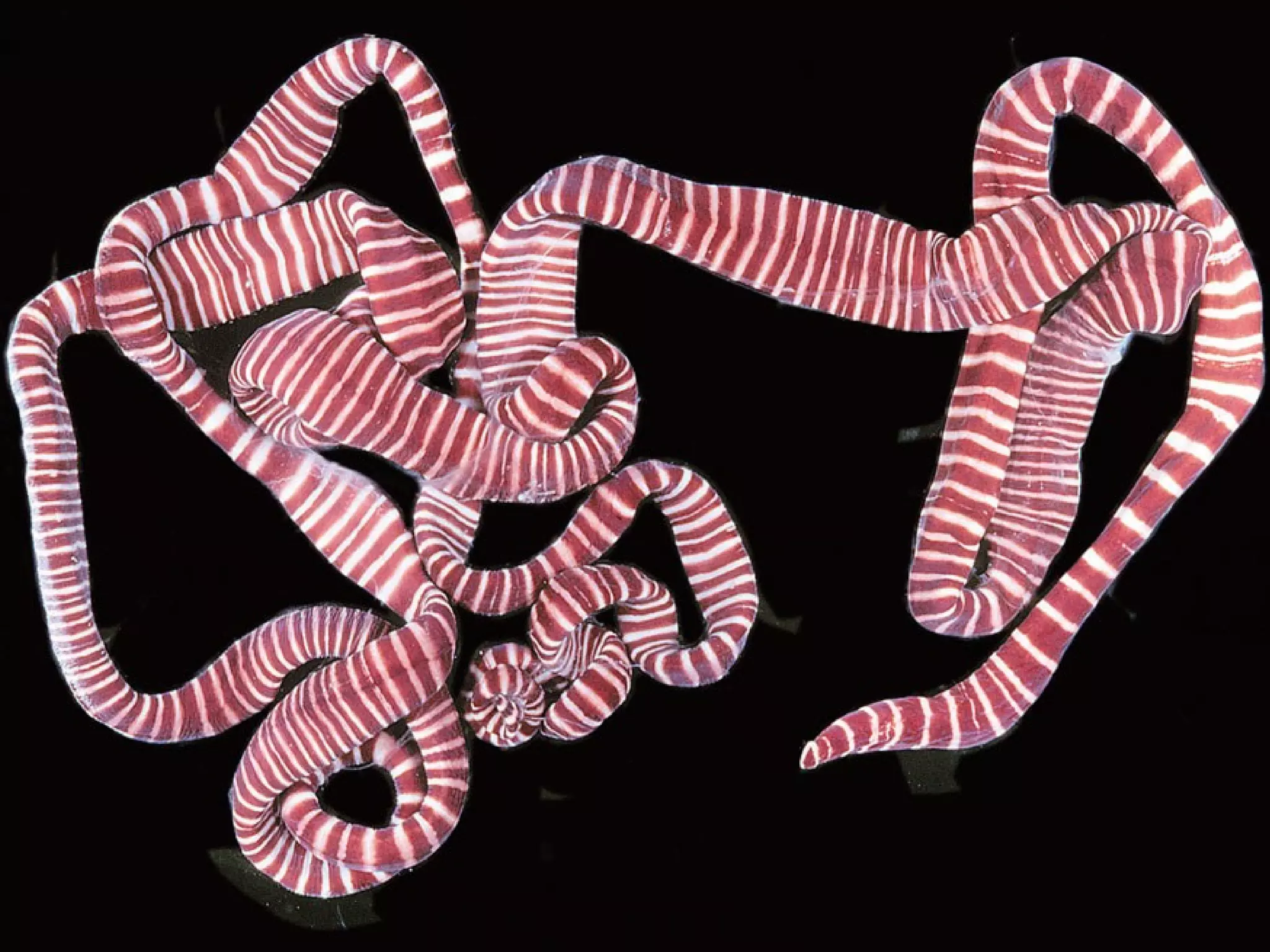
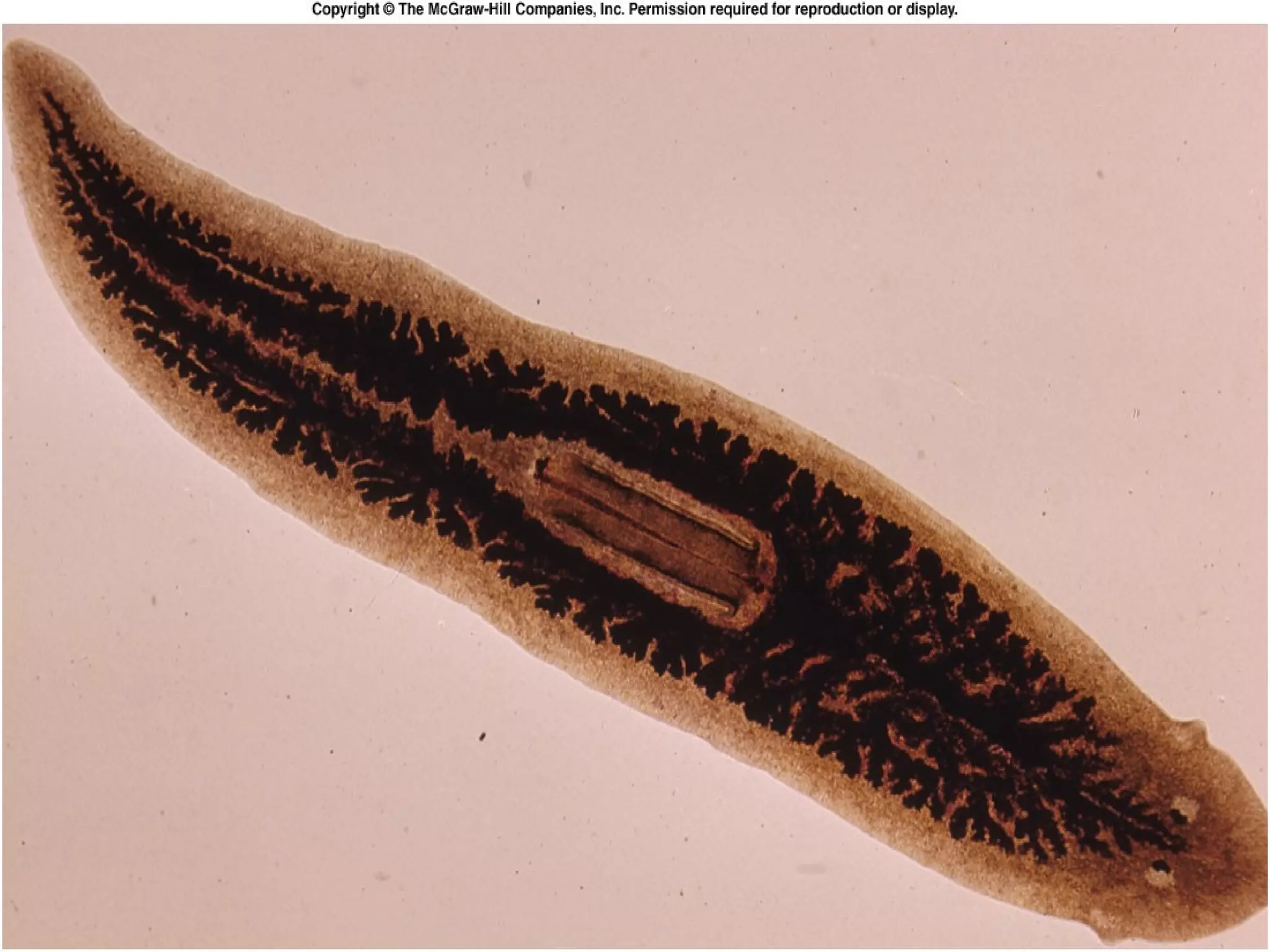
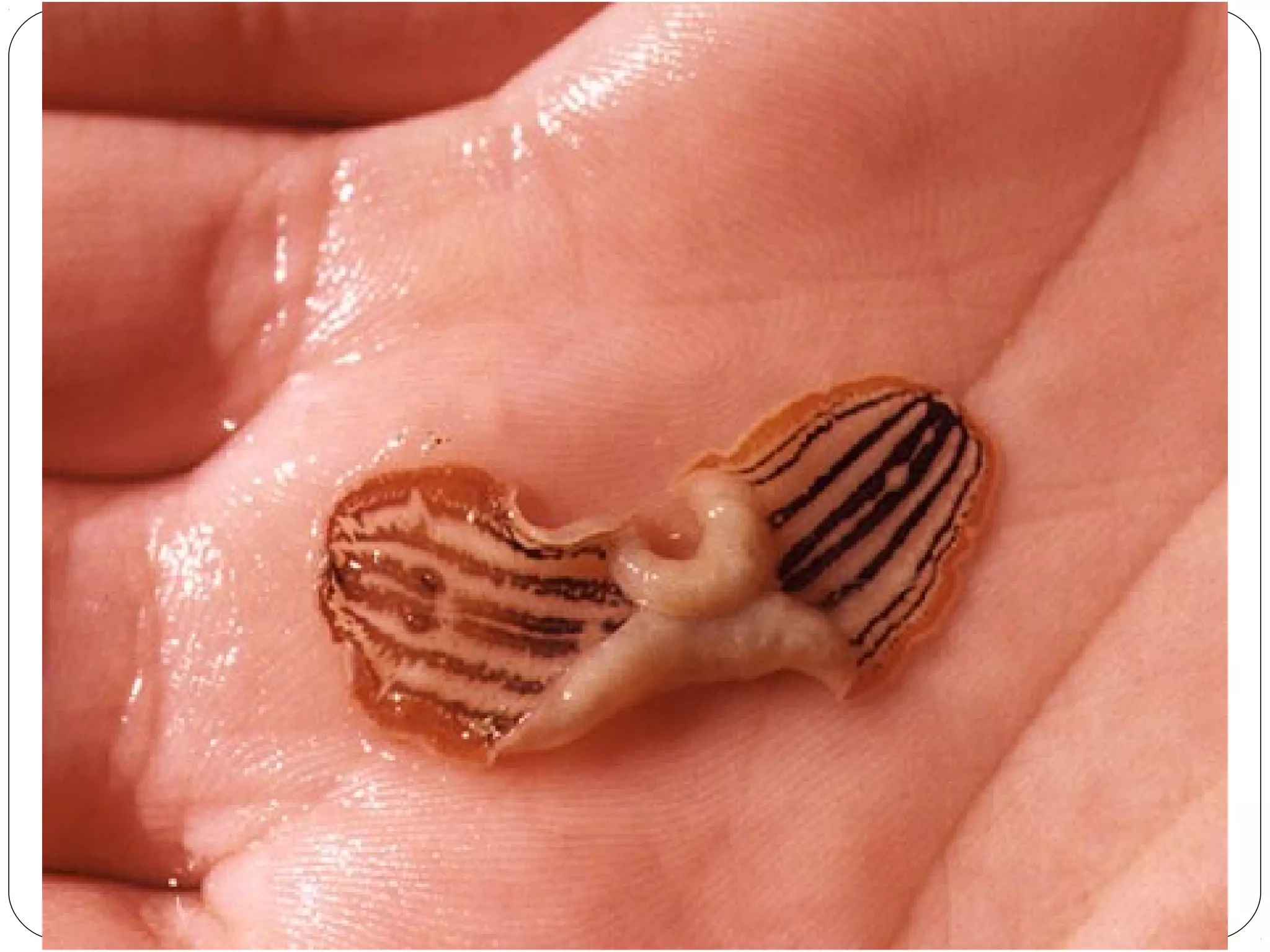
