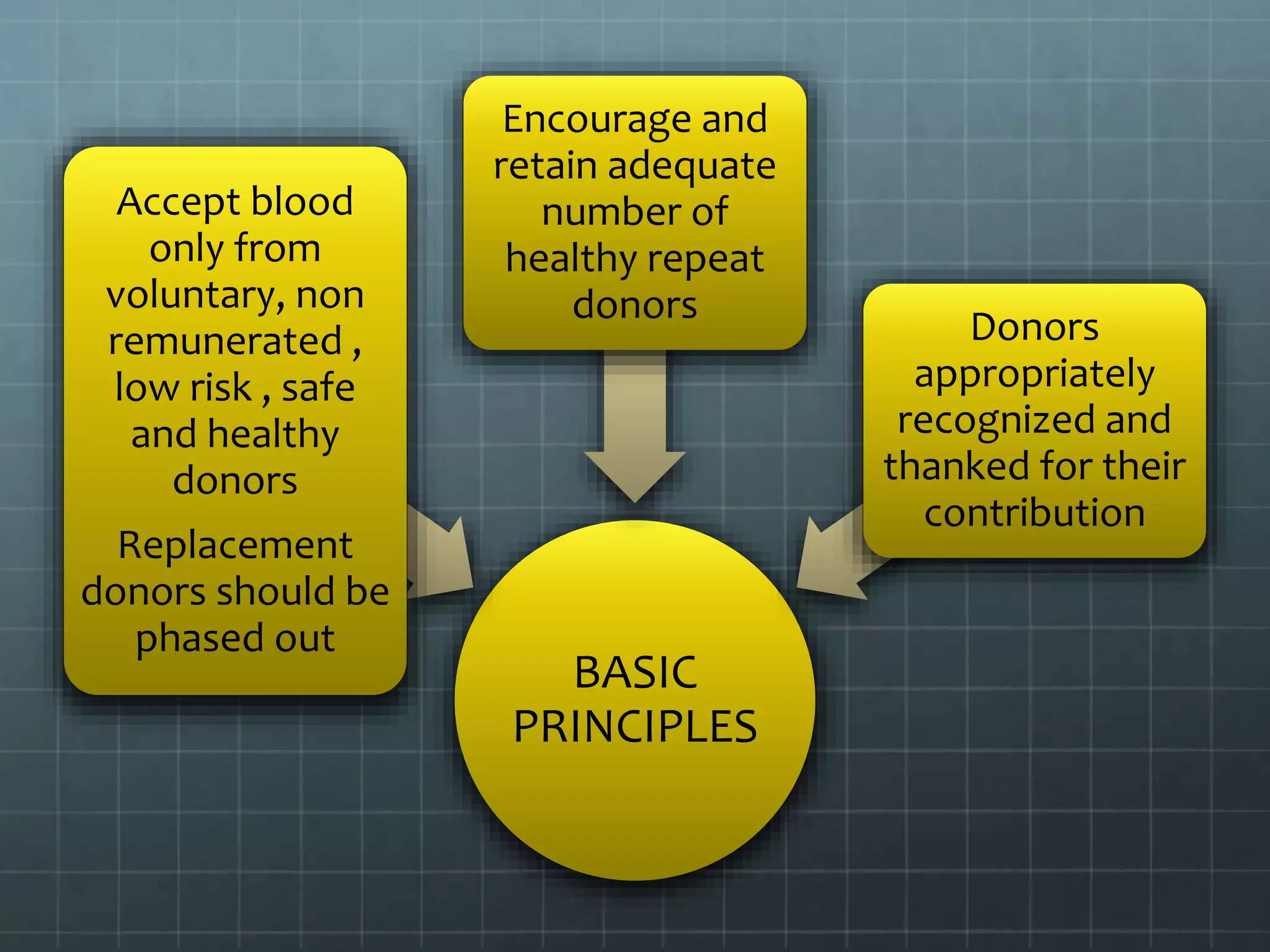
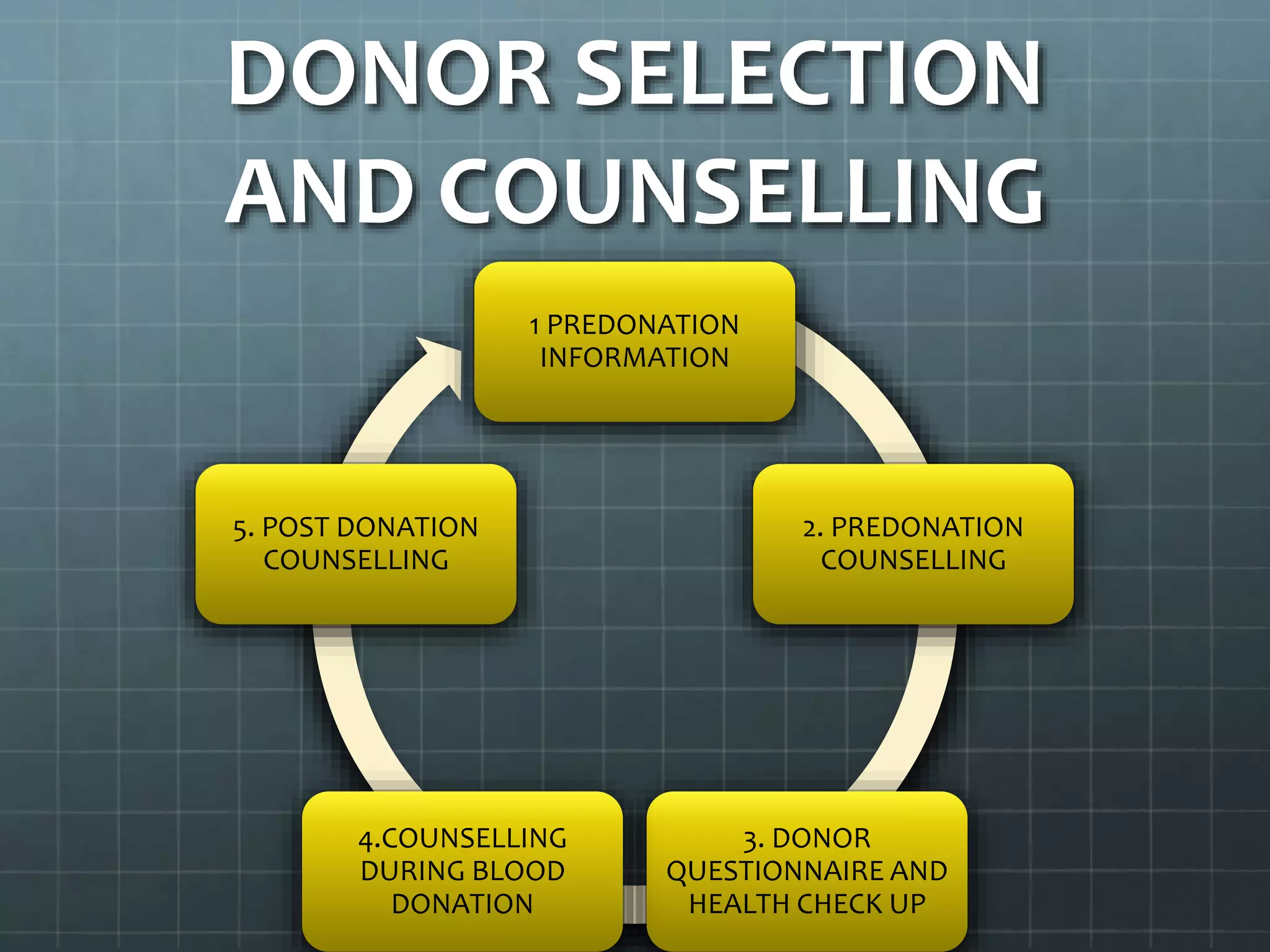
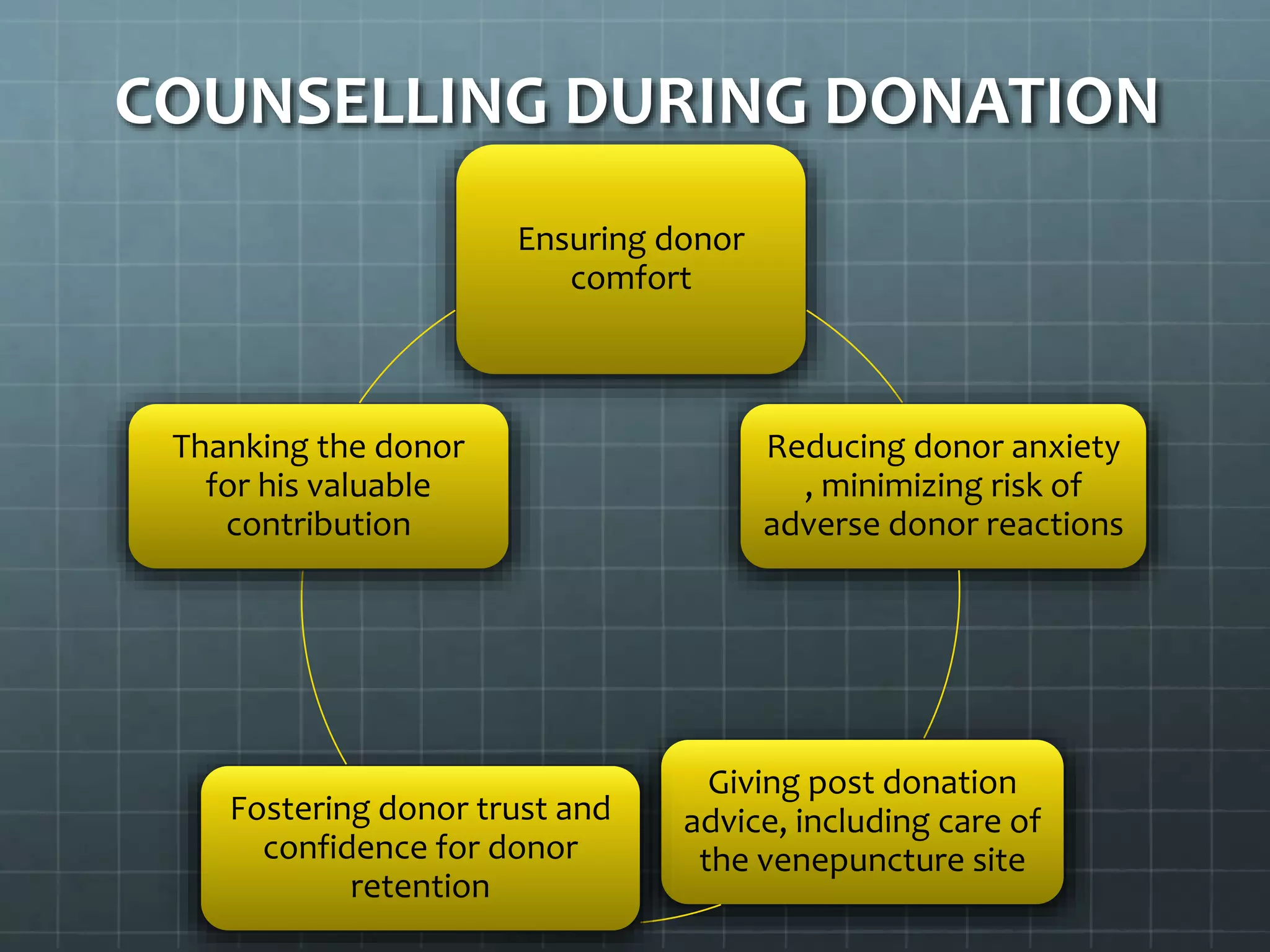
The revised NBTC guidelines for blood donor selection and deferral aim to ensure a safe and sufficient blood supply by accepting blood only from healthy, voluntary, non-remunerated donors. Key recommendations include comprehensive donor screening, informed consent, and various deferral criteria based on health conditions and risk behaviors. The guidelines also emphasize the importance of donor motivation, retention, and post-donation care to foster donor trust and regular contributions.