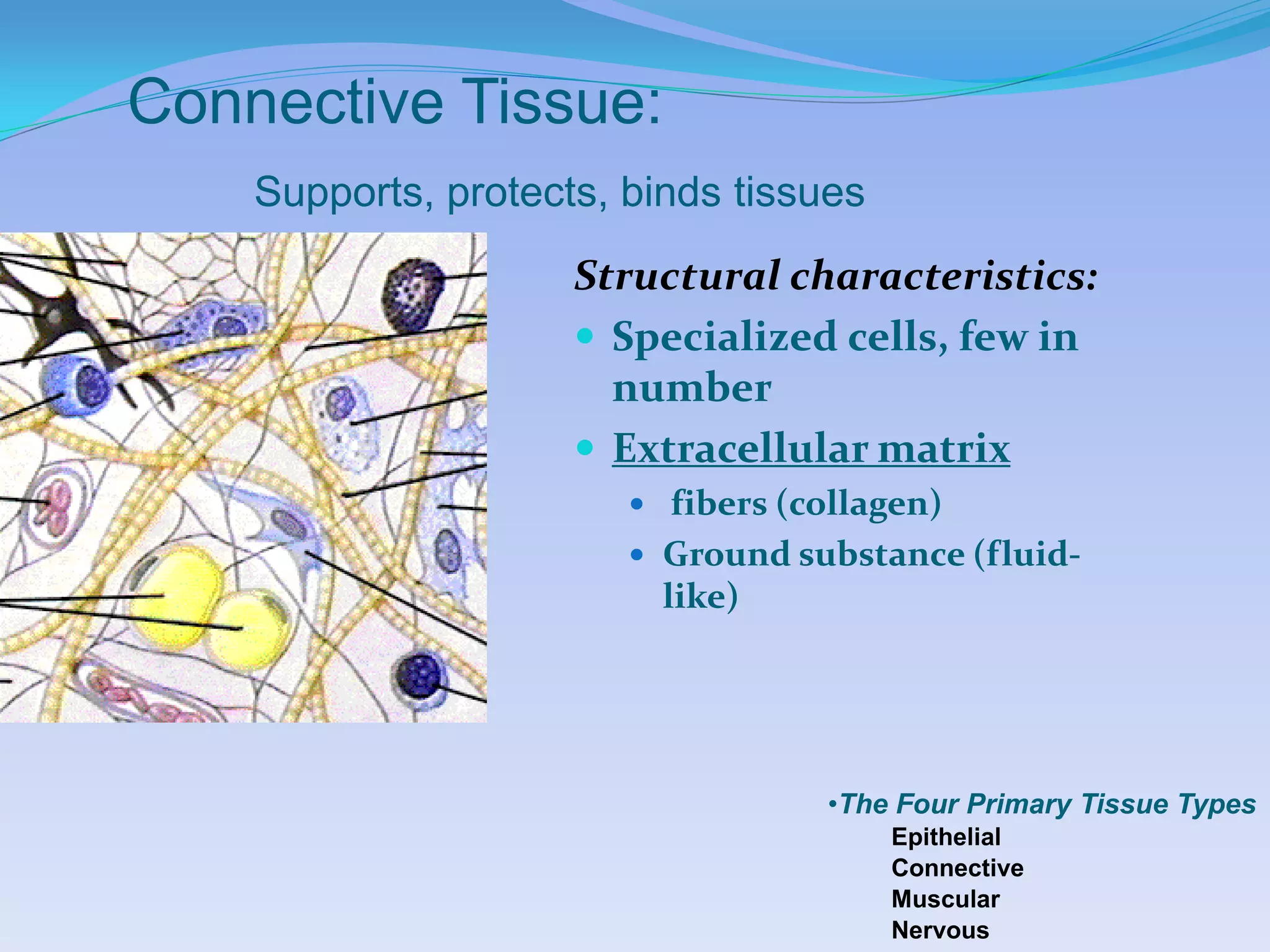
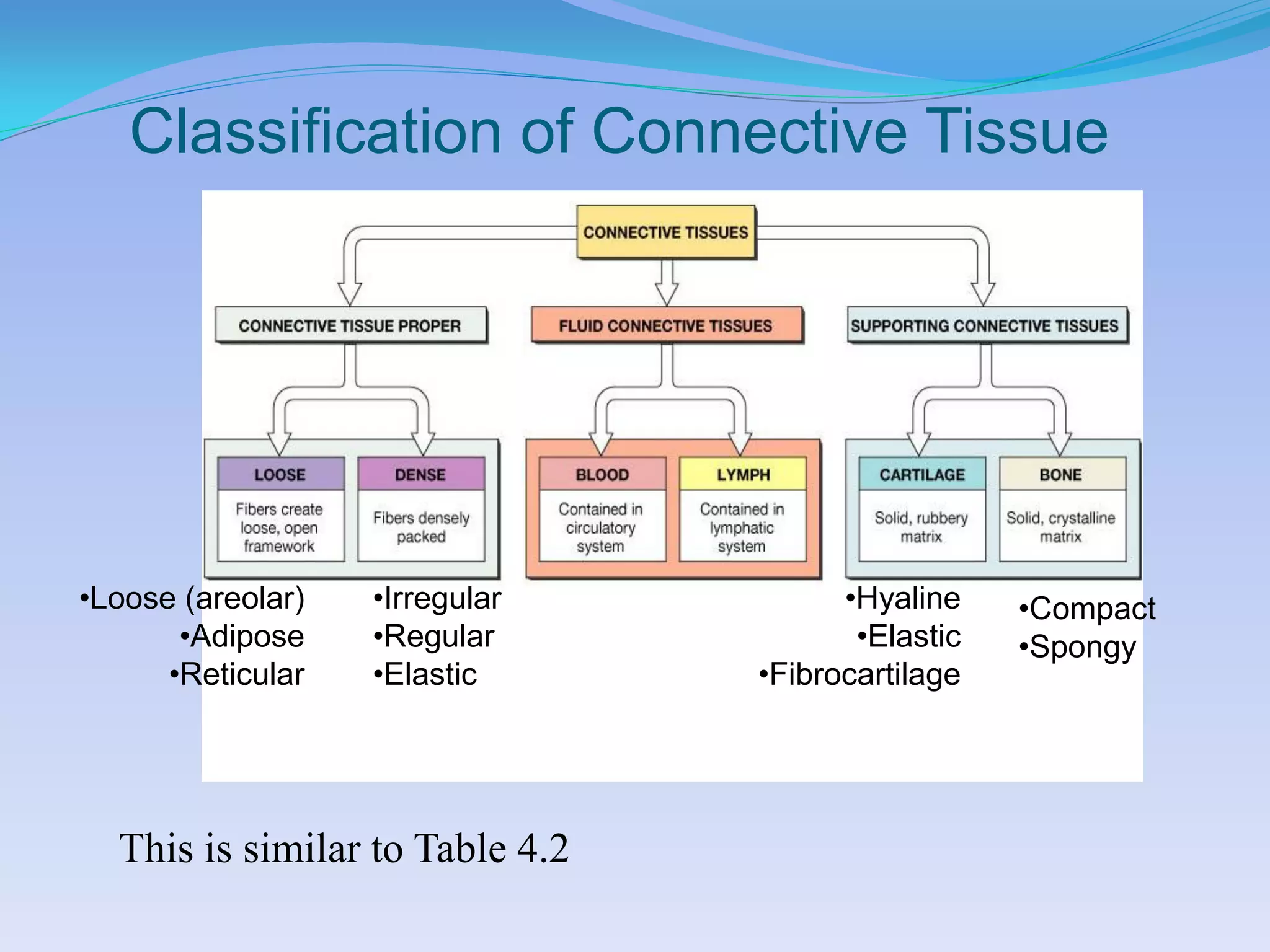
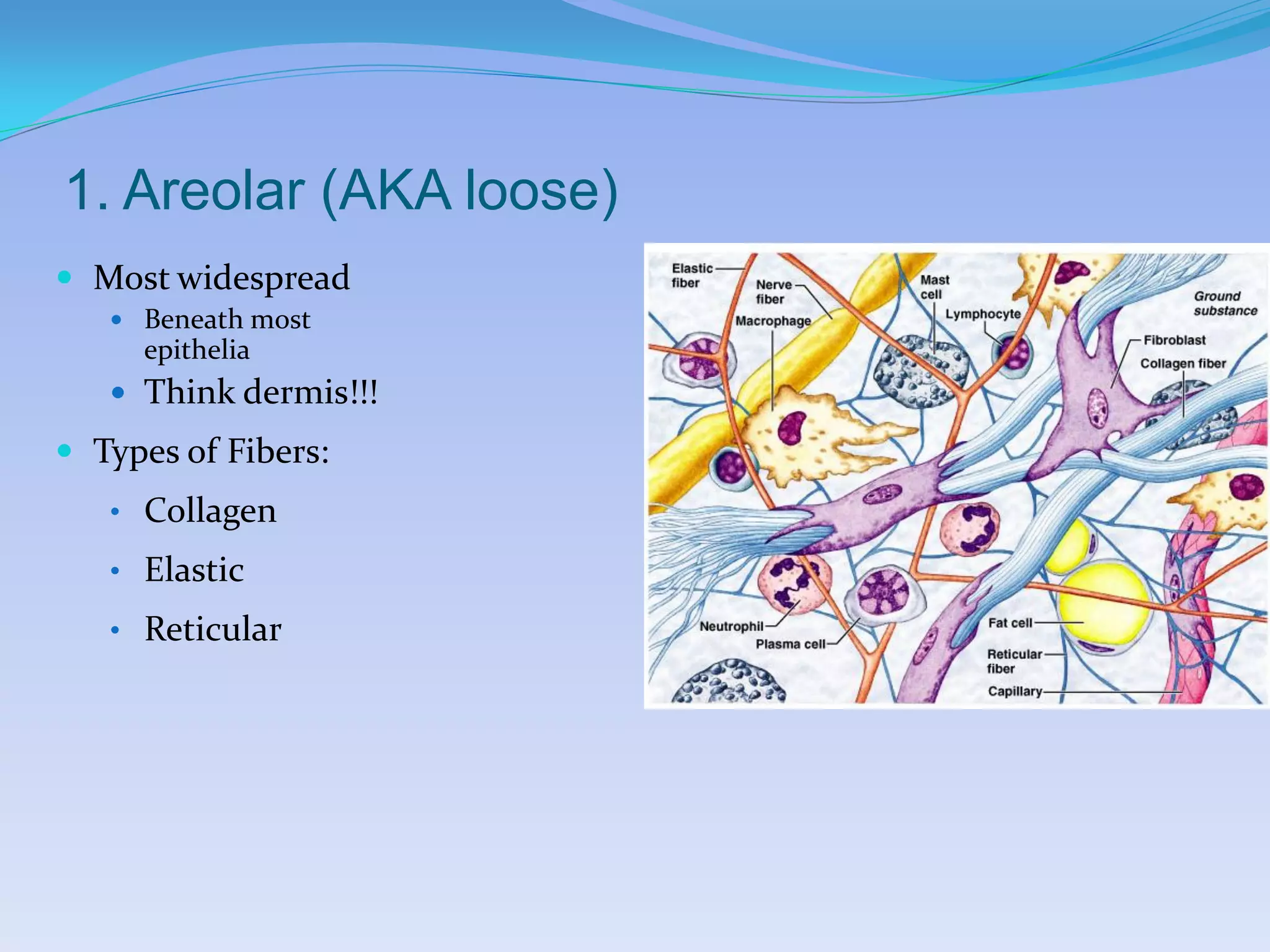
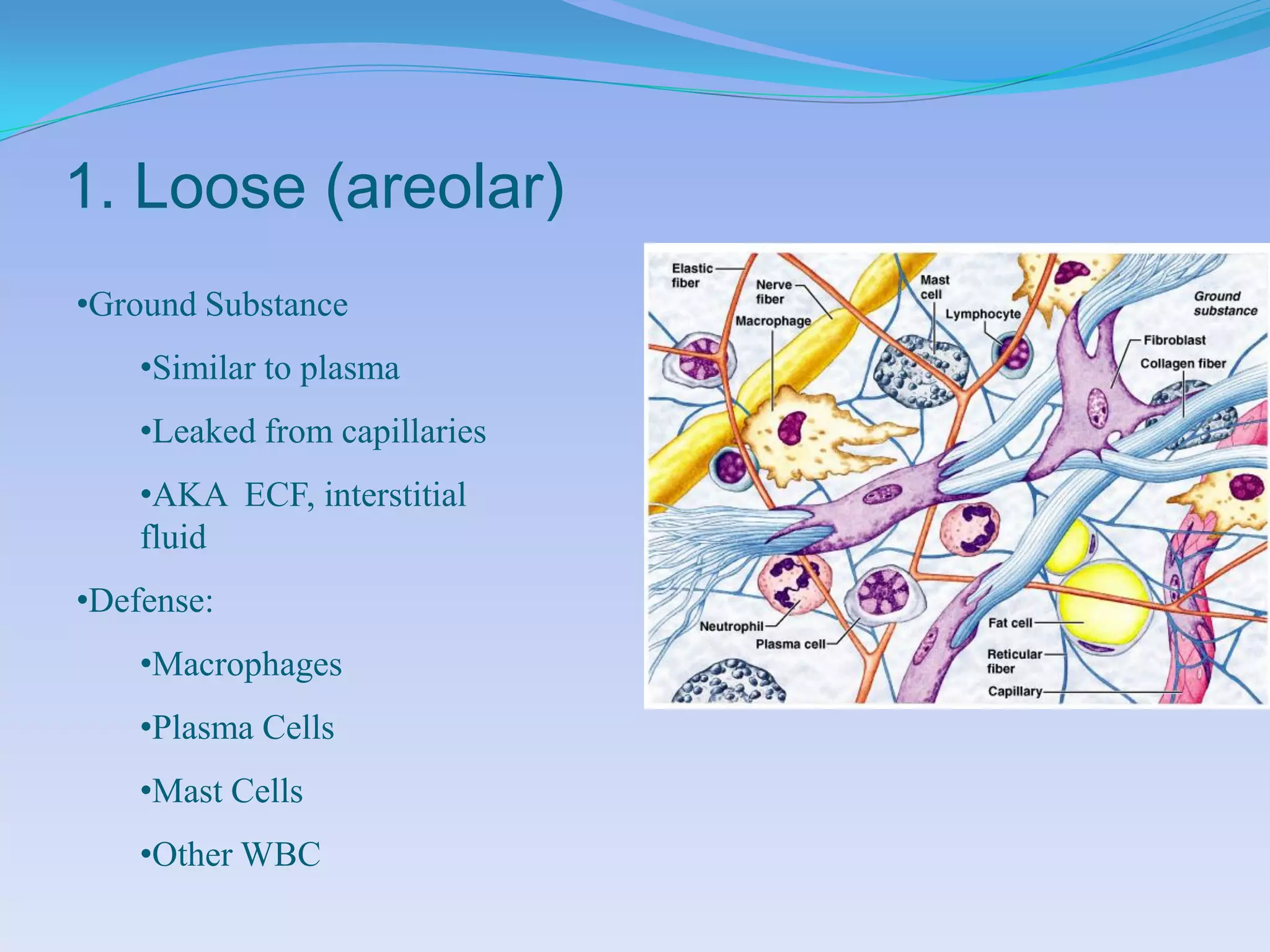
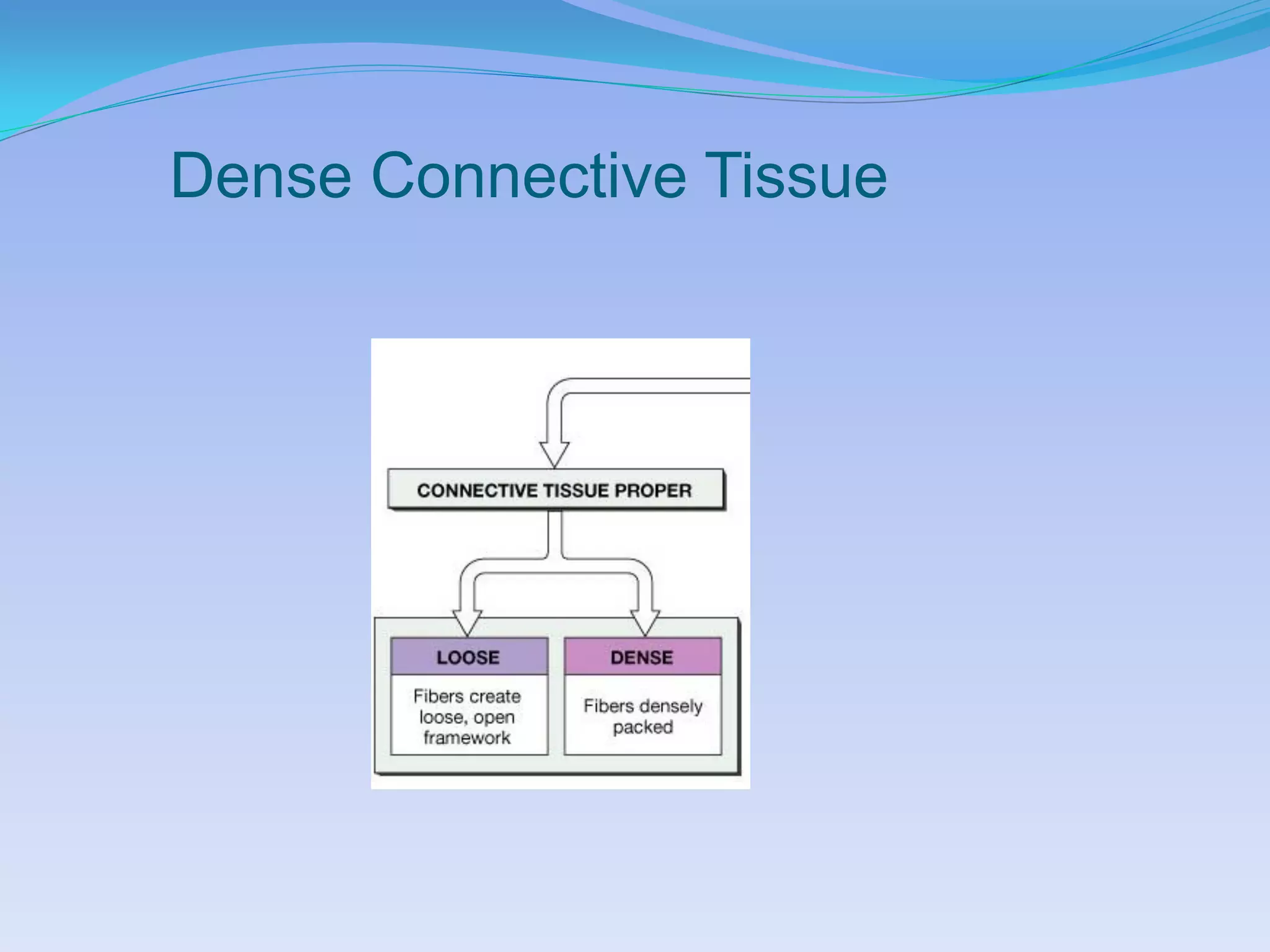