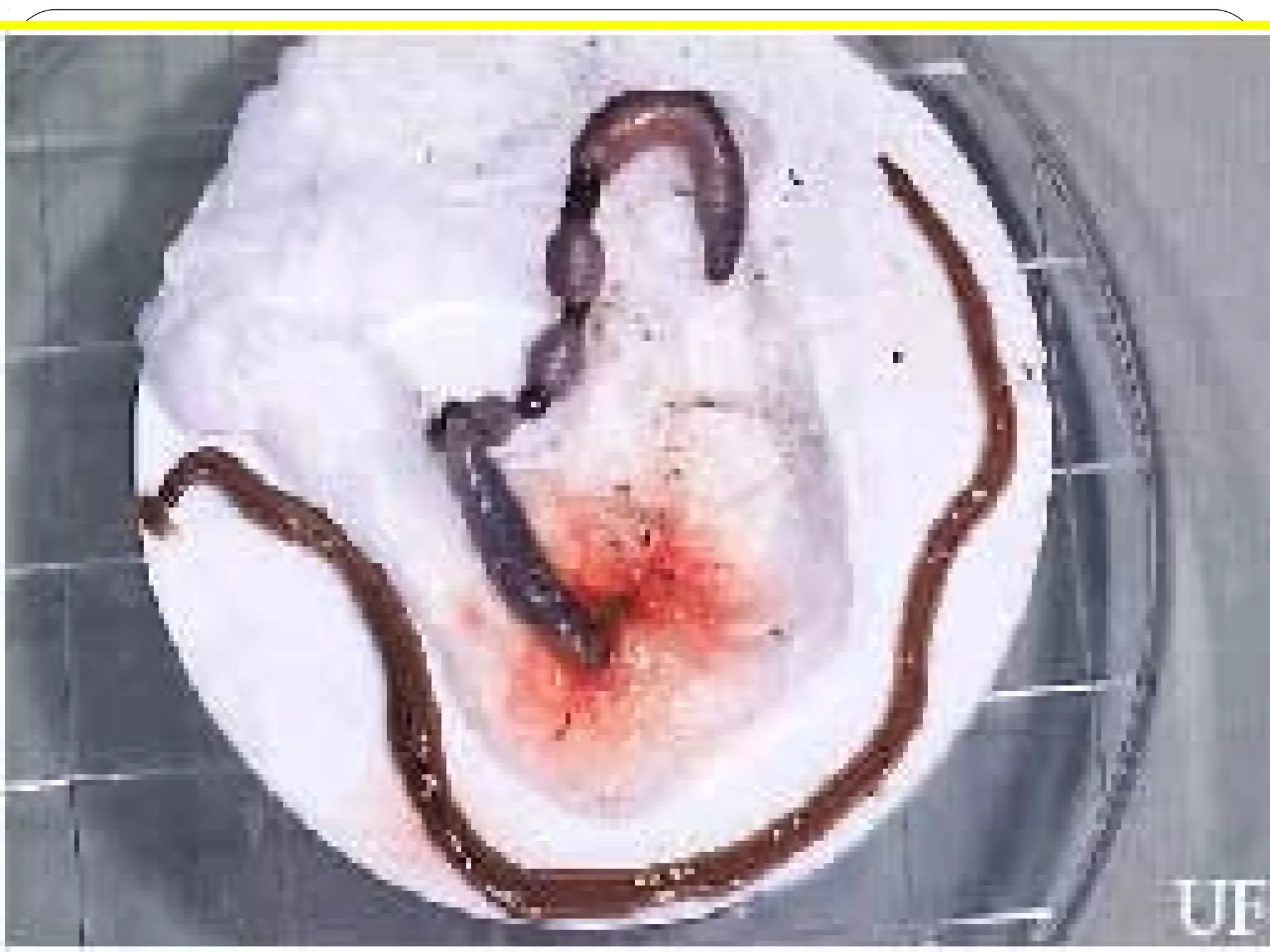
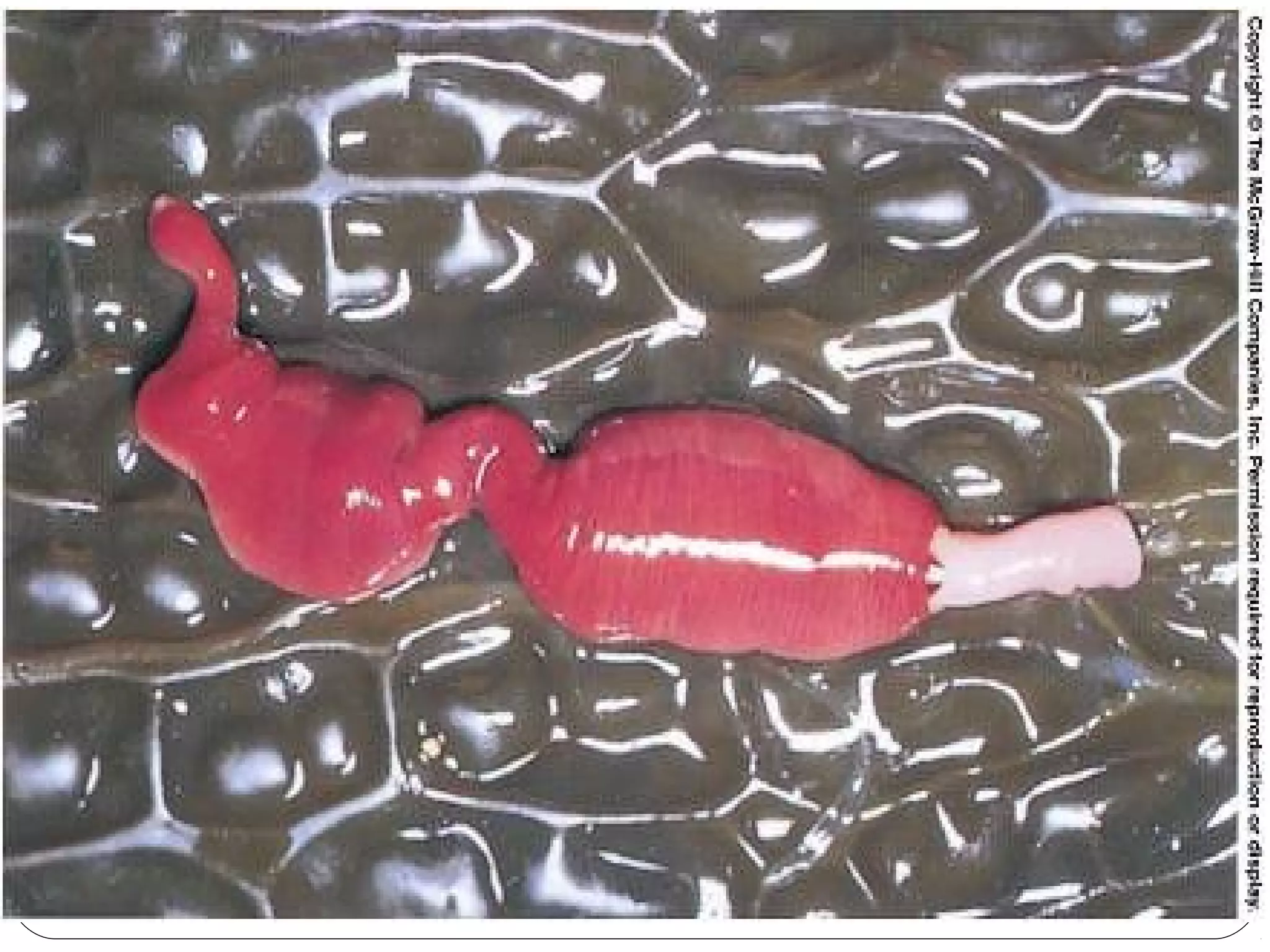
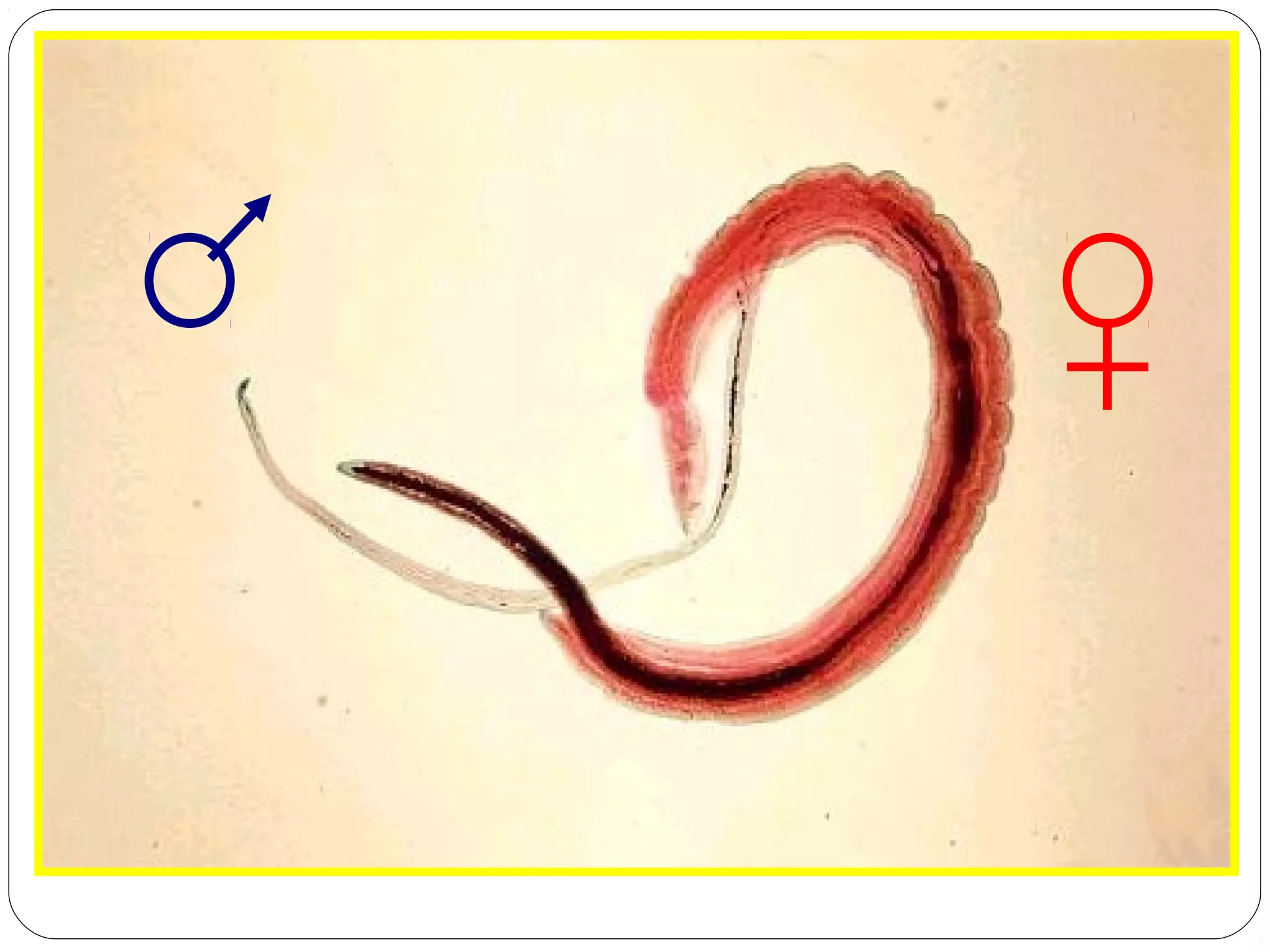
