Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times




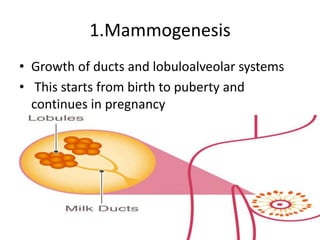
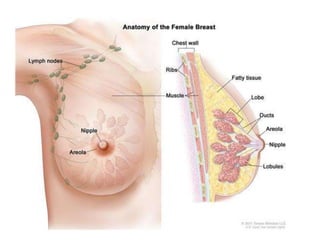
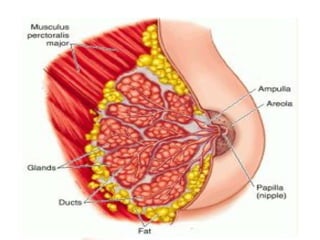

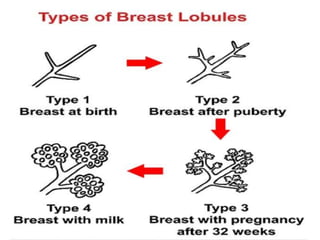





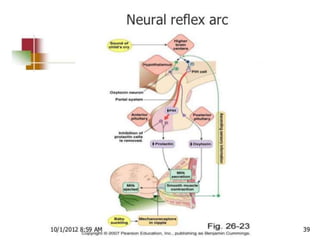








This document discusses lactation and its management. It is divided into four stages: mammogenesis, lactogenesis, galactokinesis, and galactopoiesis. Mammogenesis involves the development of the breasts into a functional state, starting from birth through puberty and continuing in pregnancy. During pregnancy, progesterone, estrogen, and prolactin contribute to increased growth and differentiation of breast structures. The secretion from breasts is called colostrum, which starts during pregnancy and is higher in protein, vitamin A, sodium, and chloride than mature breast milk.






