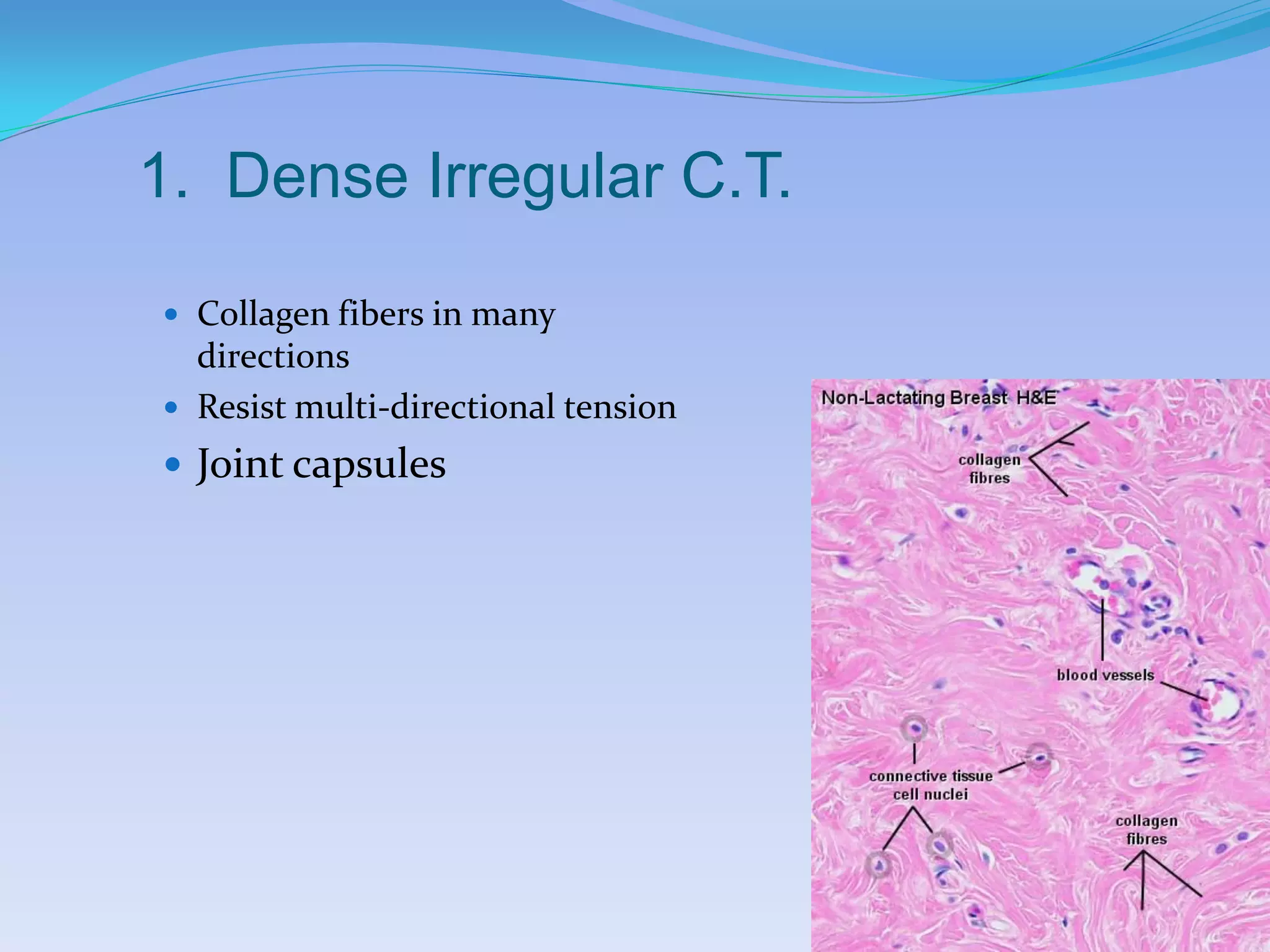
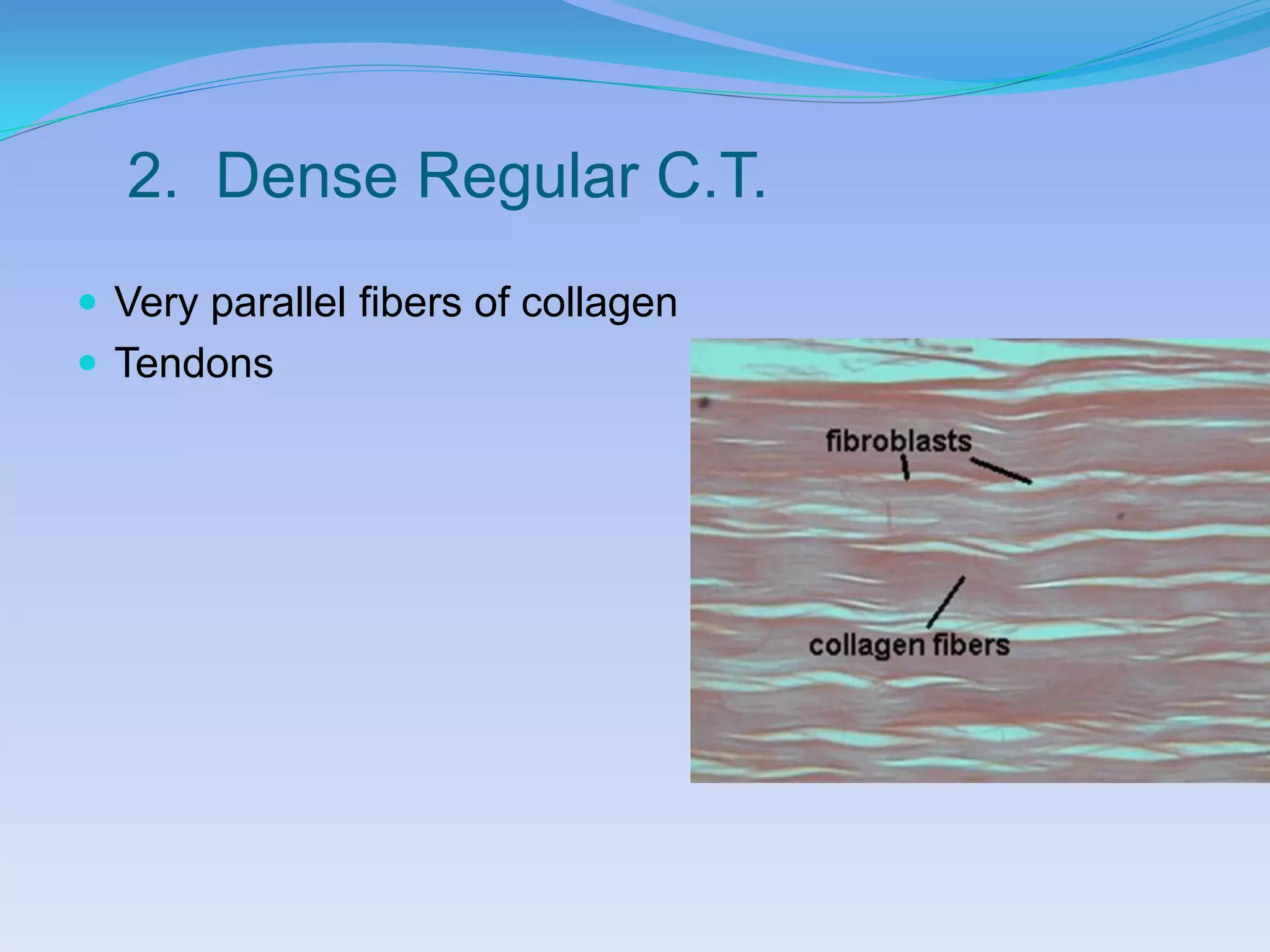
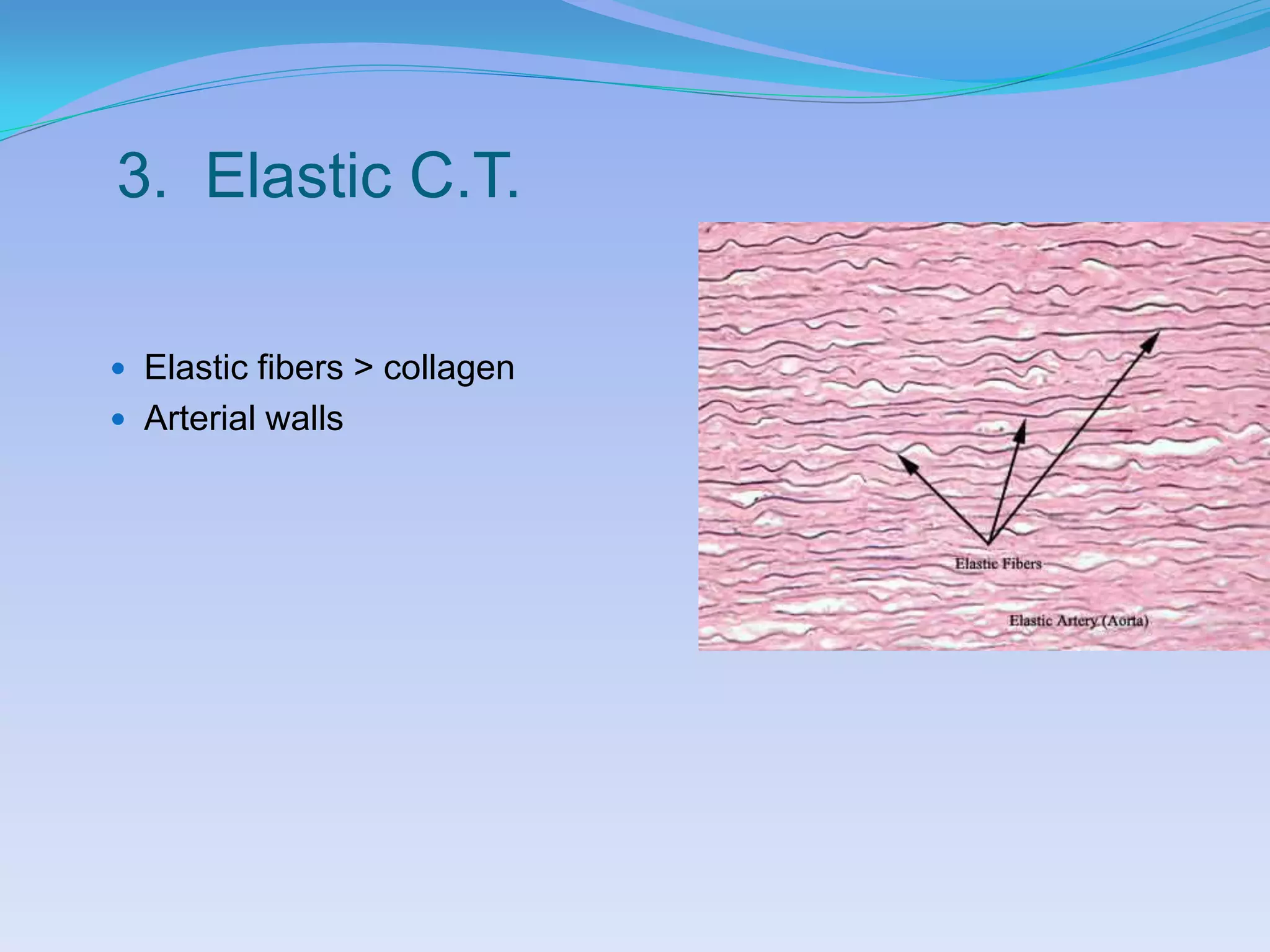
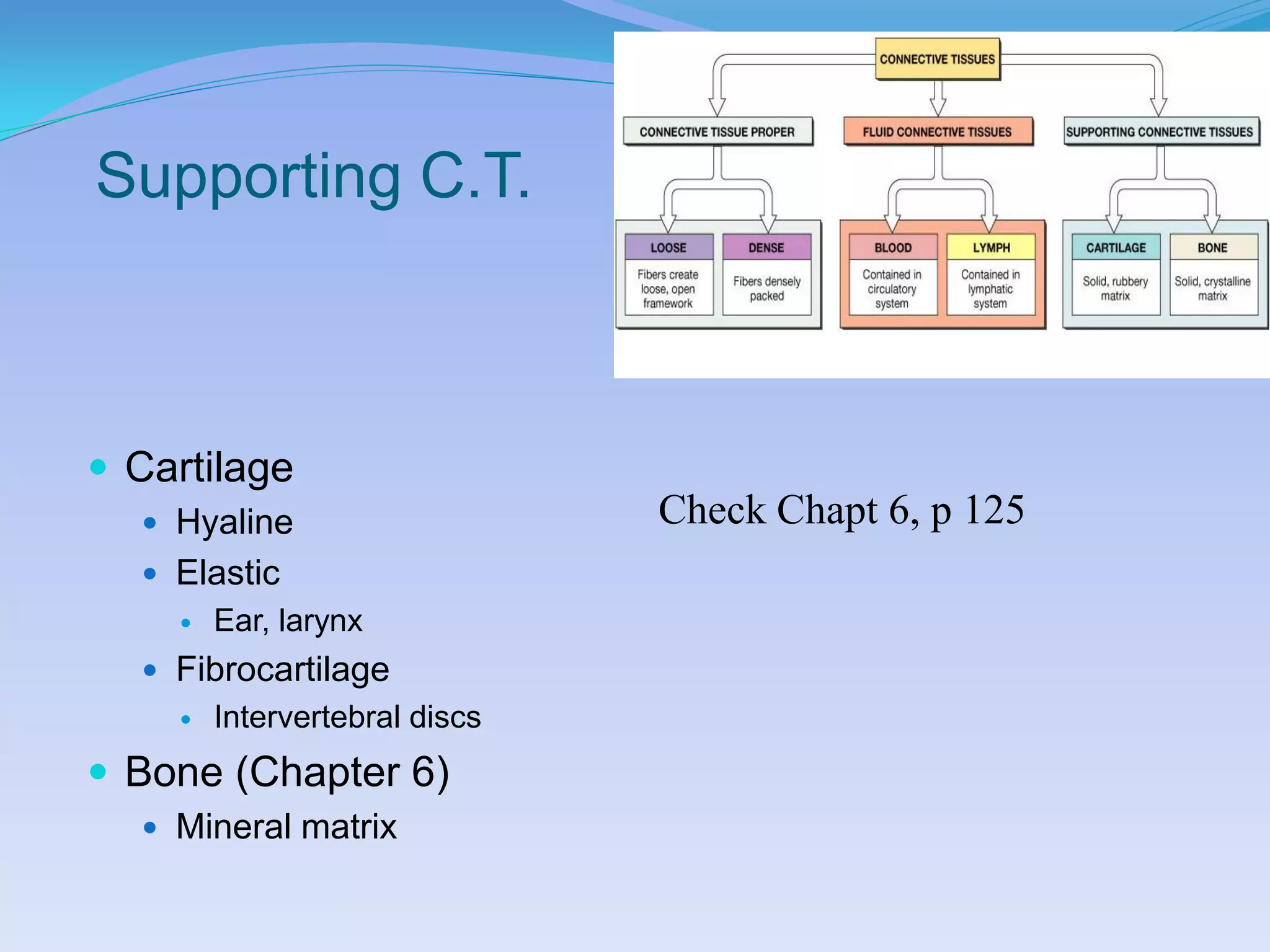