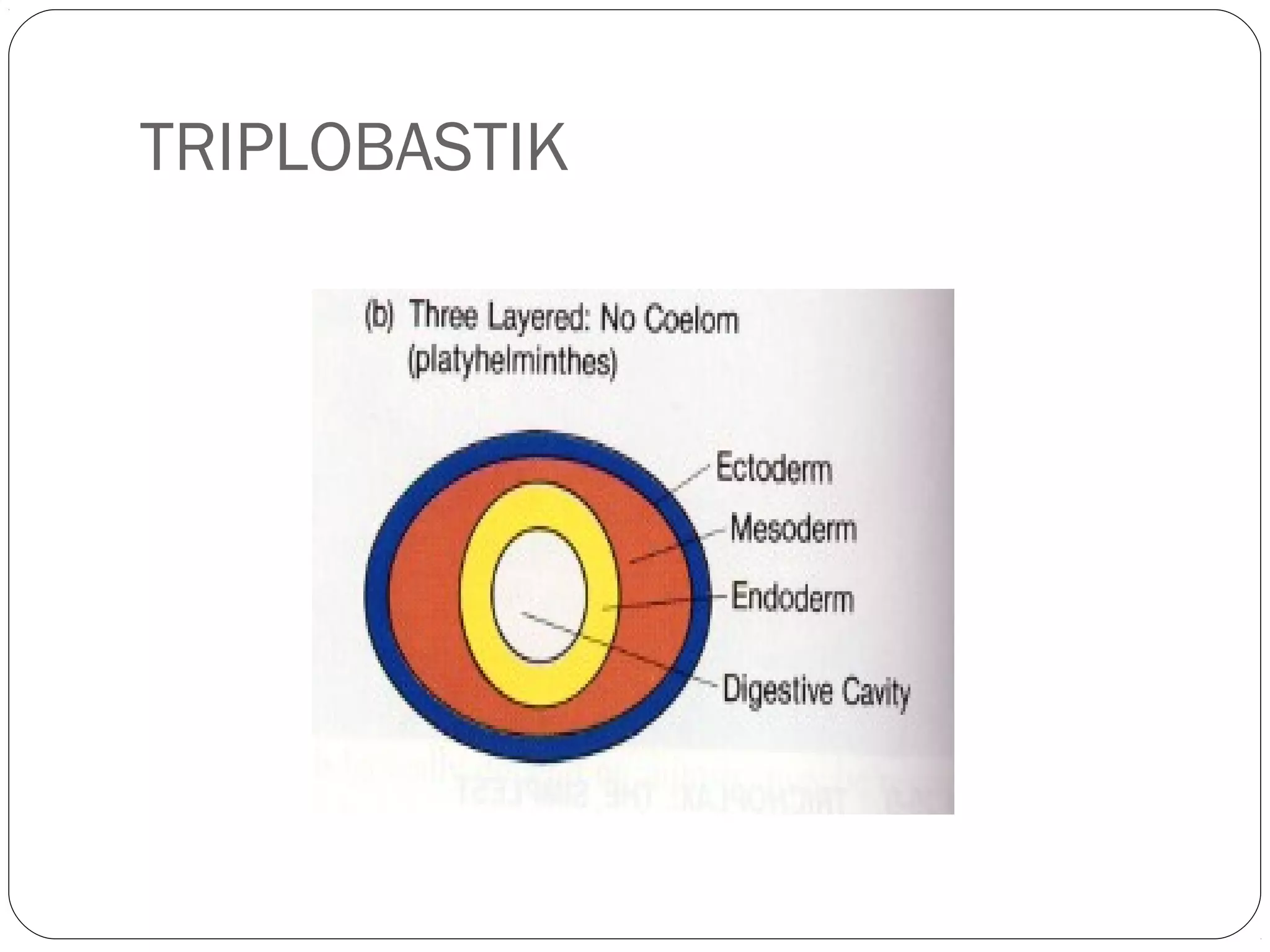
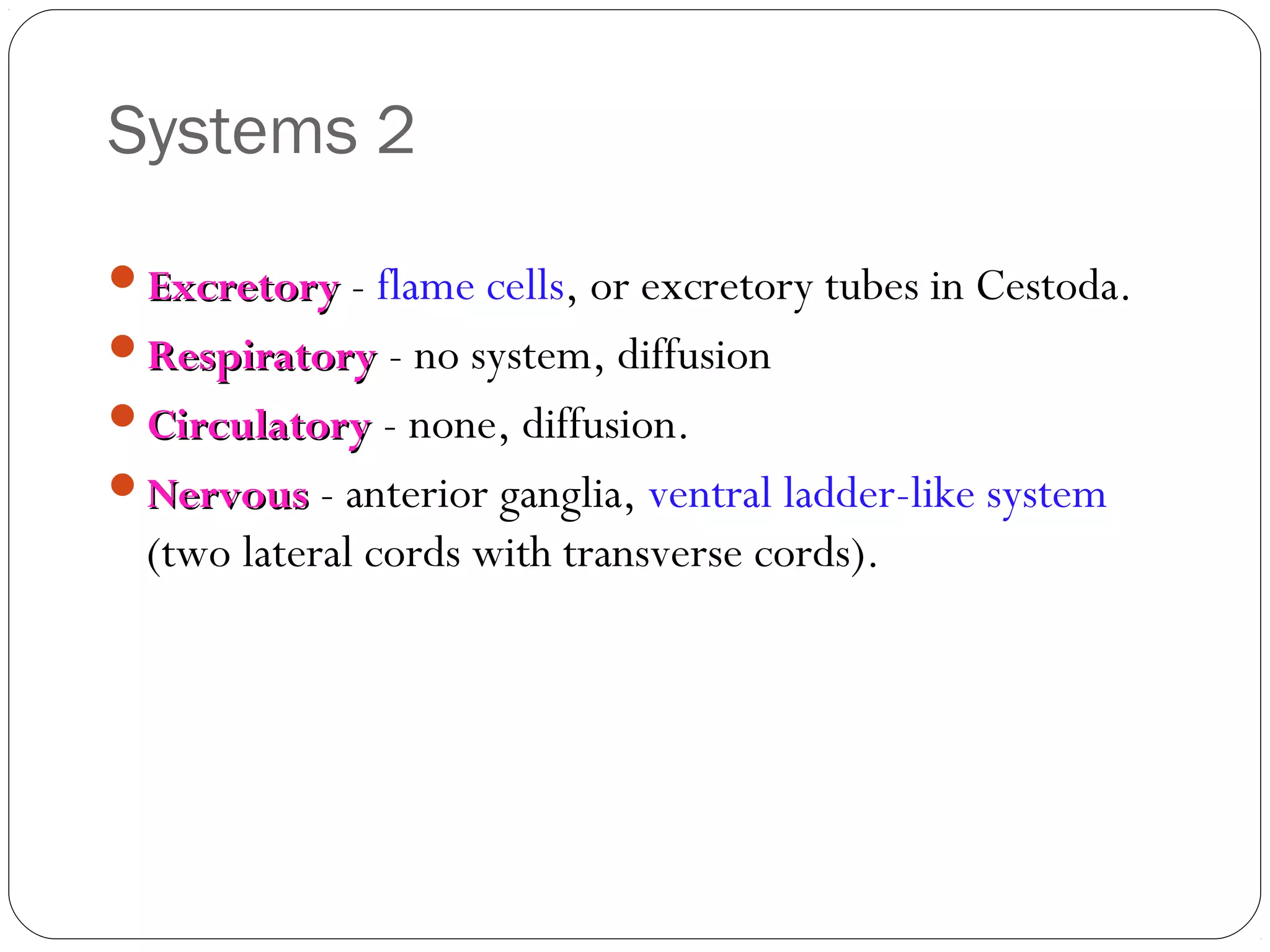
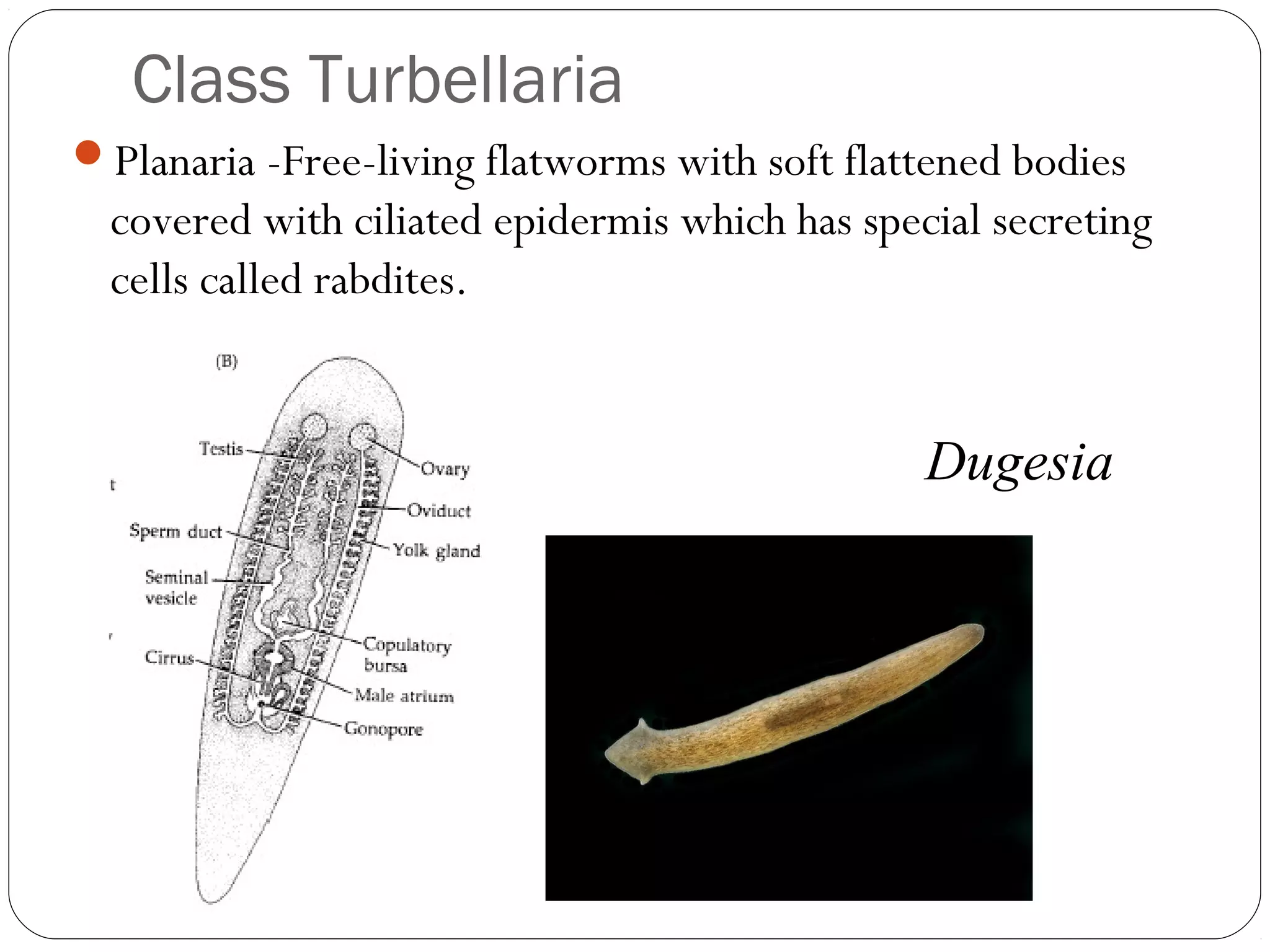
