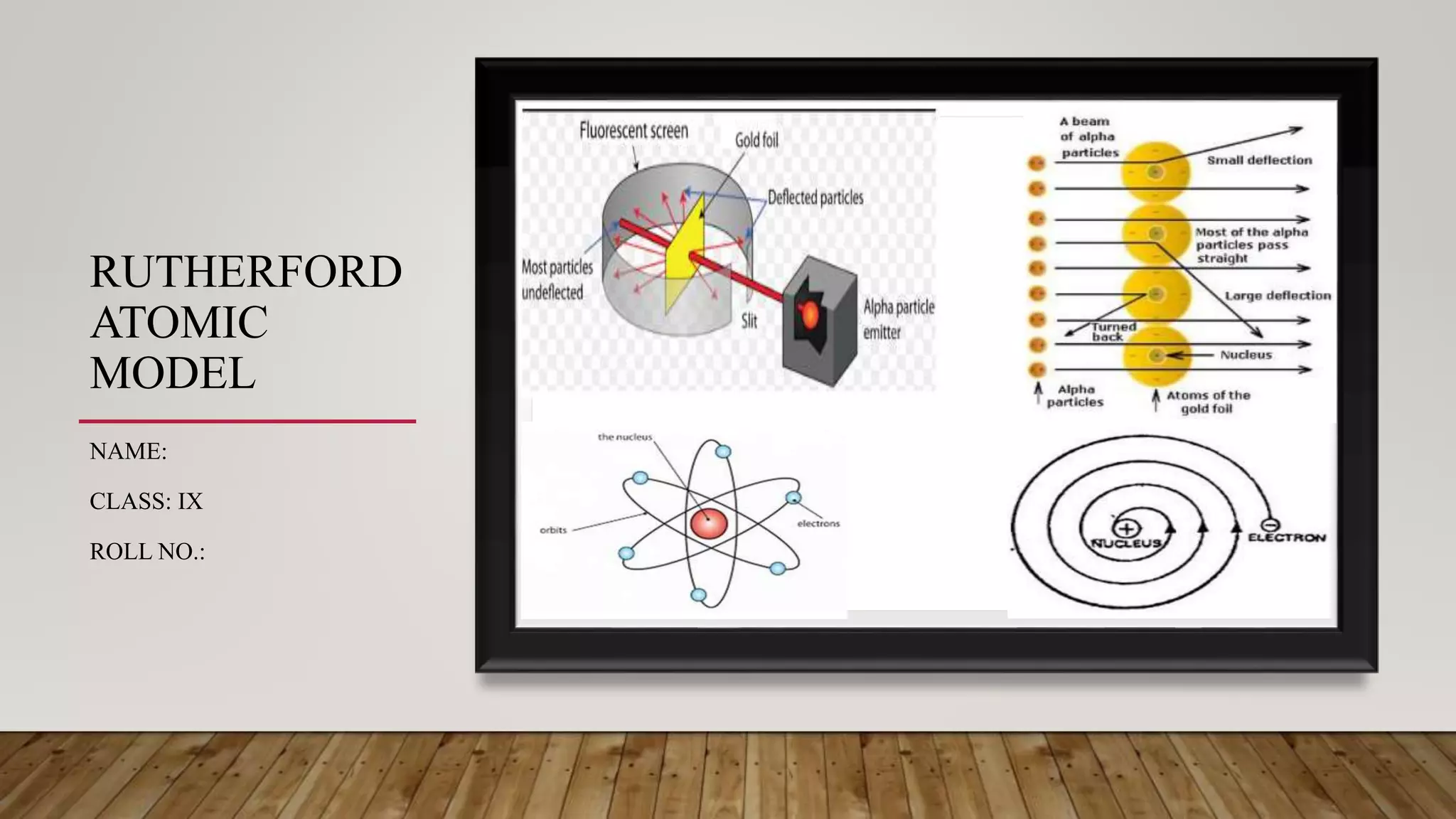
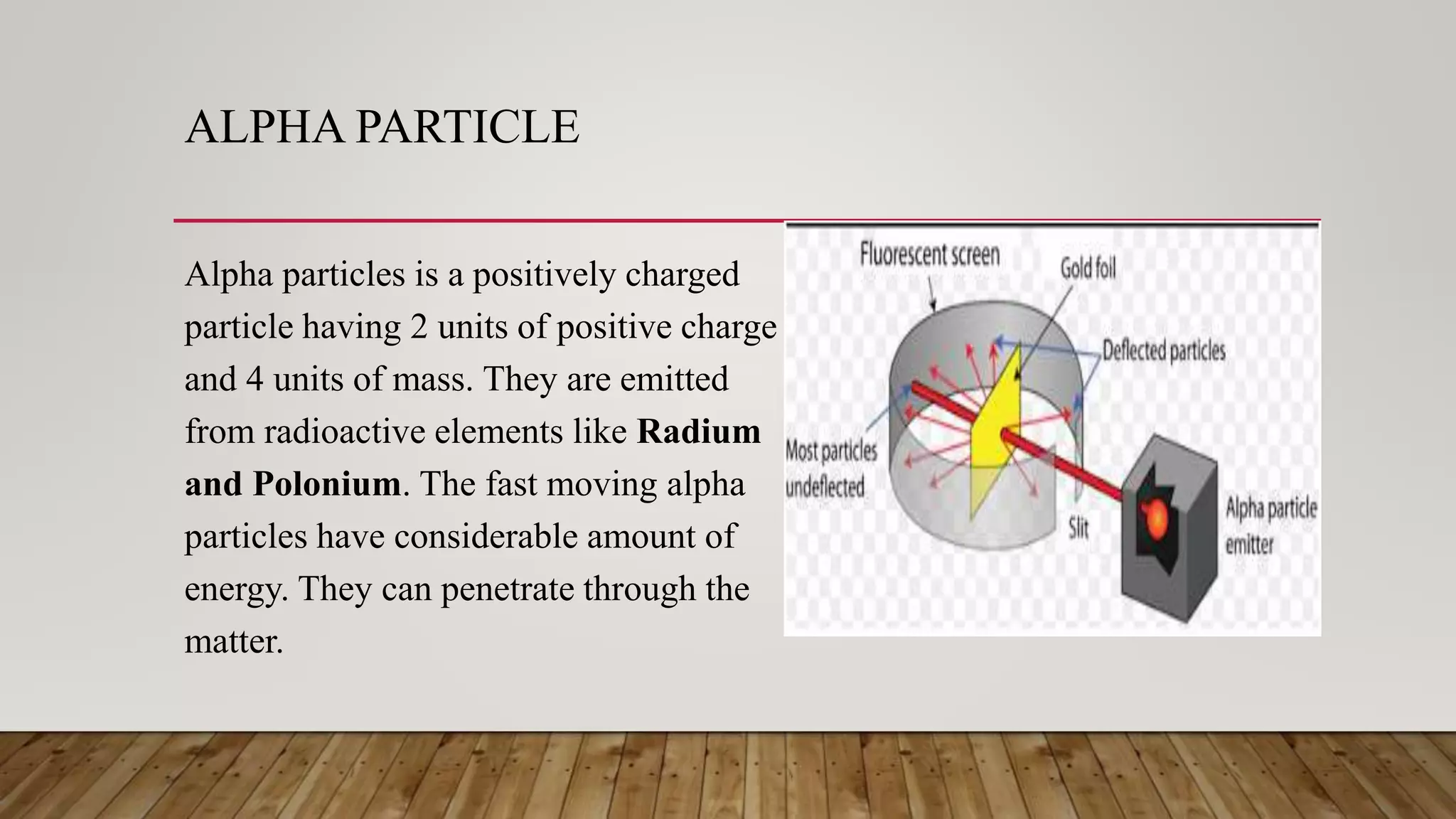
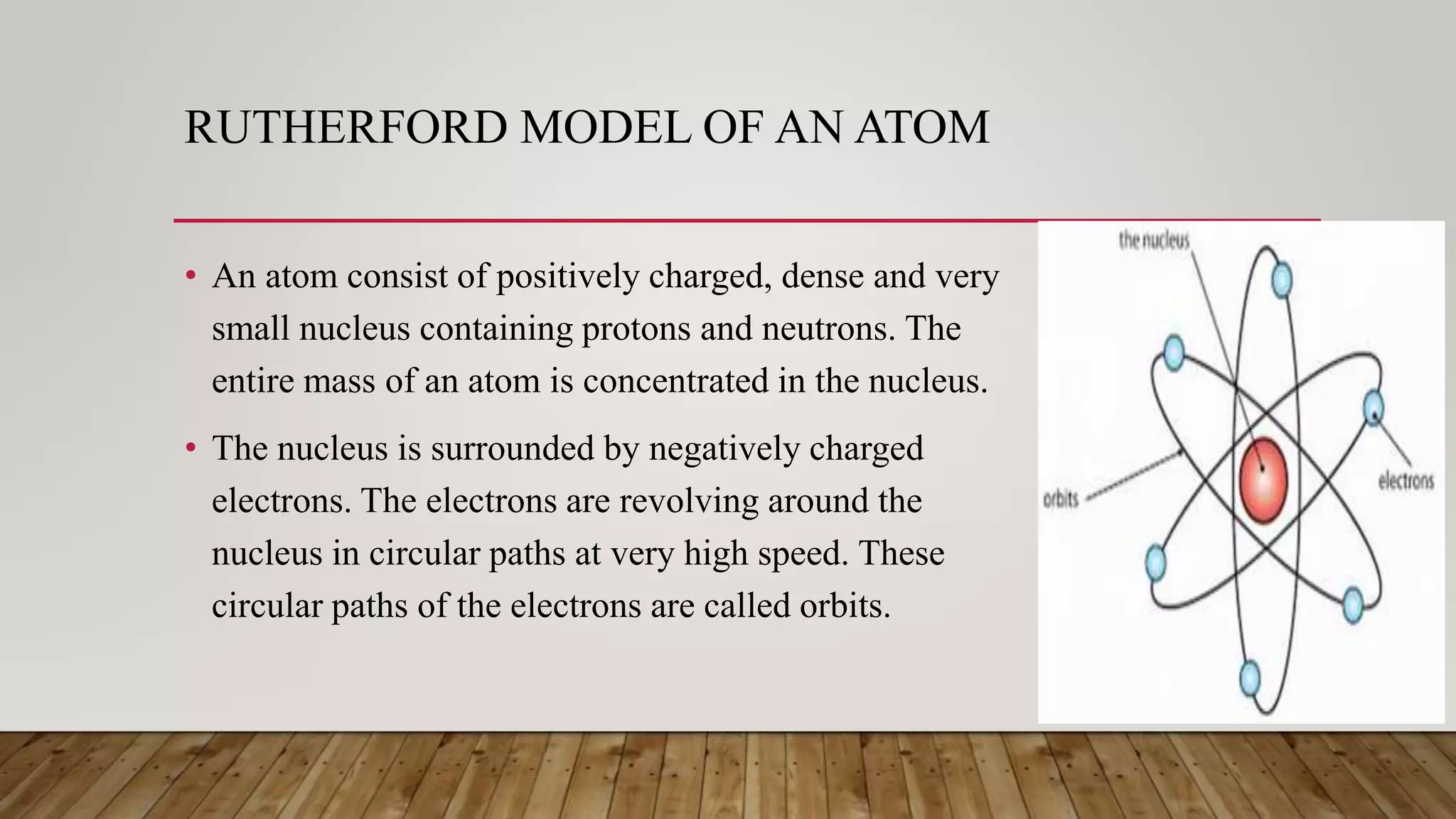