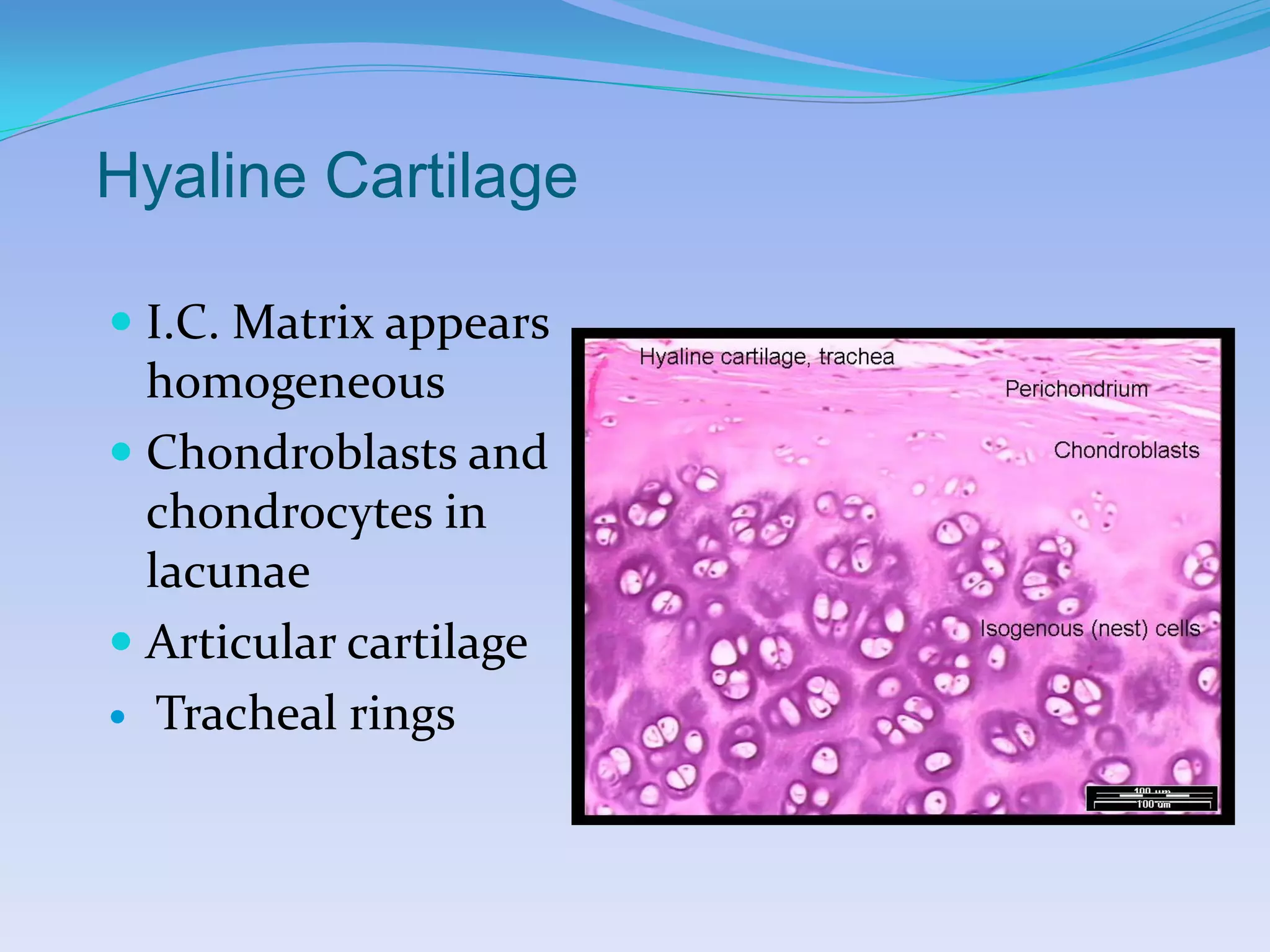
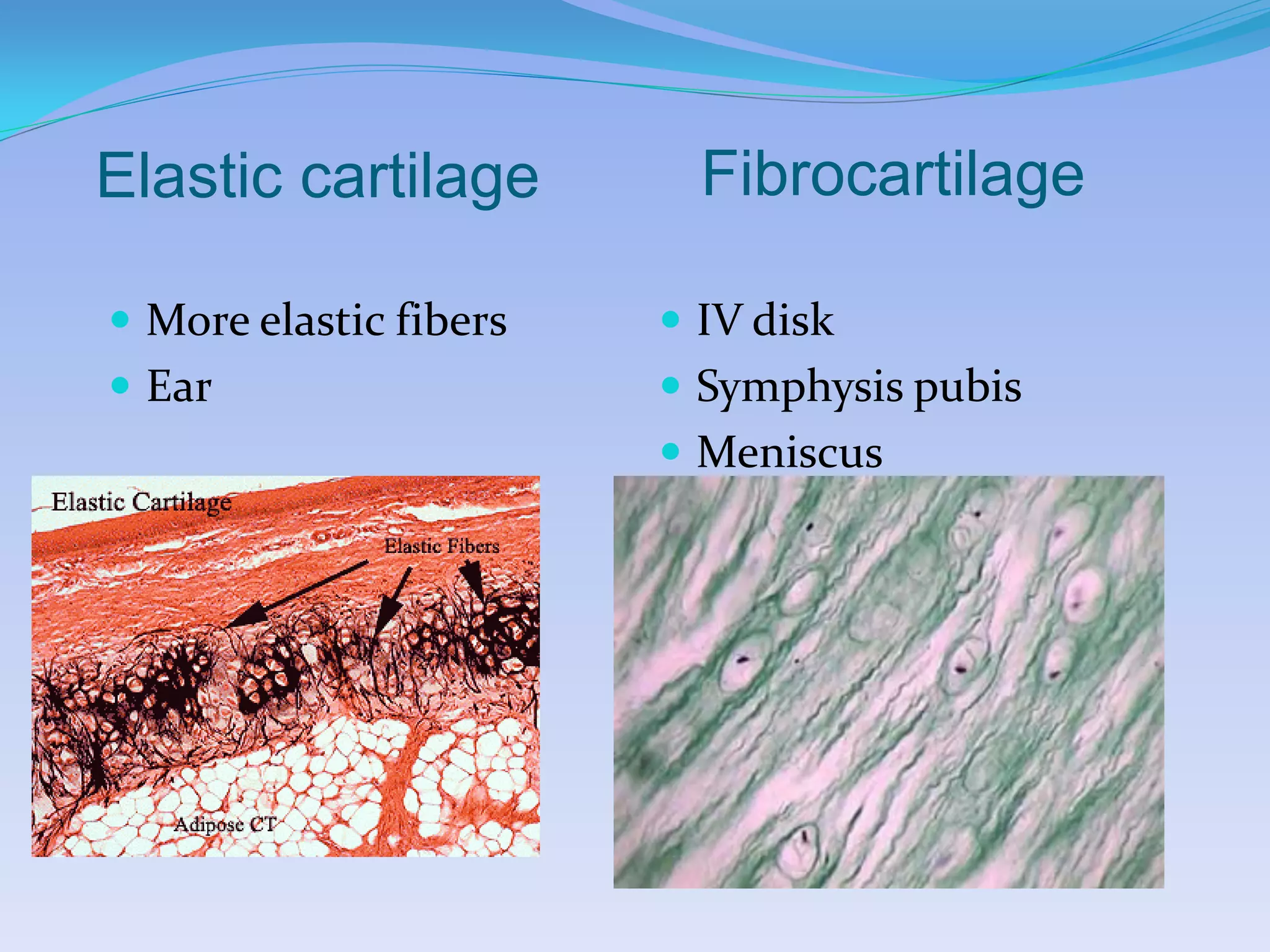
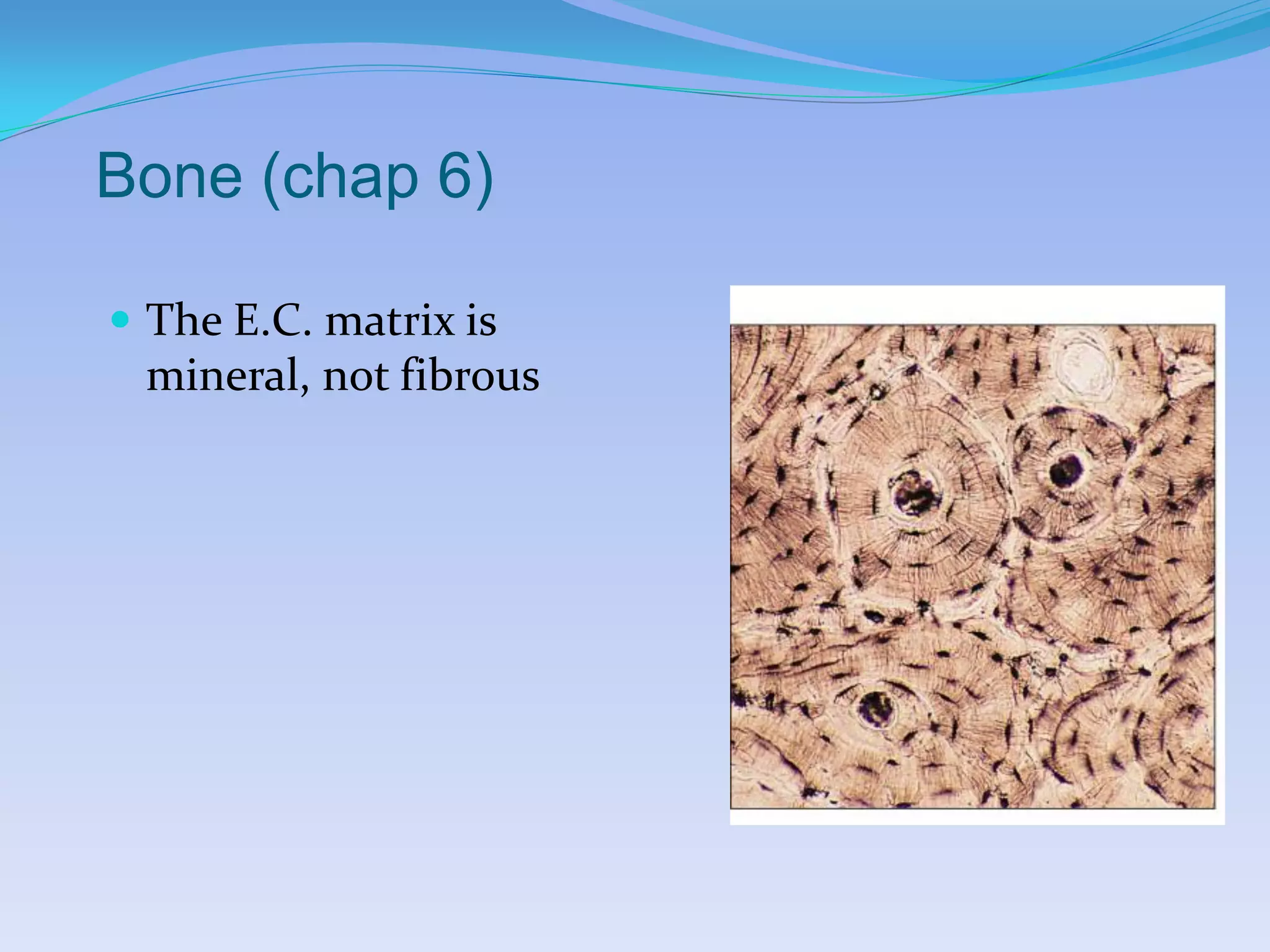
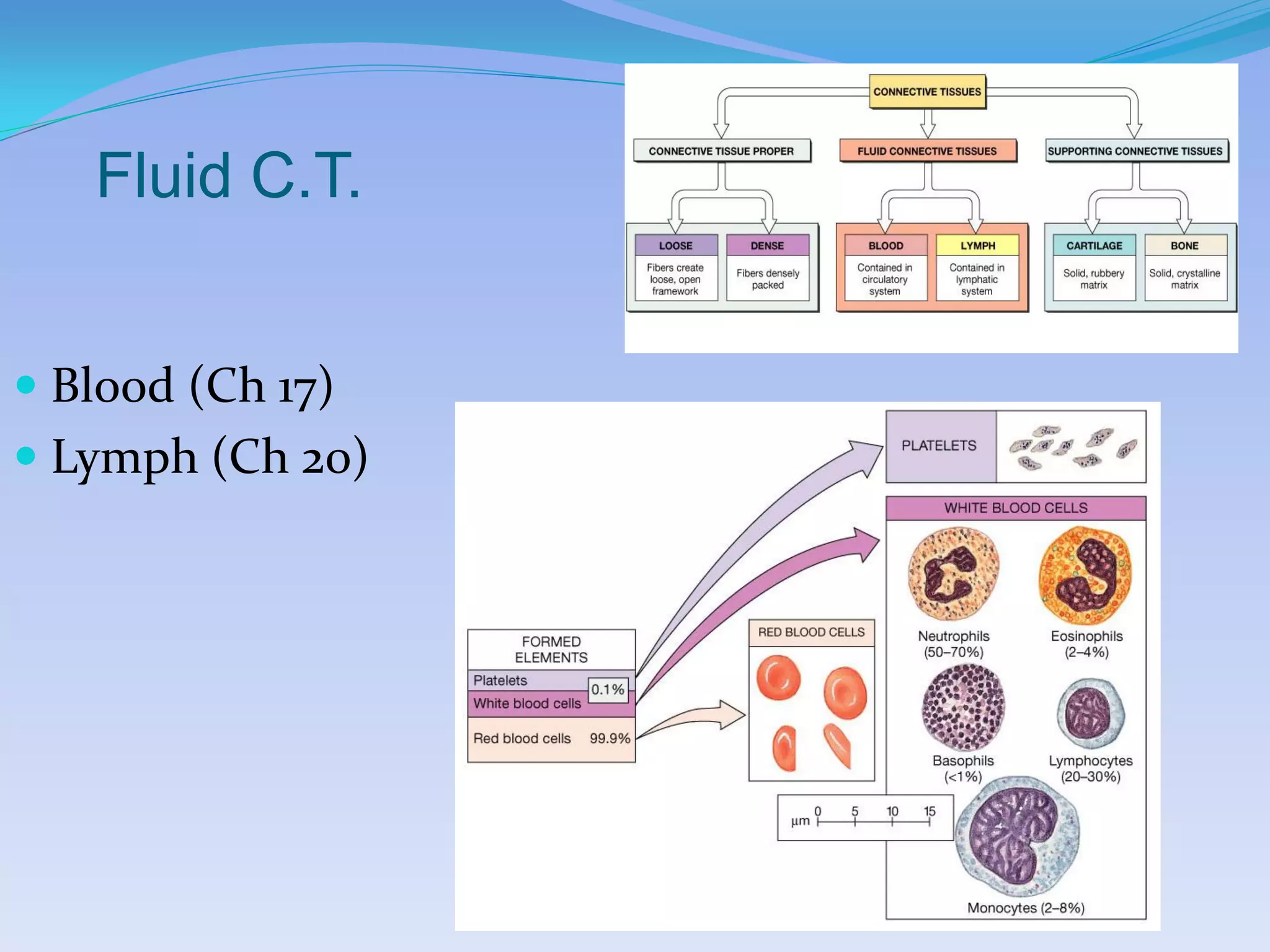
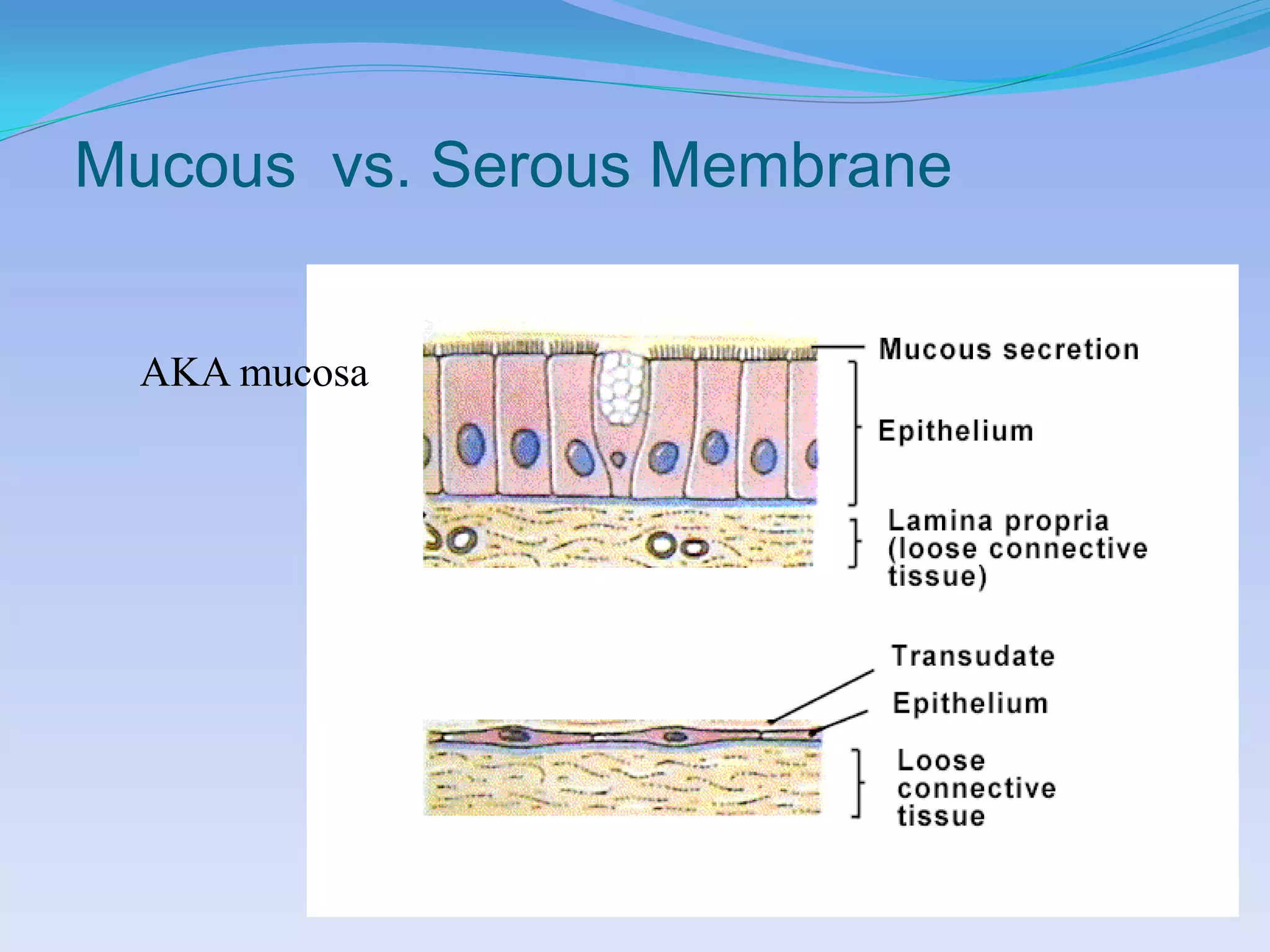