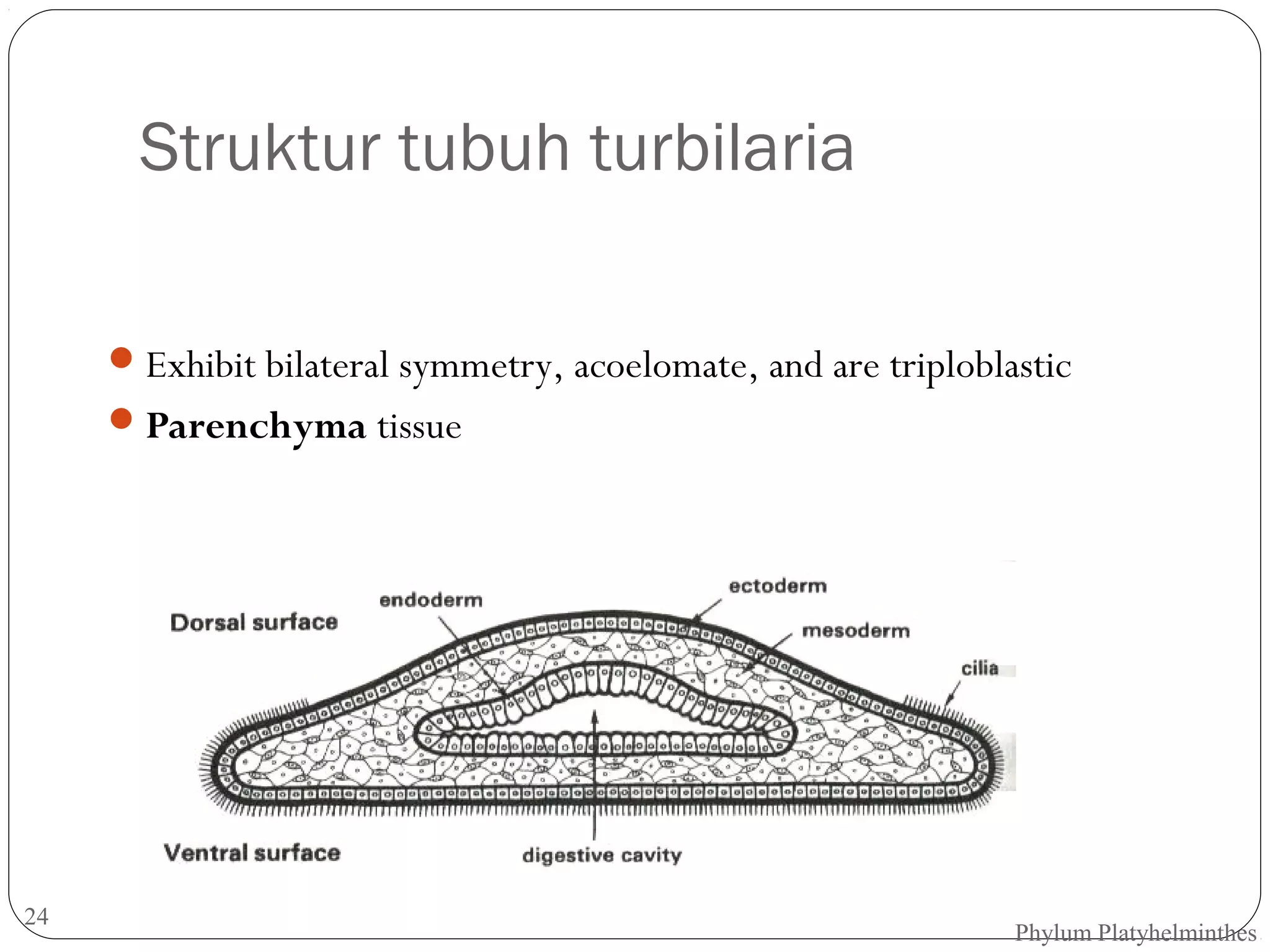
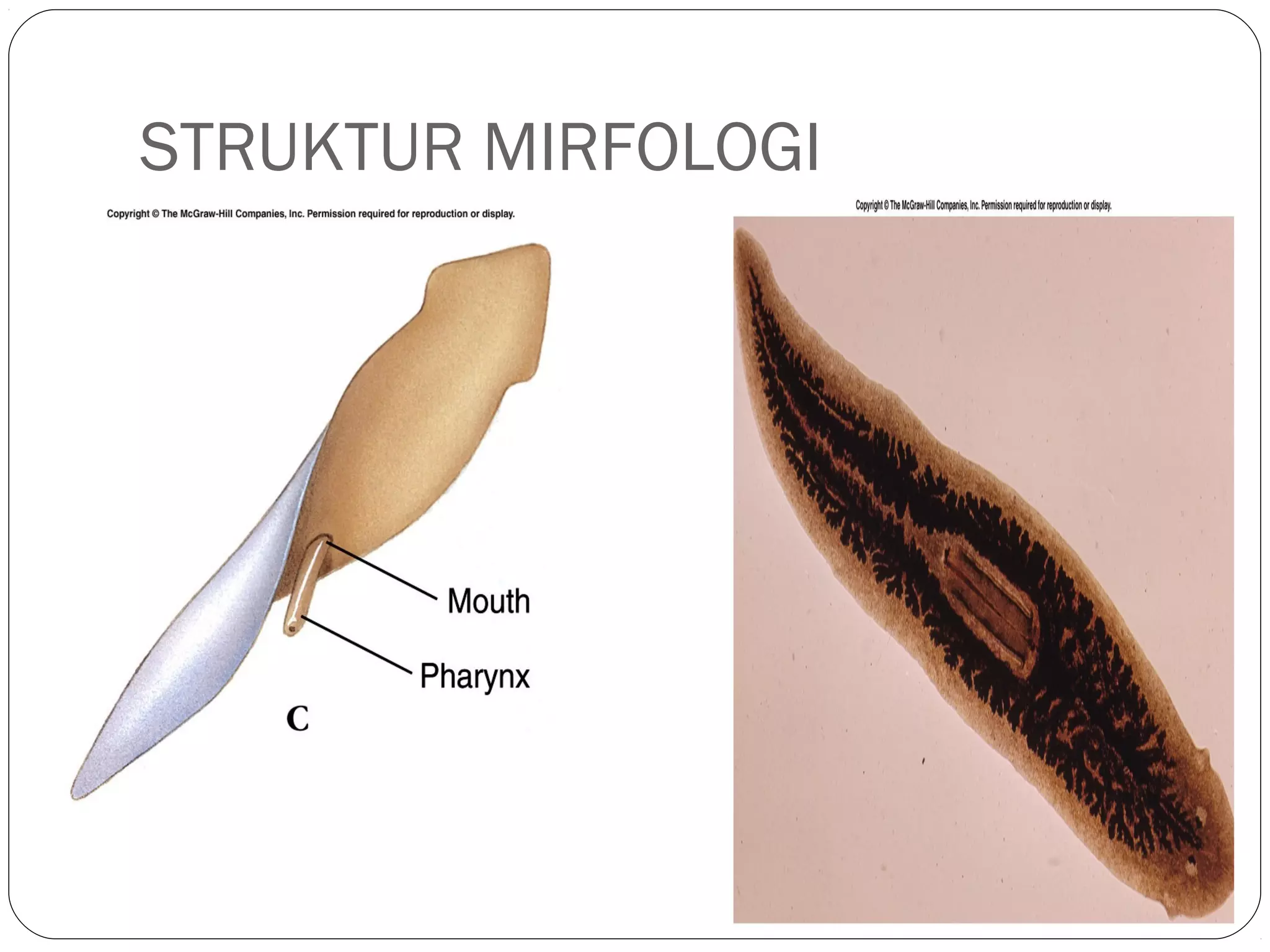
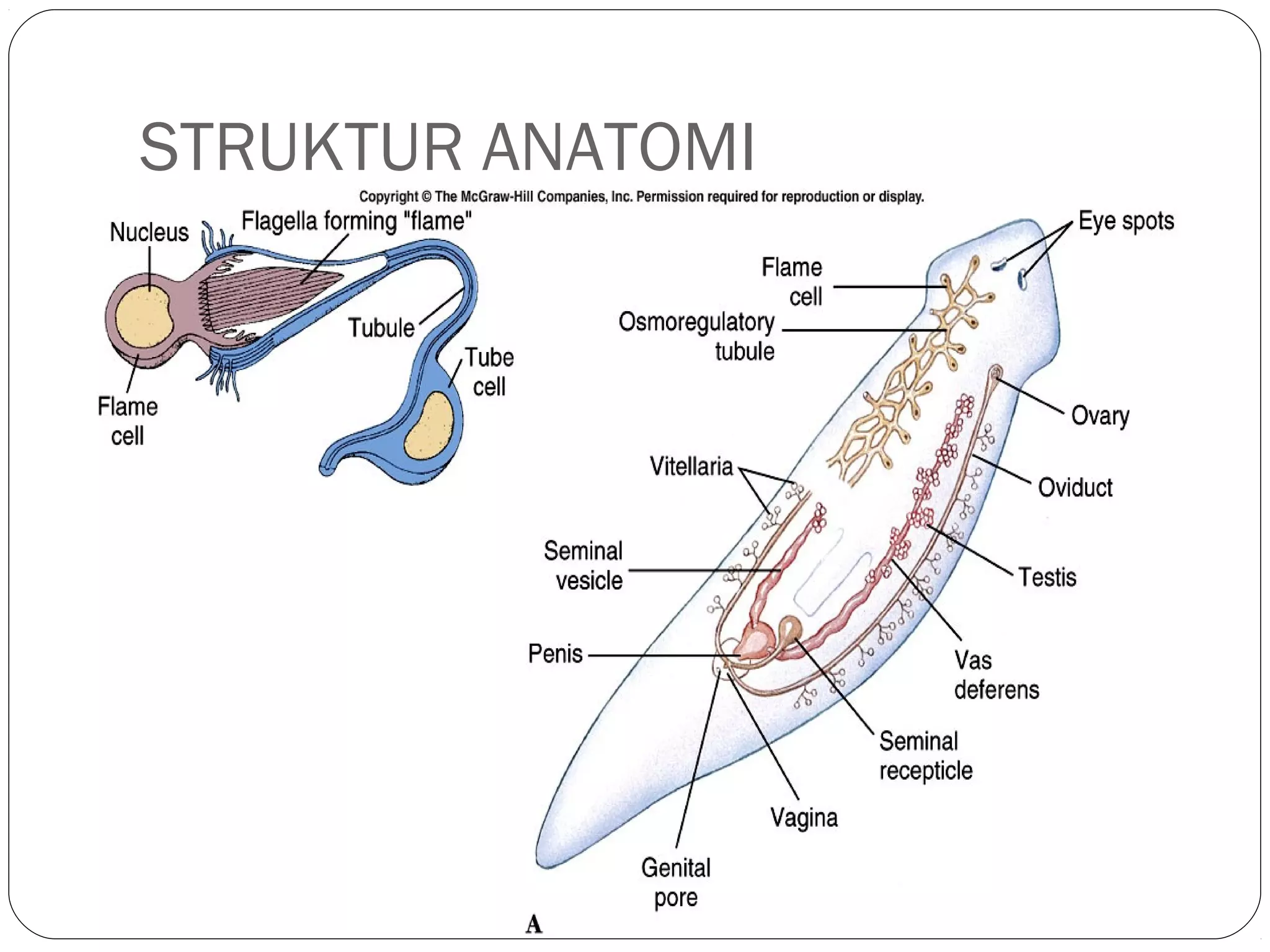
