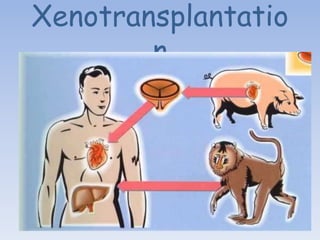
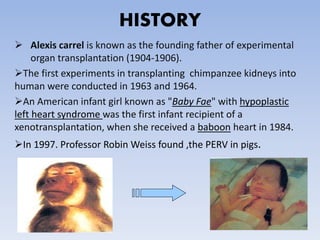
Xenotransplantation involves transplanting cells, tissues, or organs from one species to another, primarily from pigs to humans. It was developed to address the shortage of donor organs for transplantation in humans. While xenotransplantation could save many lives, it faces significant challenges including rejection from antibodies and T-cells, the risk of zoonotic disease transmission, and difficulties ensuring the organ functions properly across species barriers. Researchers are working to overcome these obstacles through genetic engineering of donor animals, developing better immunosuppression protocols, and monitoring for potential viruses. Current research focuses on transplanting pig tissues rather than whole organs. If the challenges can be resolved, xenotransplantation may provide a temporary treatment option for many in need of