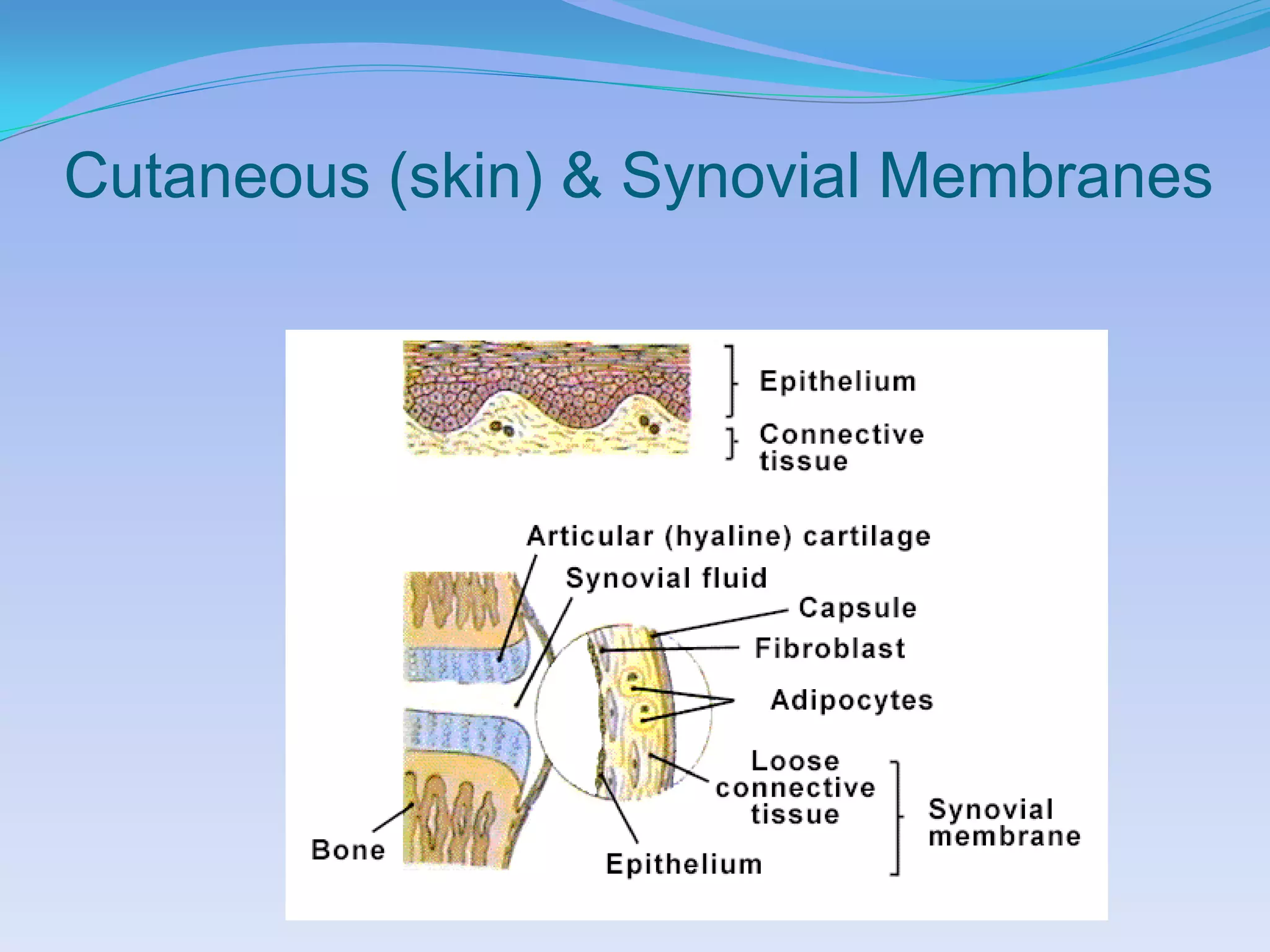
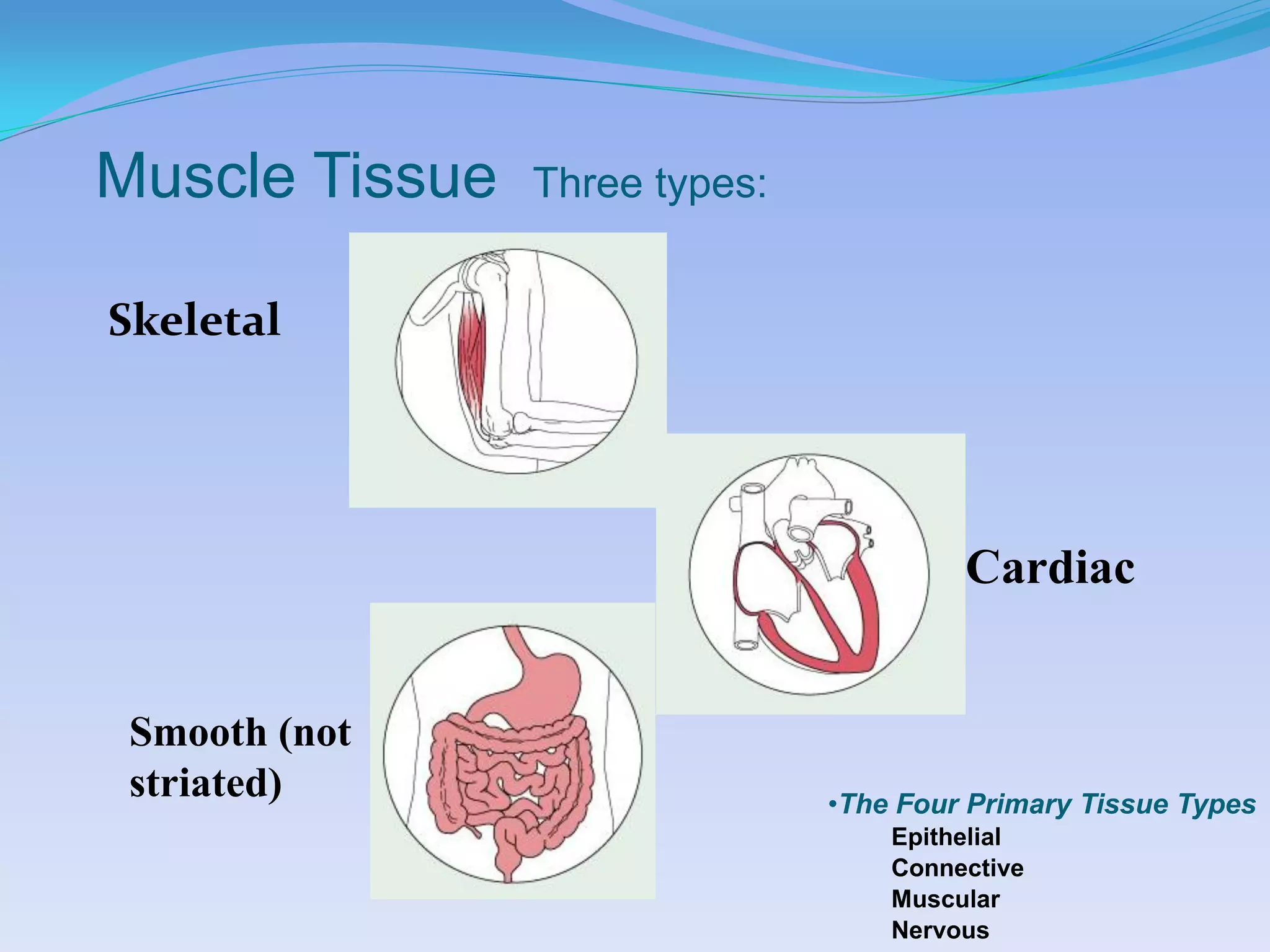
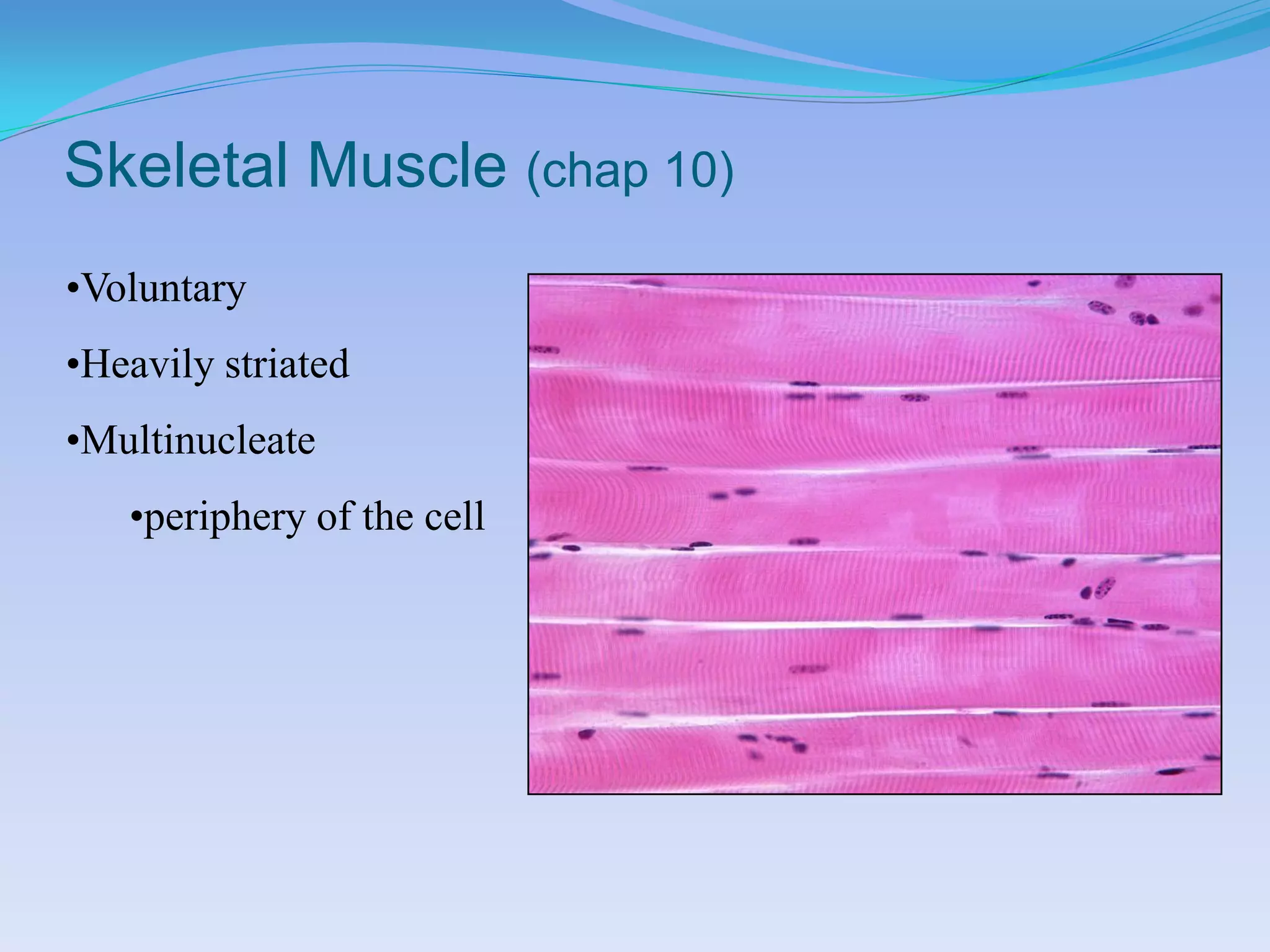
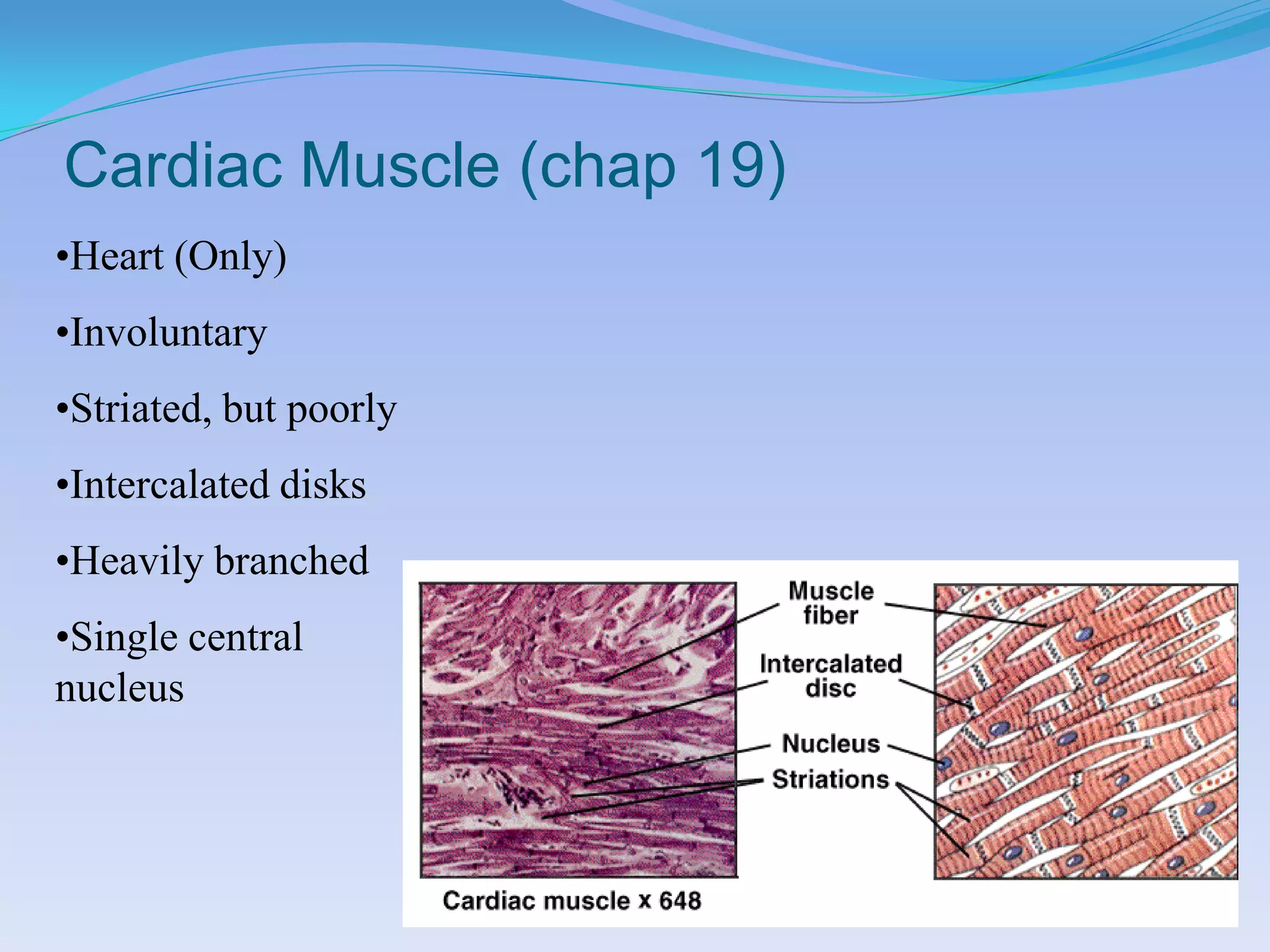