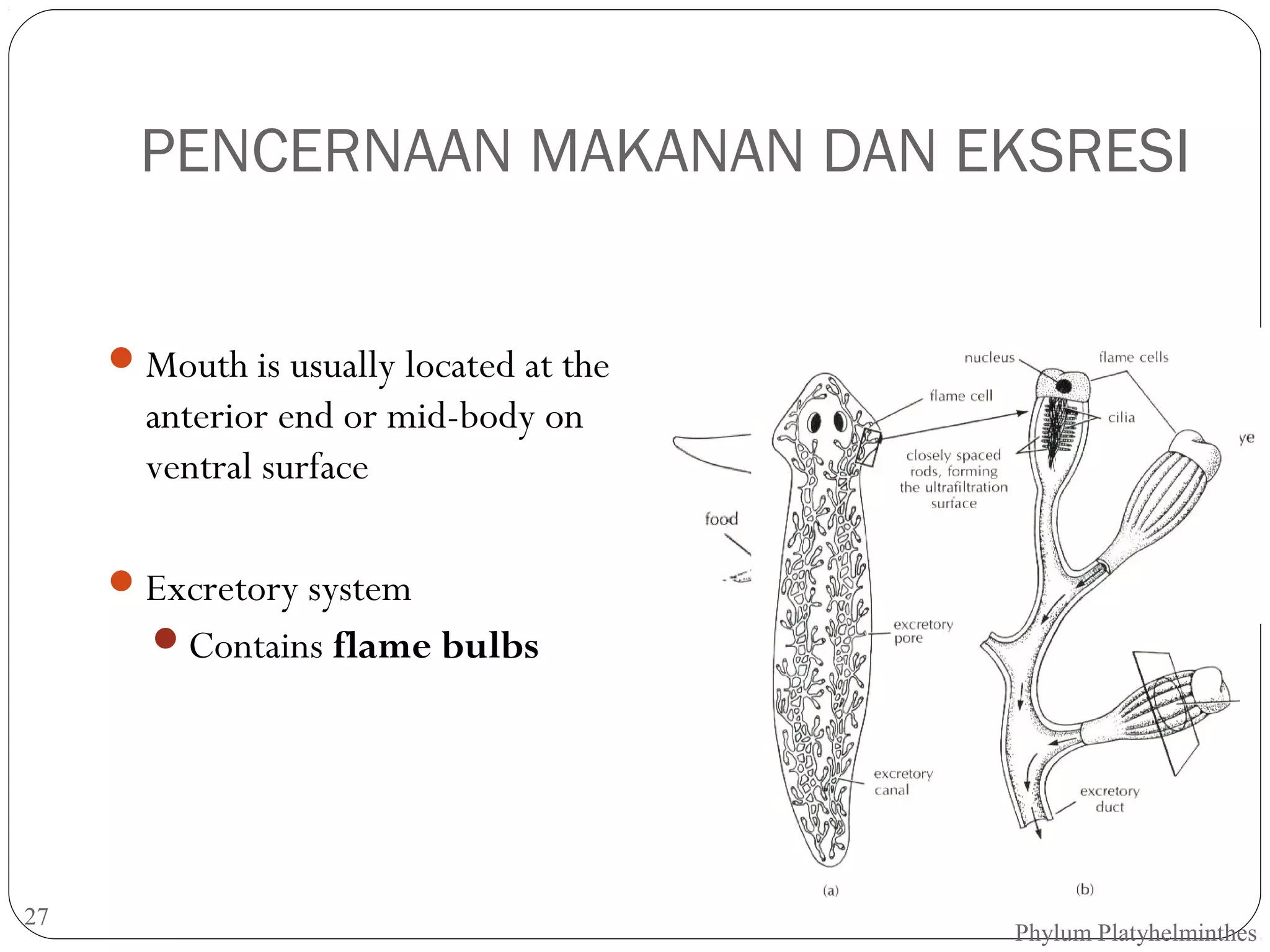
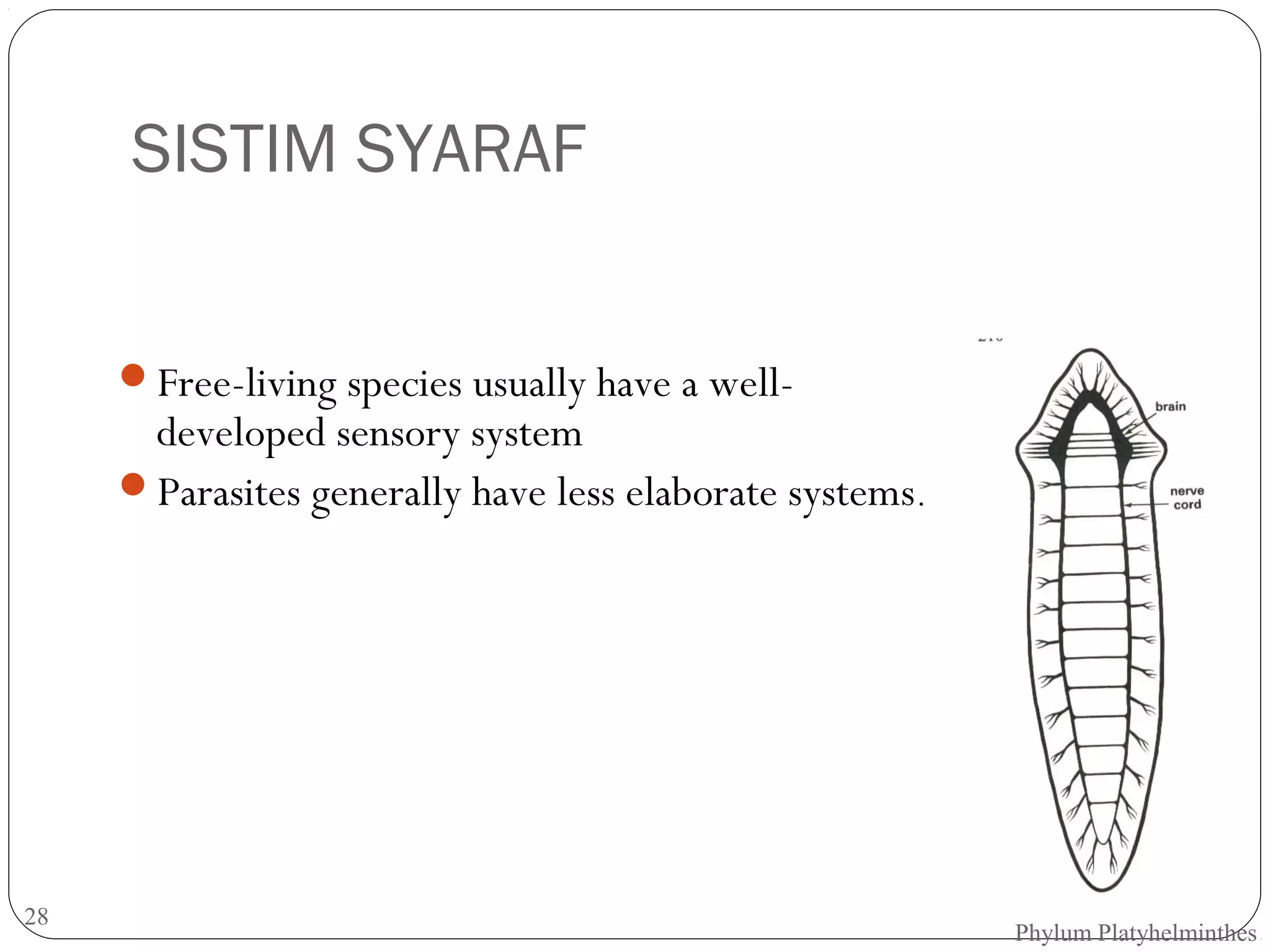
