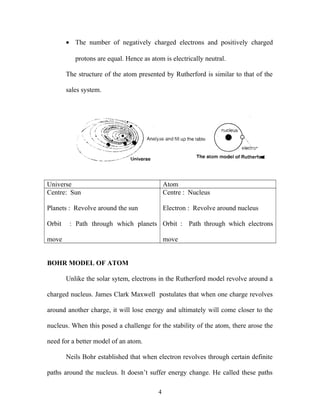
Rutherford conducted an experiment involving gold foil and alpha particles that revealed the structure of atoms. He discovered that atoms have a small, dense nucleus at their center that contains positive charge, and electrons orbit the nucleus. This Rutherford model of the atom likened the atom to the solar system, but Bohr later refined the model by proposing that electrons can only orbit in certain fixed energy levels. Bohr's model helped explain the stability of atoms and allowed for electrons to move between defined energy shells.