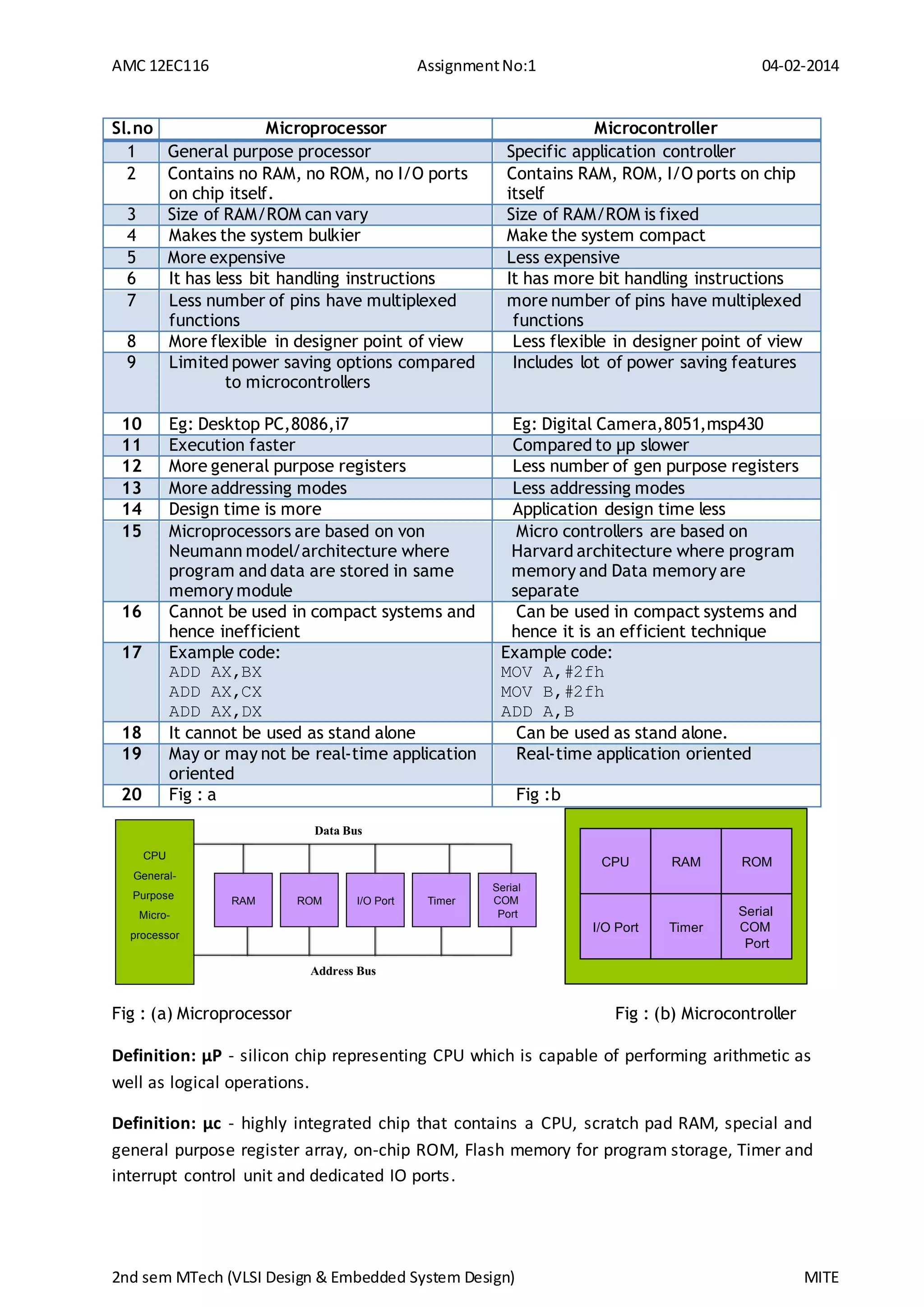
Microprocessors and microcontrollers are both integrated circuits that contain a CPU, but they have key differences. Microprocessors are general purpose processors that do not contain RAM, ROM, or I/O ports on the chip itself, while microcontrollers are application specific and contain RAM, ROM, and I/O ports on a single chip. Microcontrollers are more compact, less expensive, and include more power saving features than microprocessors. Examples of microprocessors include the 8086 and i7, while microcontrollers include the 8051 and msp430.