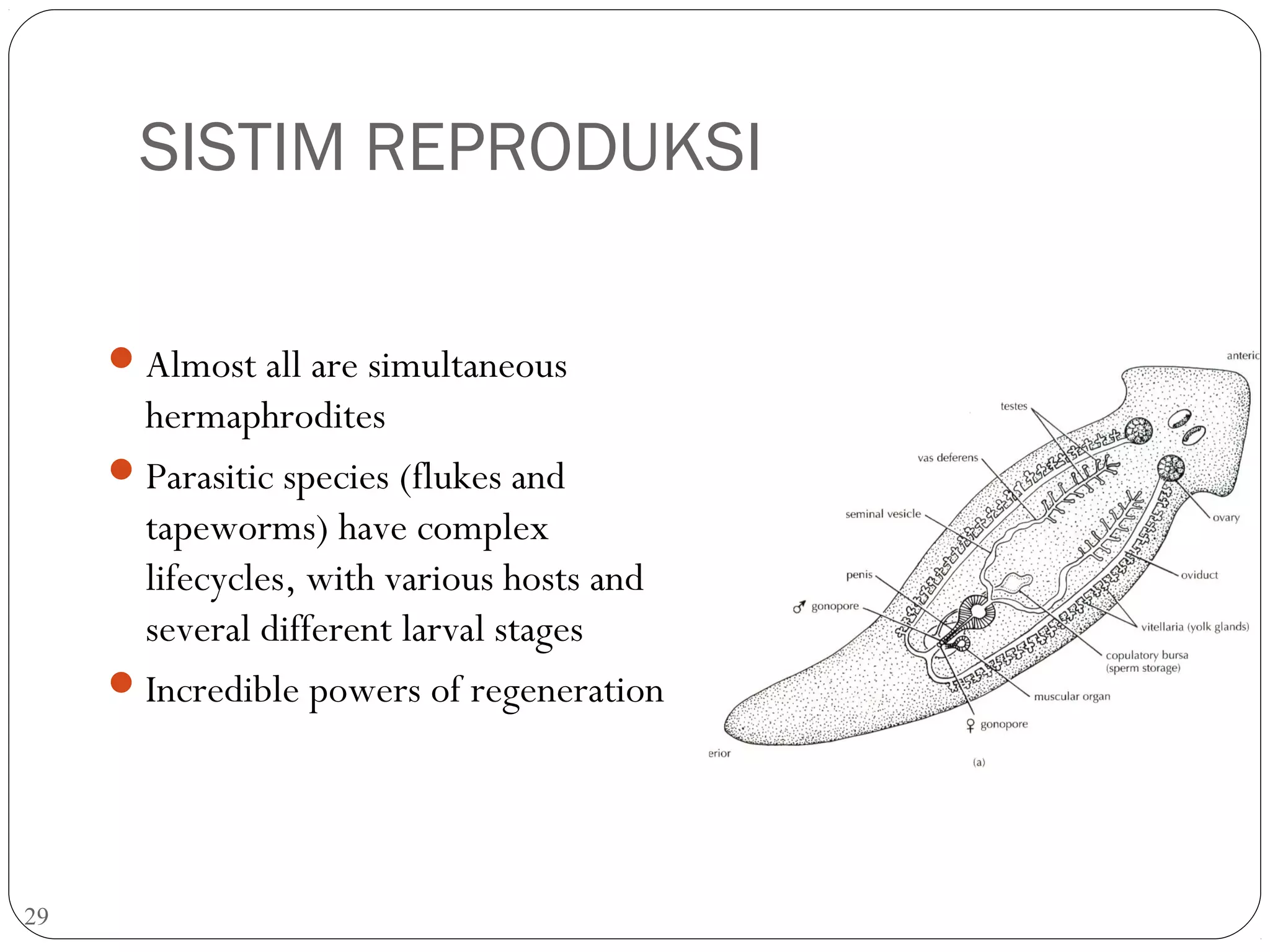
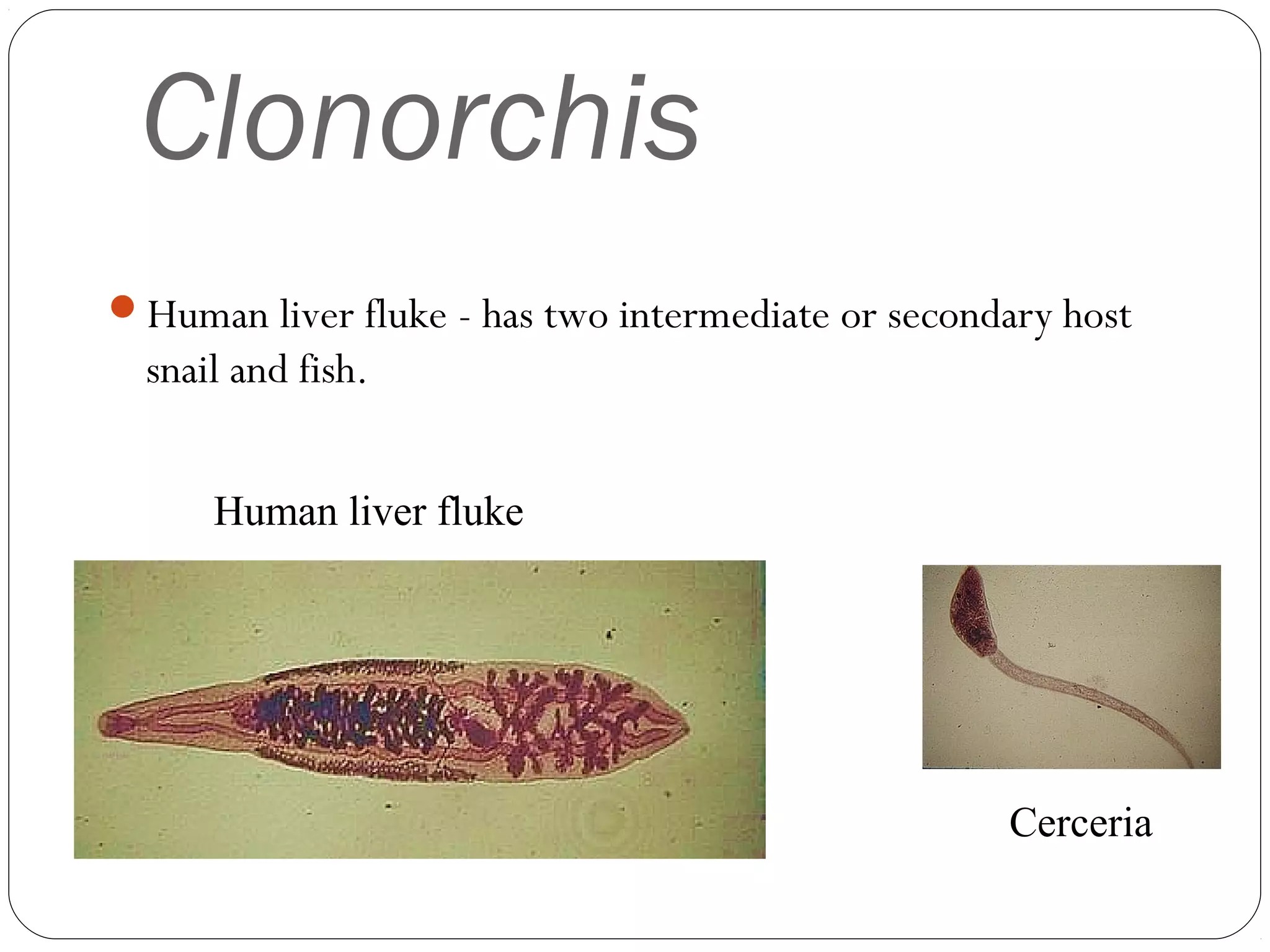
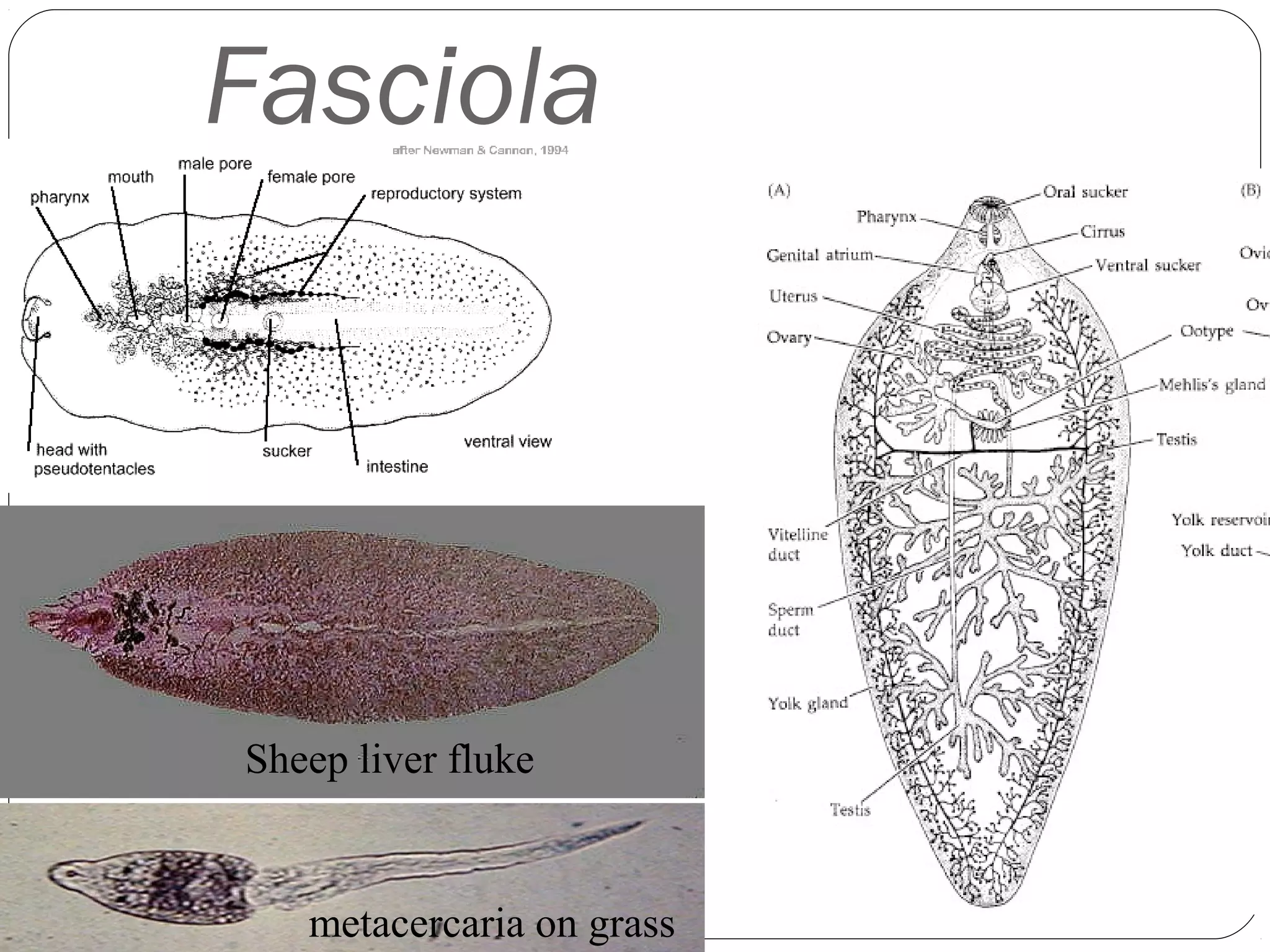
