.jpg)
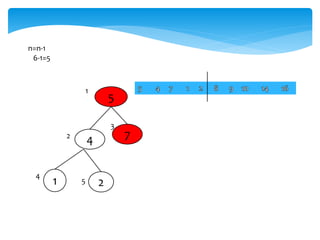
![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],A[5])
4 5
1
7
2
3
4
1
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-48-320.jpg)
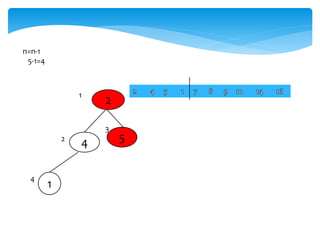

![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],[4])
4 22
3
4
1
1
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-51-320.jpg)
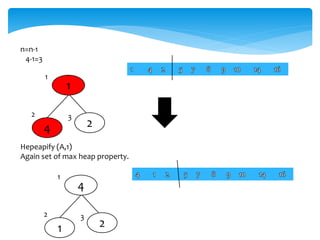
![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],[3])
1 4
2 3
2
1
n=n-1
3-1=2
1
2
2
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-53-320.jpg)
![Swap(A[1],A[i])
Swap(A[1],[2])
2
2
1
1
n=n-1
2-1=1
1
1
SORTED LIST.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7f48d492-1f9a-4f2e-8406-03a47d972fac-160603111400/85/Heap-54-320.jpg)


