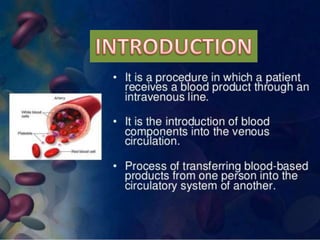
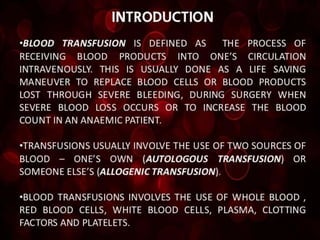
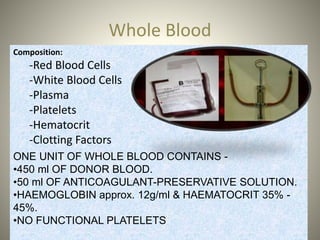
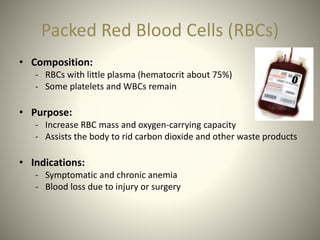
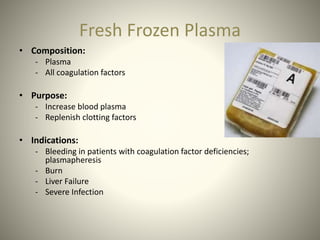
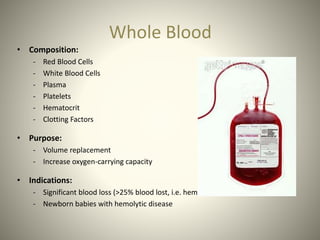
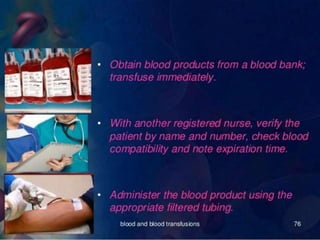
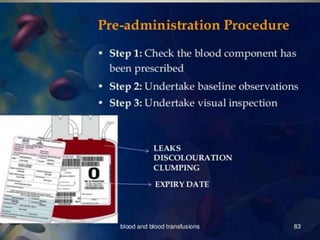
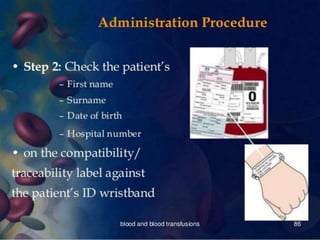
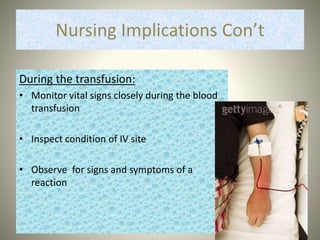
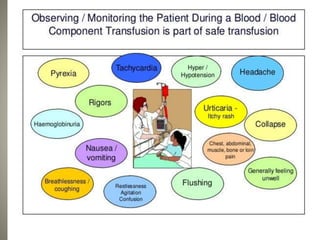
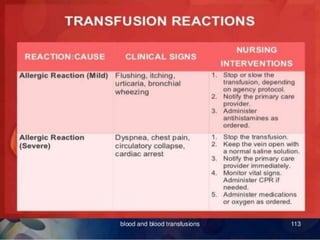
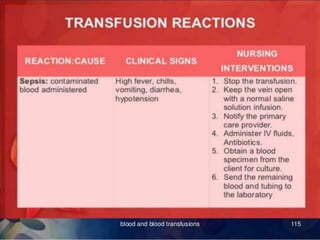
Whole blood, packed red blood cells, fresh frozen plasma, platelets, and cryoprecipitate are the main blood components used for transfusions. Each component has a specific composition and purpose. Whole blood contains all blood components and is used for volume replacement after significant blood loss. Packed red blood cells contain mostly red blood cells and increase oxygen carrying capacity, while fresh frozen plasma contains clotting factors to treat bleeding disorders. Platelets help stop bleeding and cryoprecipitate contains high levels of factor VIII and fibrinogen. Nurses must closely monitor patients during transfusions for signs of reactions and ensure appropriate screening, consent, and administration of blood products.