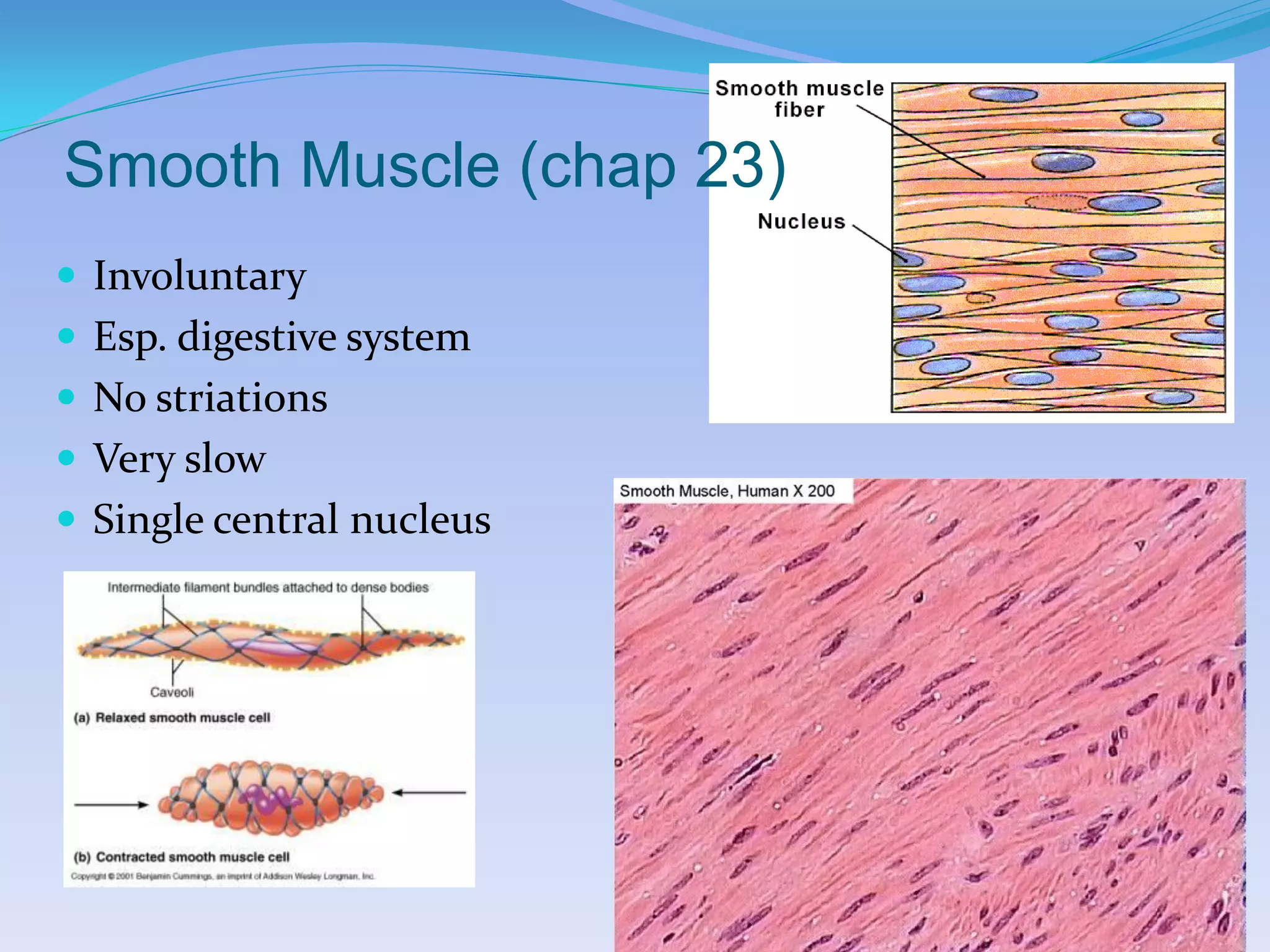
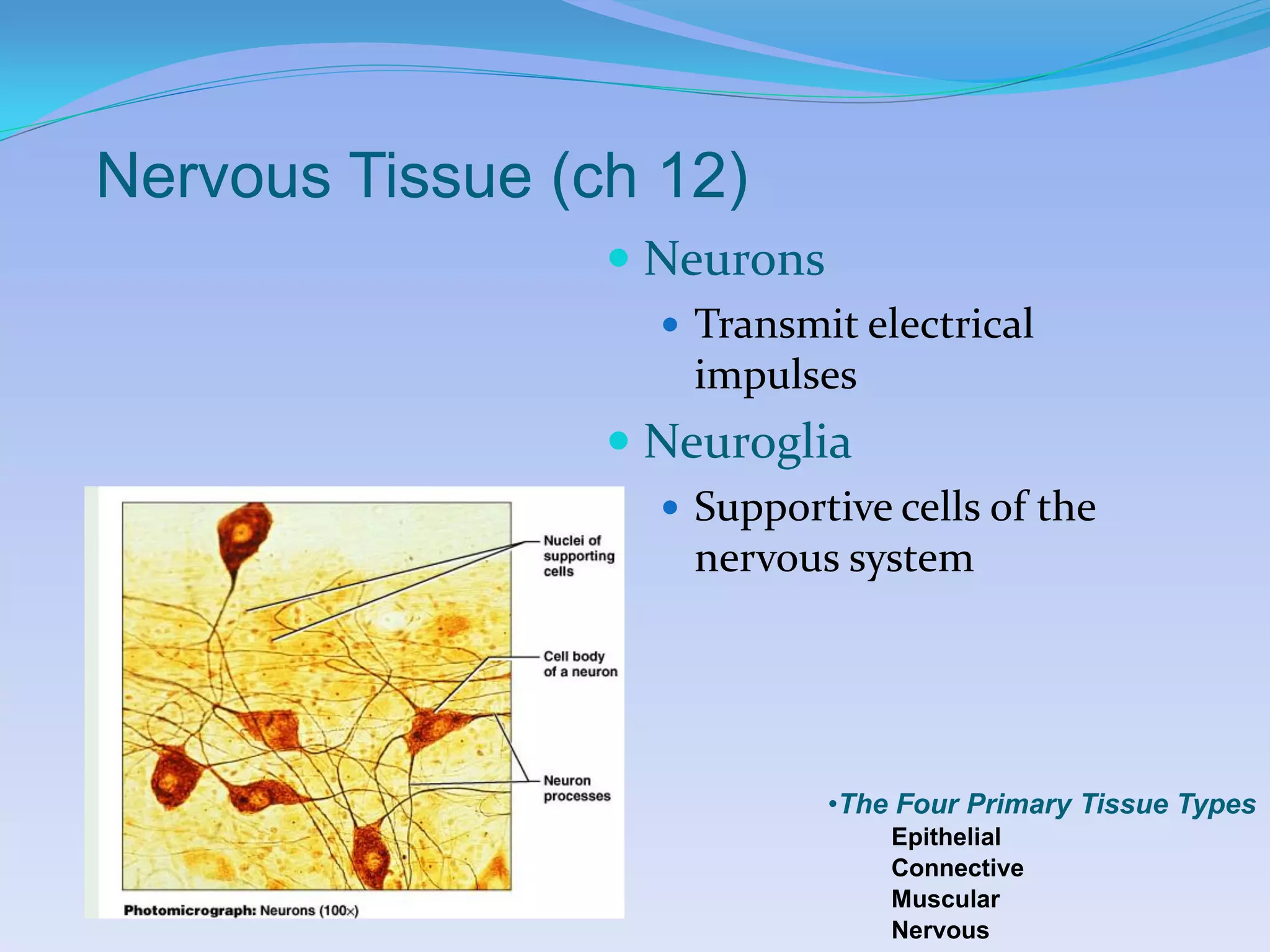
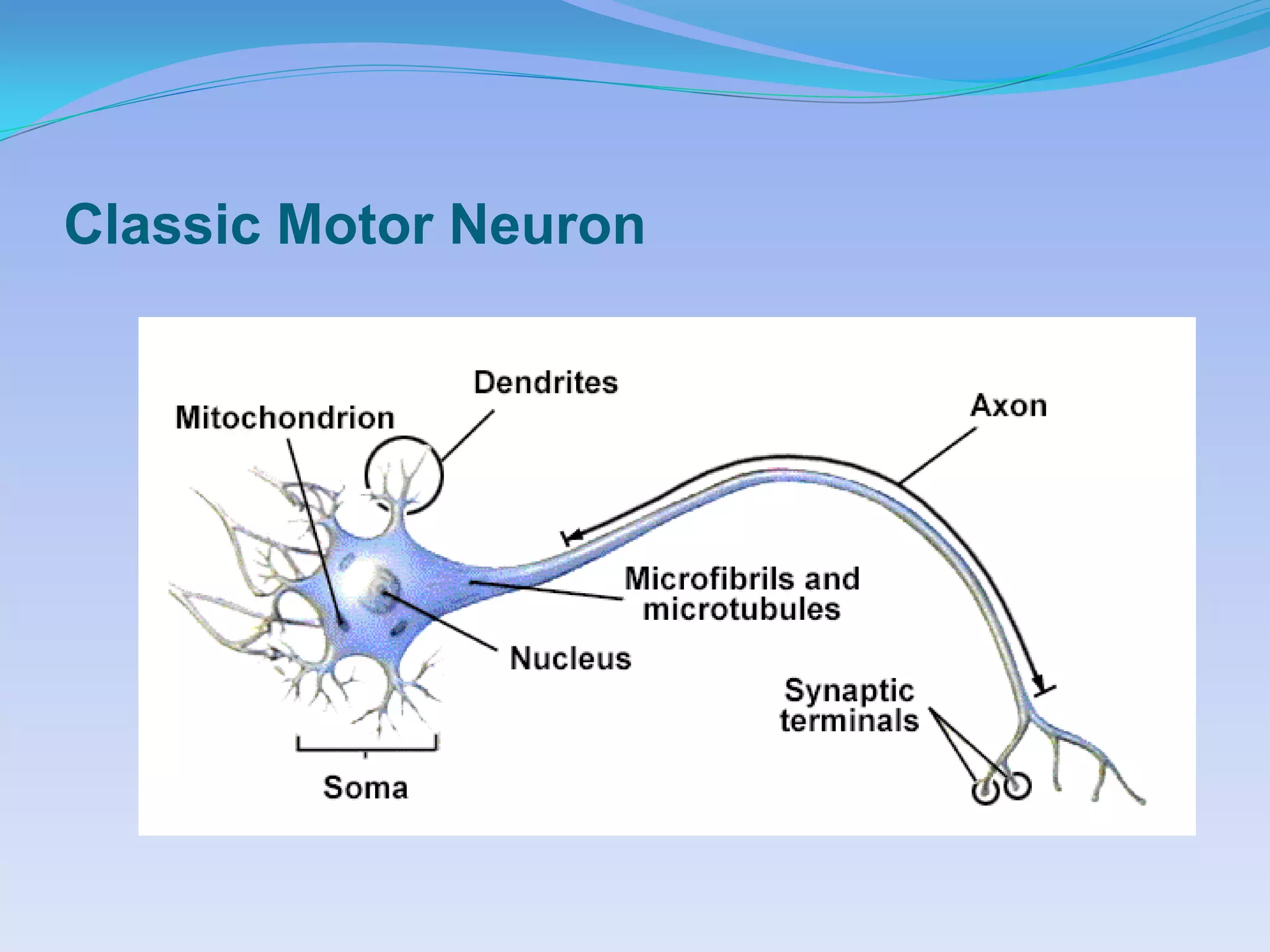
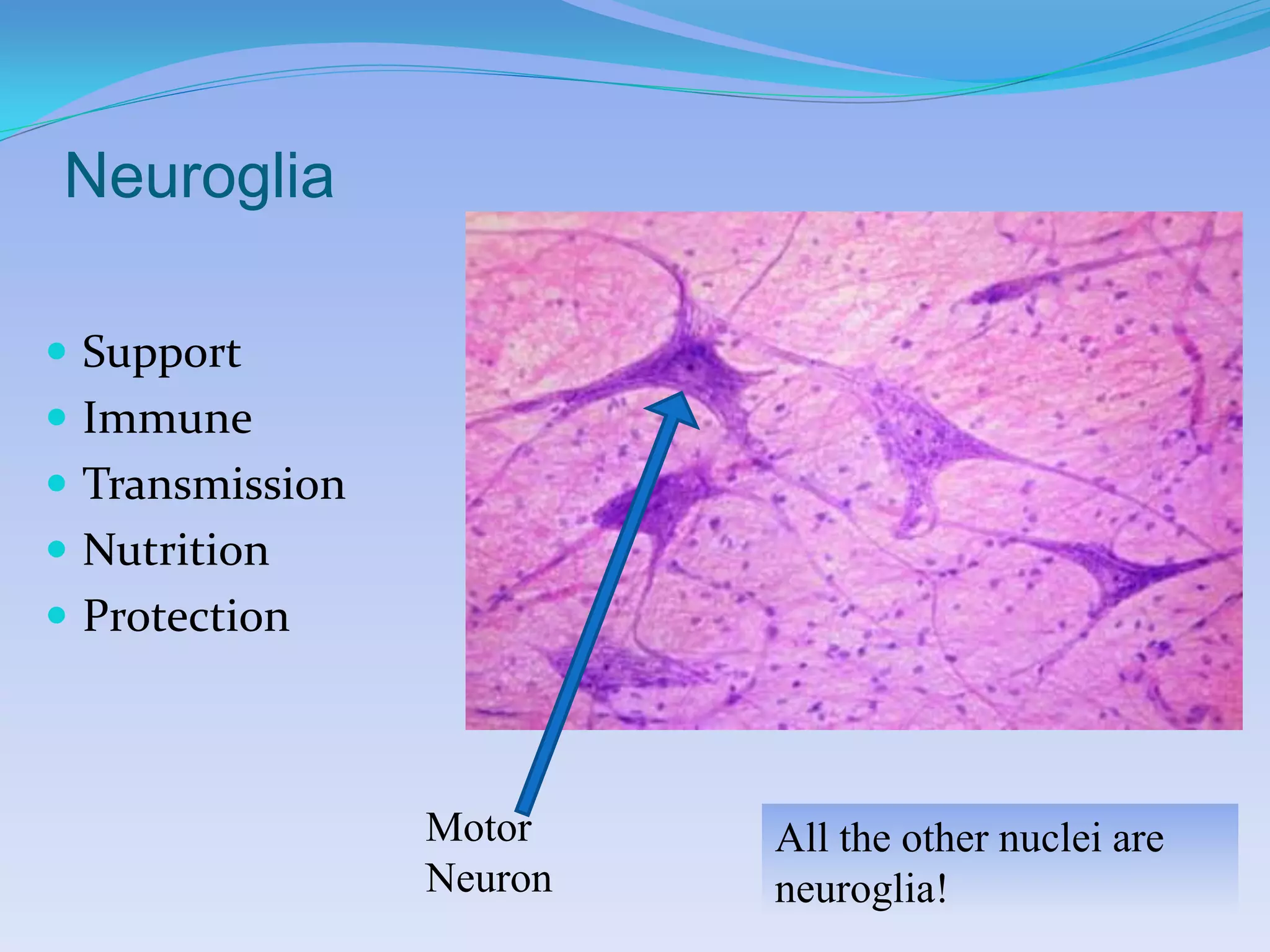
This document summarizes the four primary tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. It provides details on the characteristics and functions of connective tissue, including the different classifications. Connective tissue includes loose connective tissue (areolar and adipose tissue), dense connective tissue (irregular, regular, and elastic), and special connective tissues like cartilage and bone. It also discusses the three main types of muscle tissue - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Finally, it provides an overview of nervous tissue and the key cells involved.