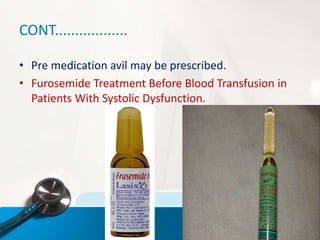
The document outlines the objectives and procedures for blood transfusions in nursing, including definitions, purposes, components, and complications. It details the necessary preparations and precautions before, during, and after transfusion, along with identification of blood types and potential reactions. It emphasizes the importance of proper administration and monitoring to mitigate risks associated with blood transfusions.

















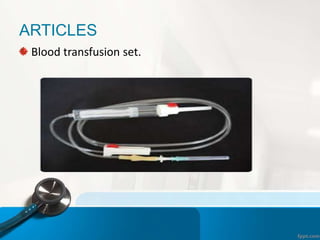
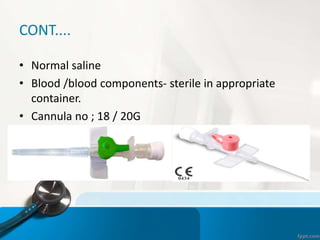





![12. Inspect the blood product[by 2 nurses] for
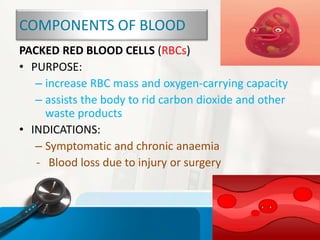
1.Identification number
2.Expiry date.
3.Compartibility
4.Patients name
5.Abnormal colour,clots,excess air etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bloodtrnsfusionnew-200415015330/85/Blood-transfusion-procedure-precaution-and-complication-37-320.jpg)


![16.Assess the condition of pt every 30minutes and if
any adverse effect is observed stop transfusion and
start saline. send urine sample ,blood sample, and
remaining blood product in container with
transfusion set, back to the blood bank.
17.Complete transfusion and administer saline [ as
per physician's order] if no adverse reaction is
observed.
18.Dispose blood product container and set in
a appropriate receptable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bloodtrnsfusionnew-200415015330/85/Blood-transfusion-procedure-precaution-and-complication-42-320.jpg)
