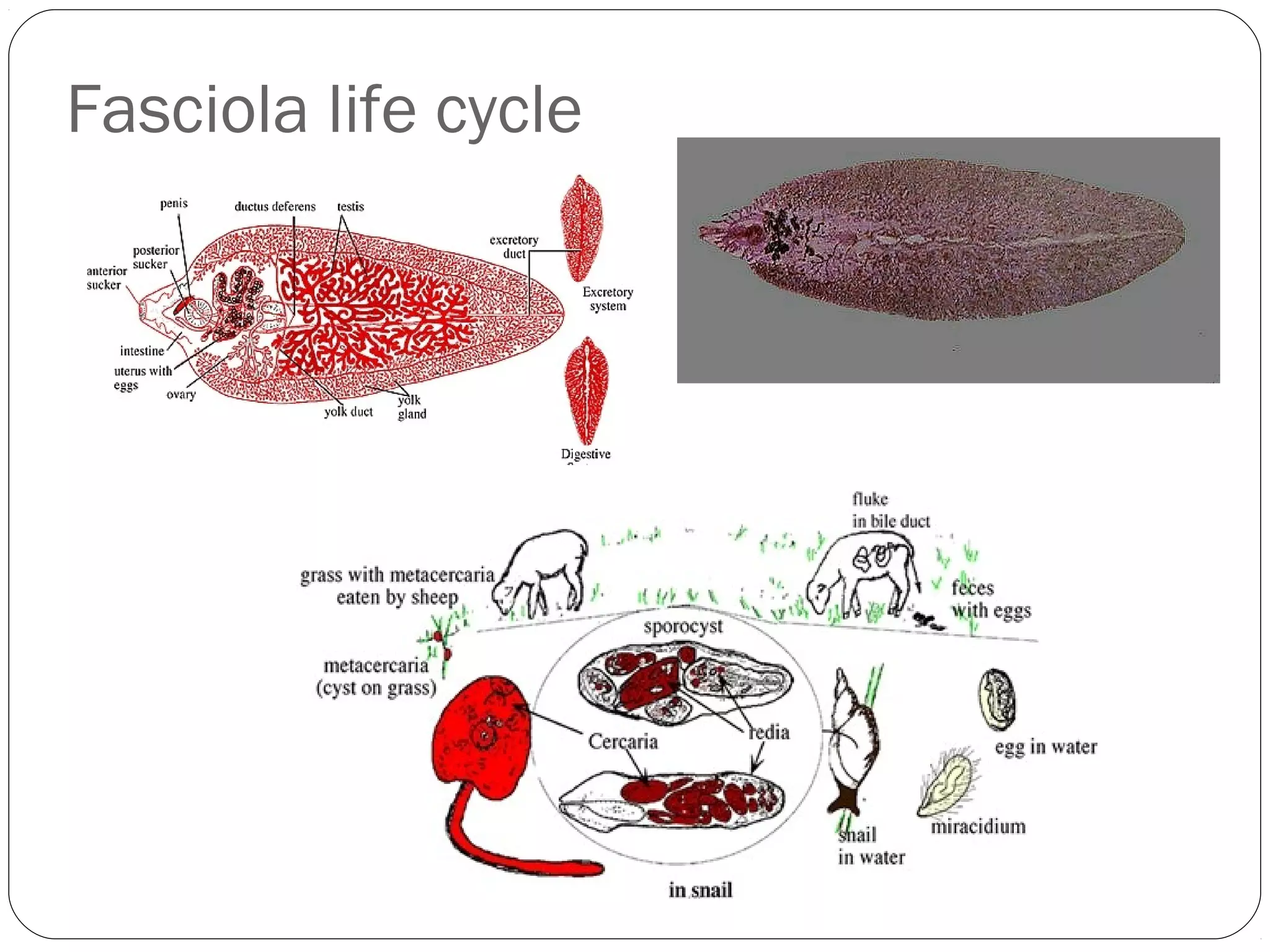
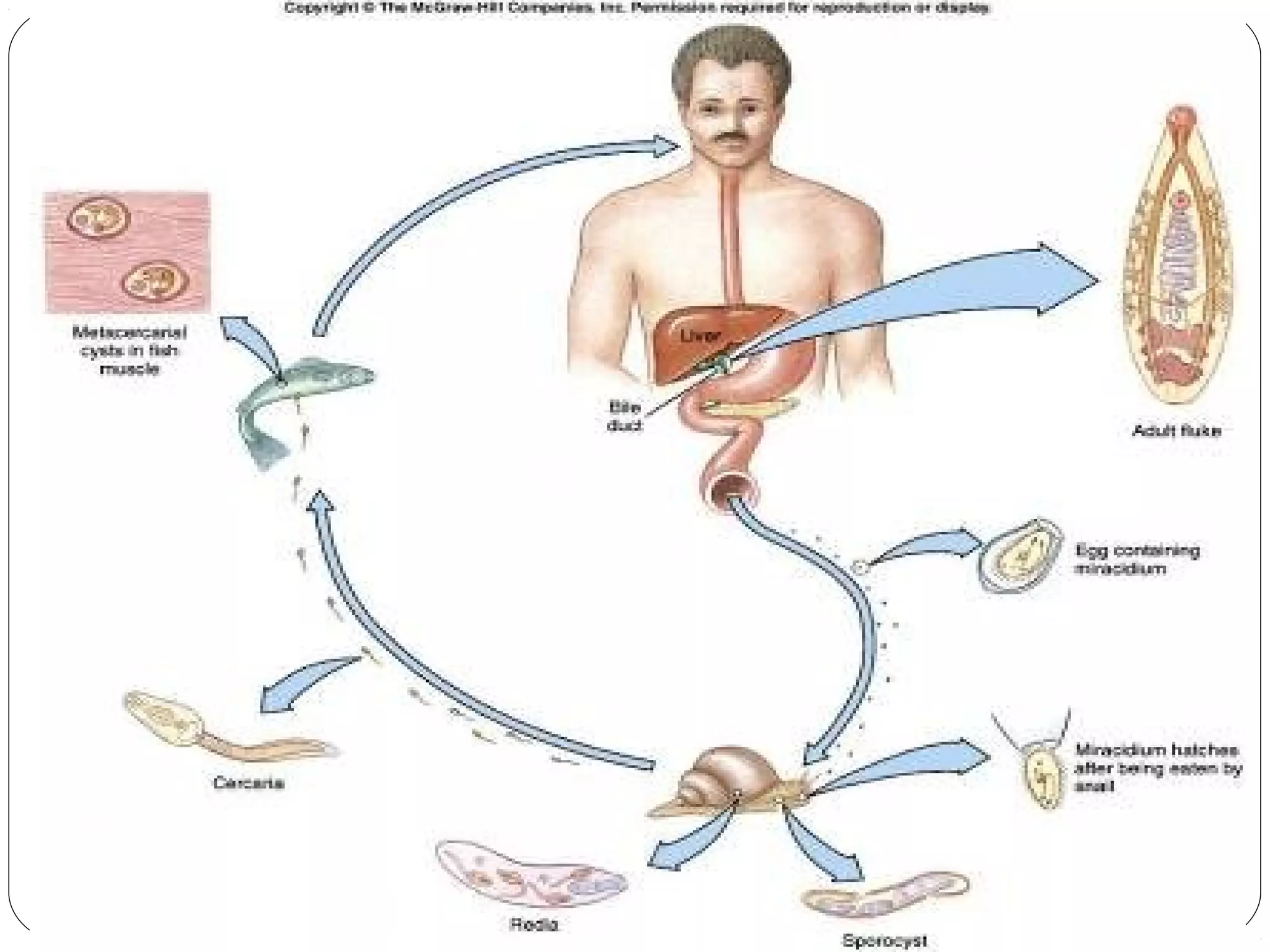
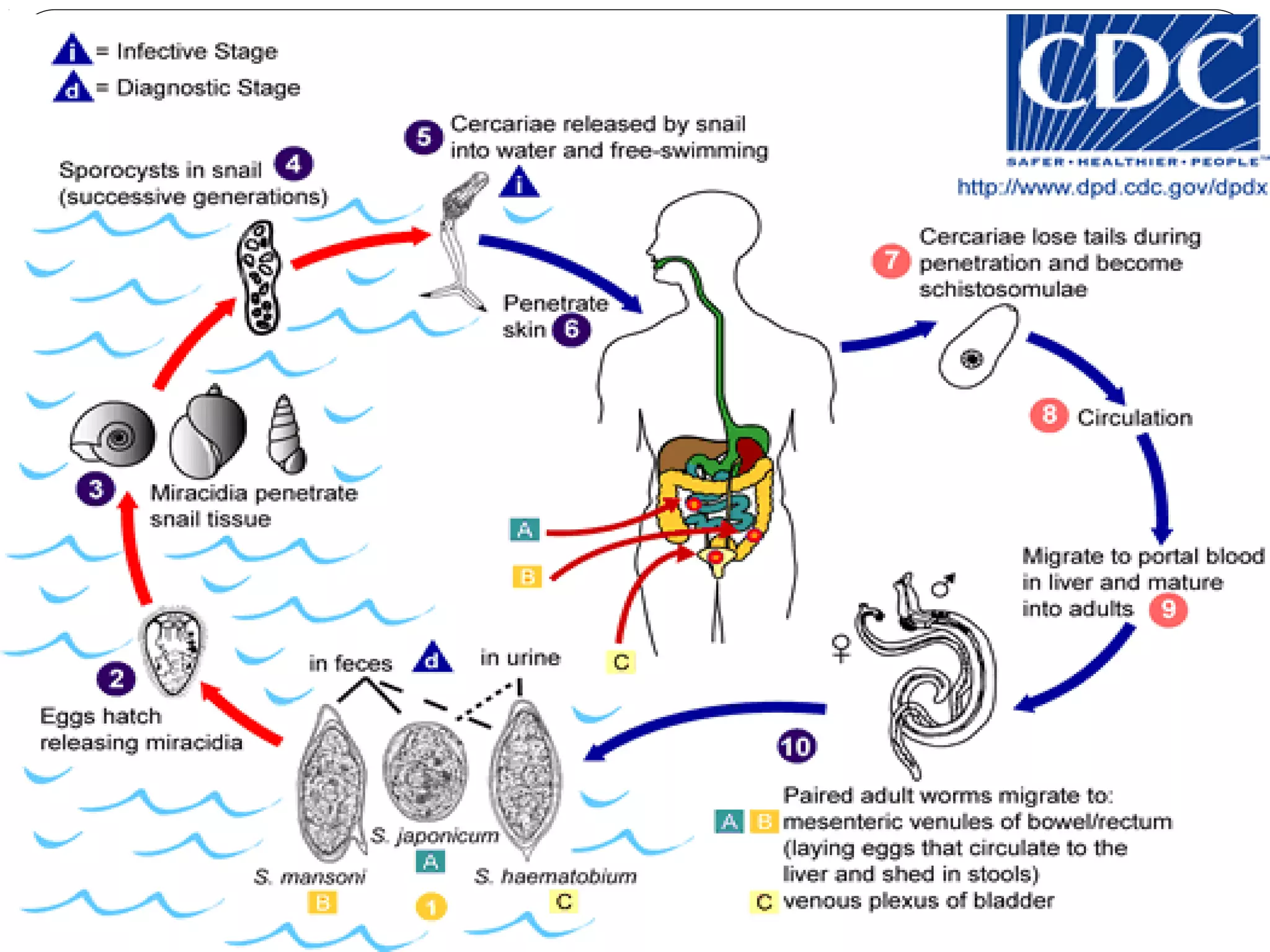