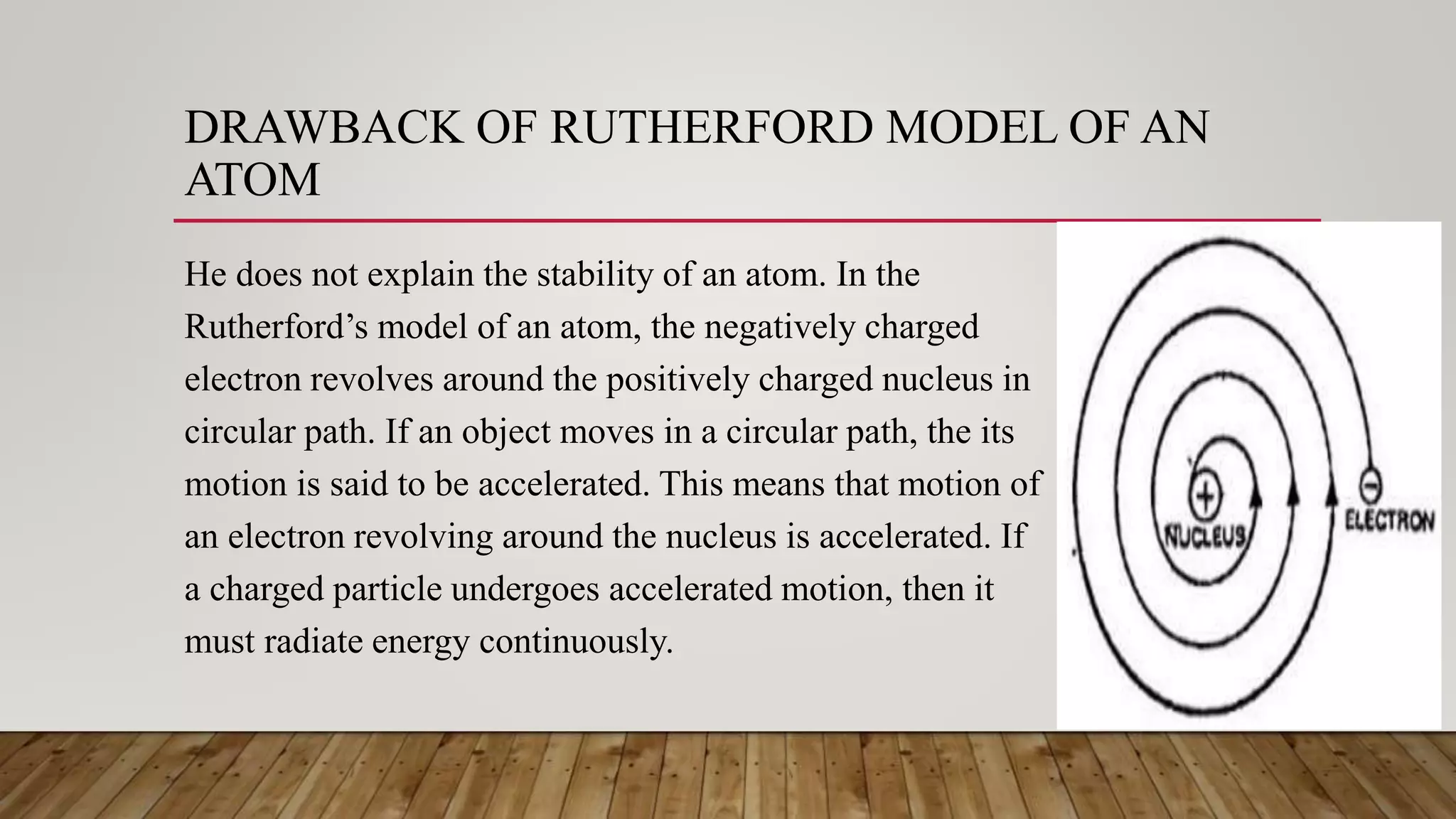
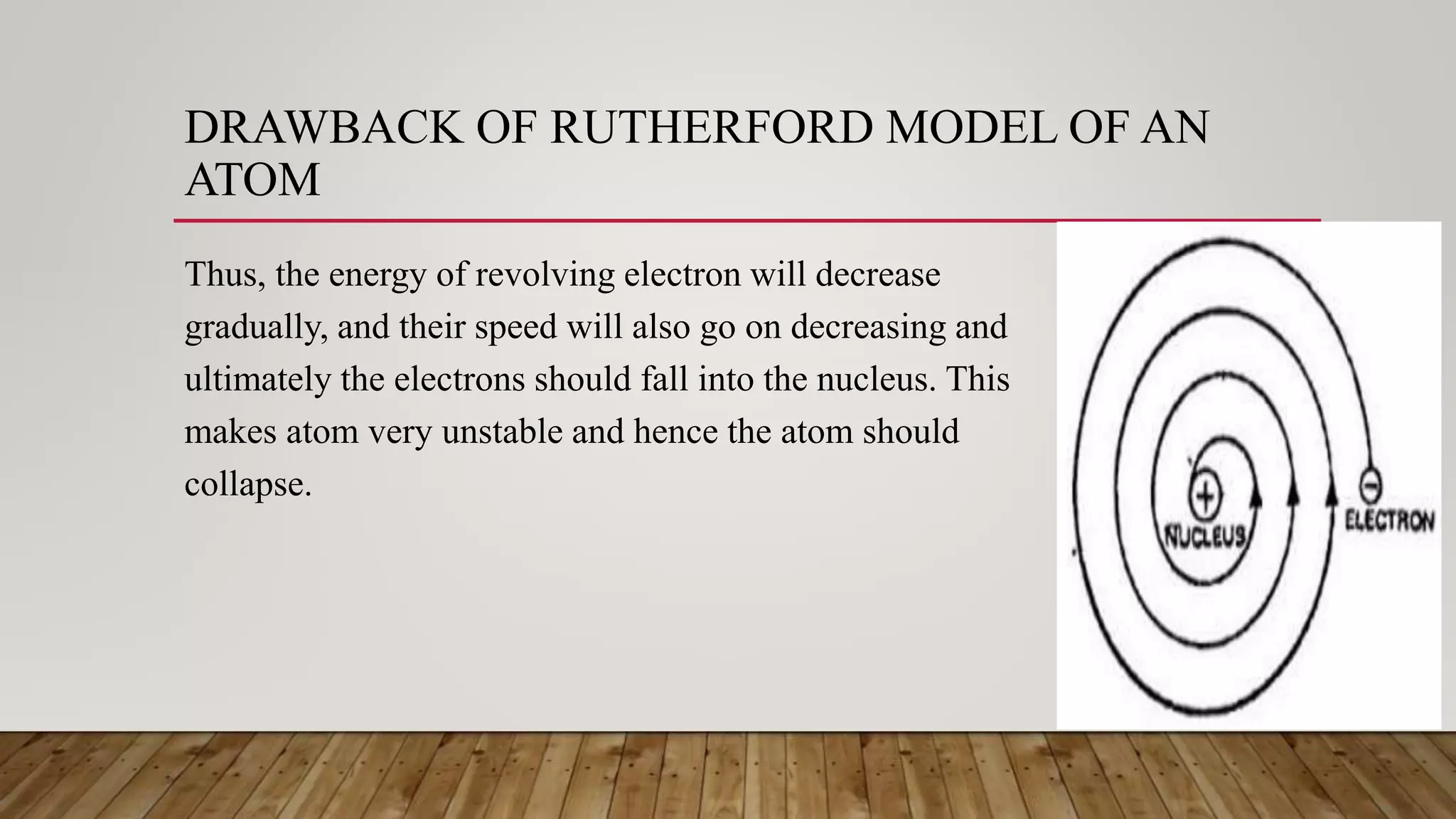
Rutherford conducted an experiment where he fired alpha particles at a thin gold foil. Most particles passed through without deflection, but some were deflected at small angles and a few were reflected back. This led Rutherford to propose an atomic model where the atom consists of a very small, dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons in orbits. However, his model did not explain atomic stability as it predicted electrons would radiate energy and spiral into the nucleus.