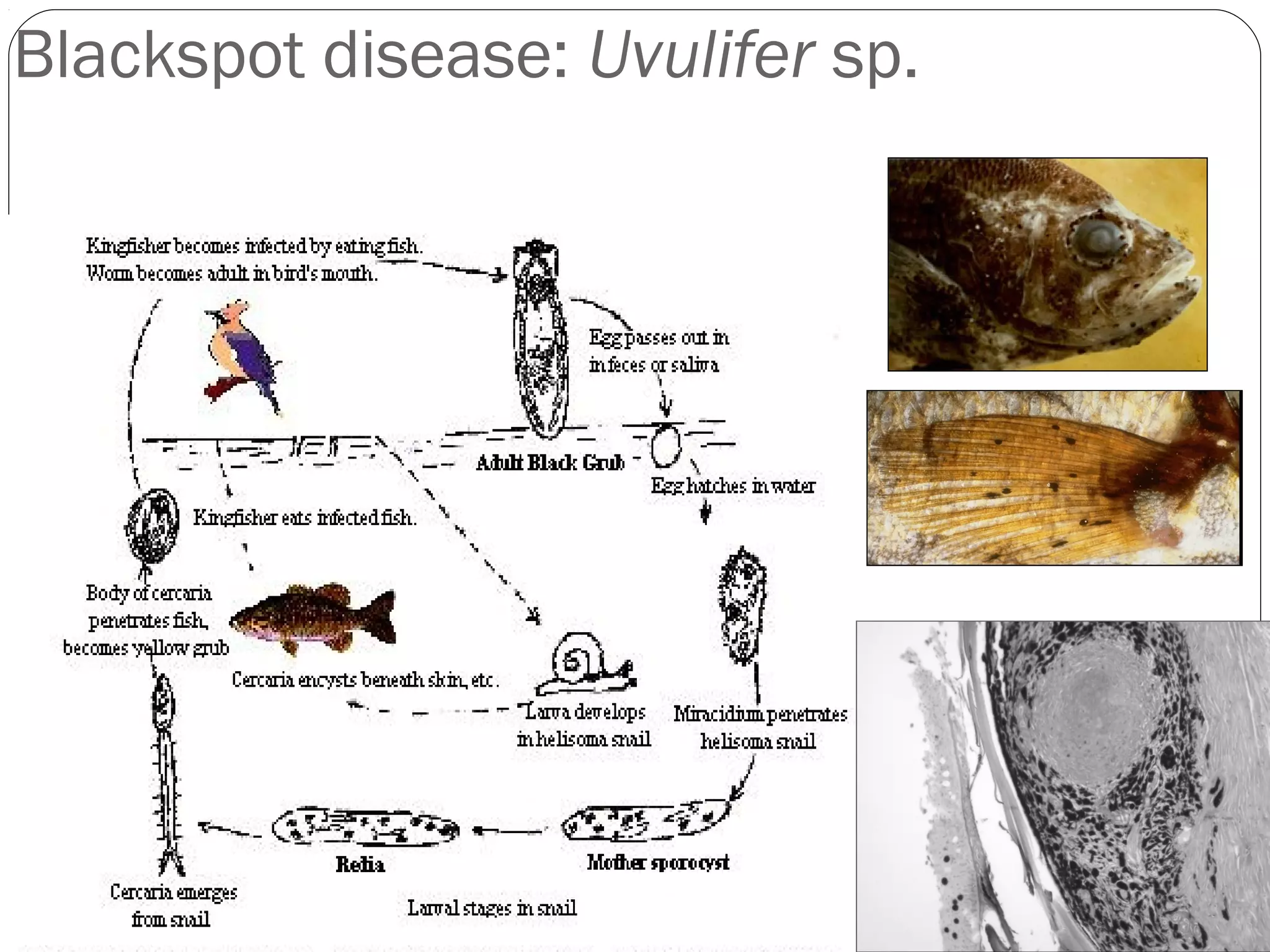
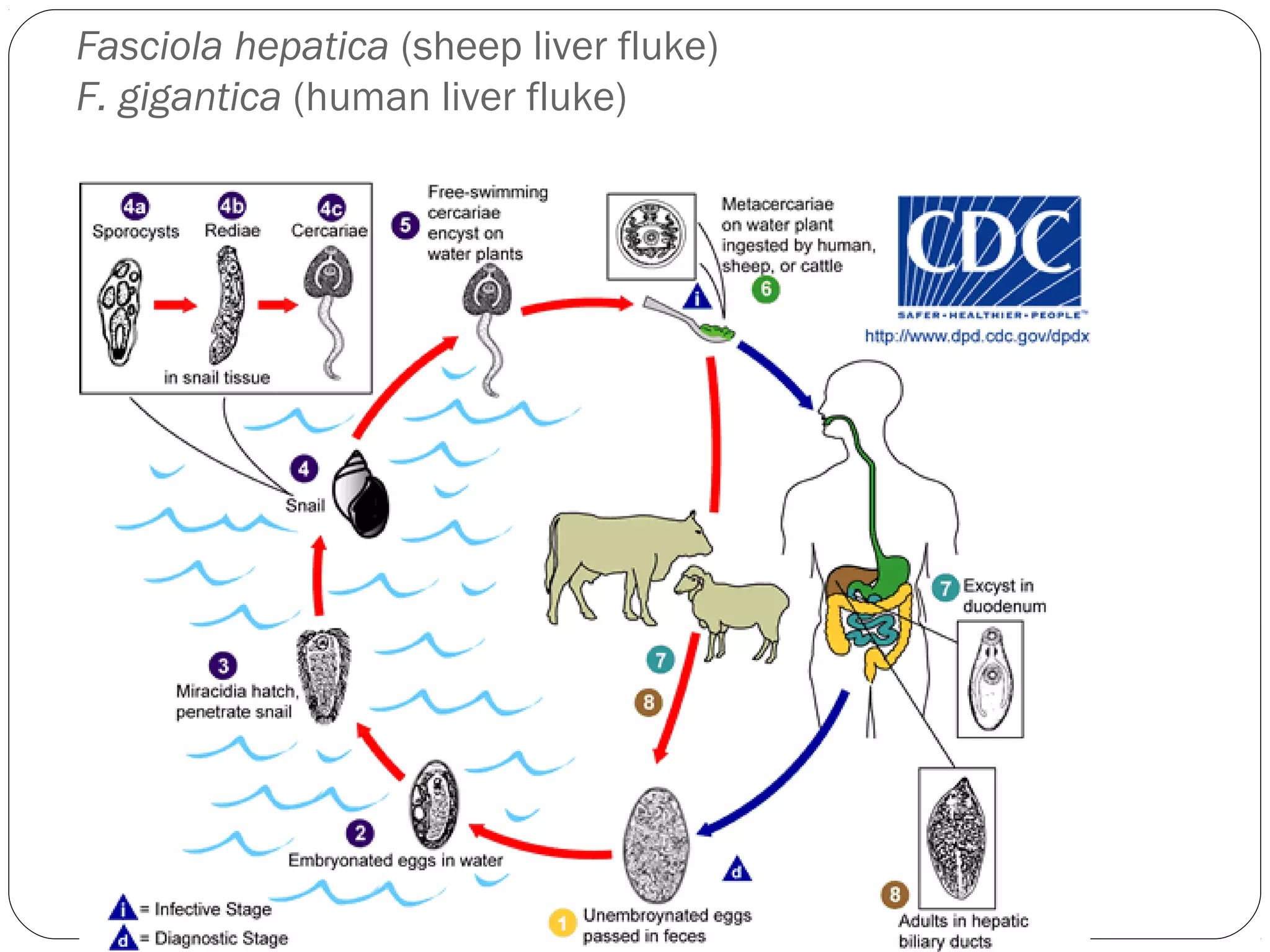
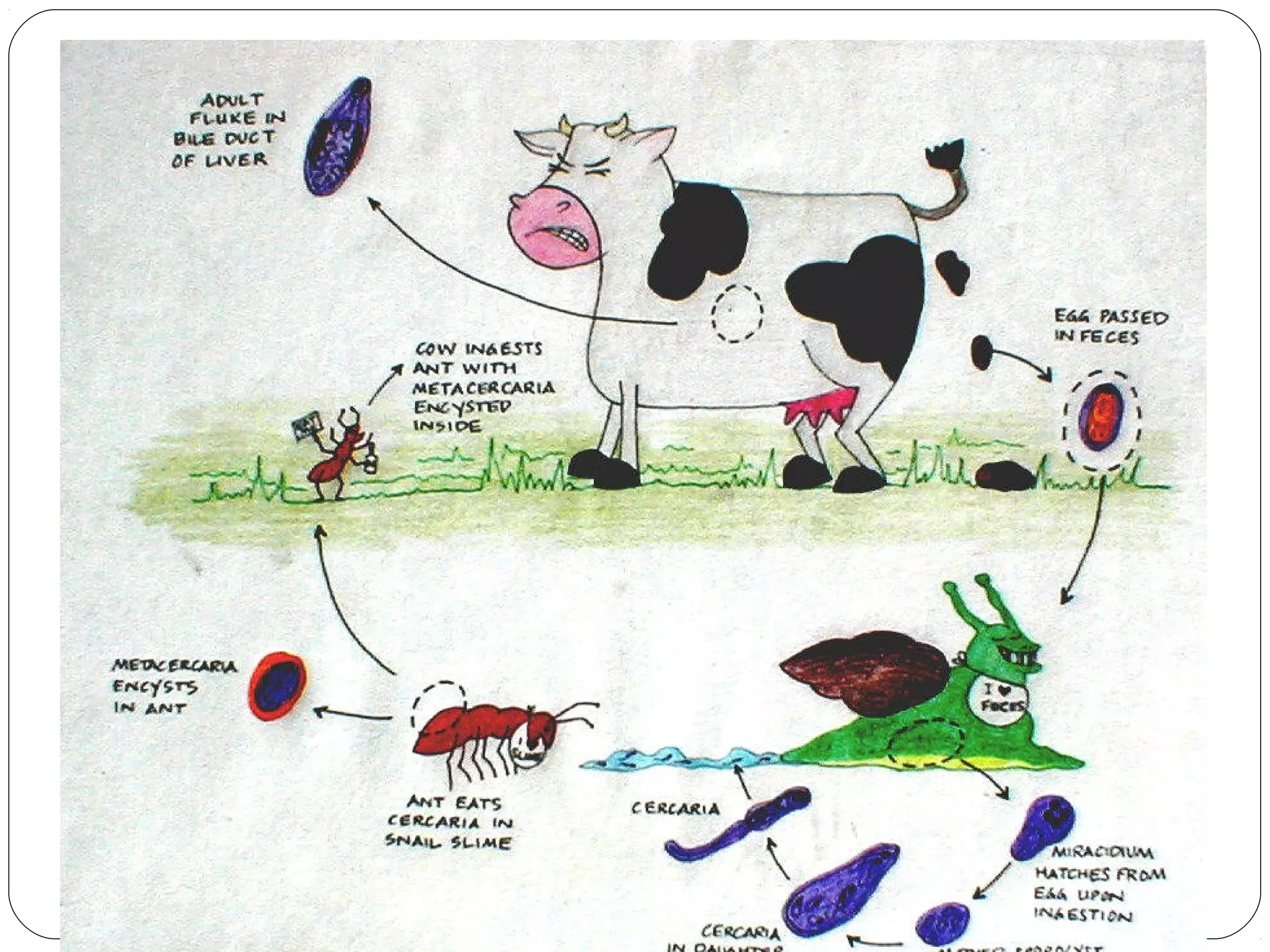
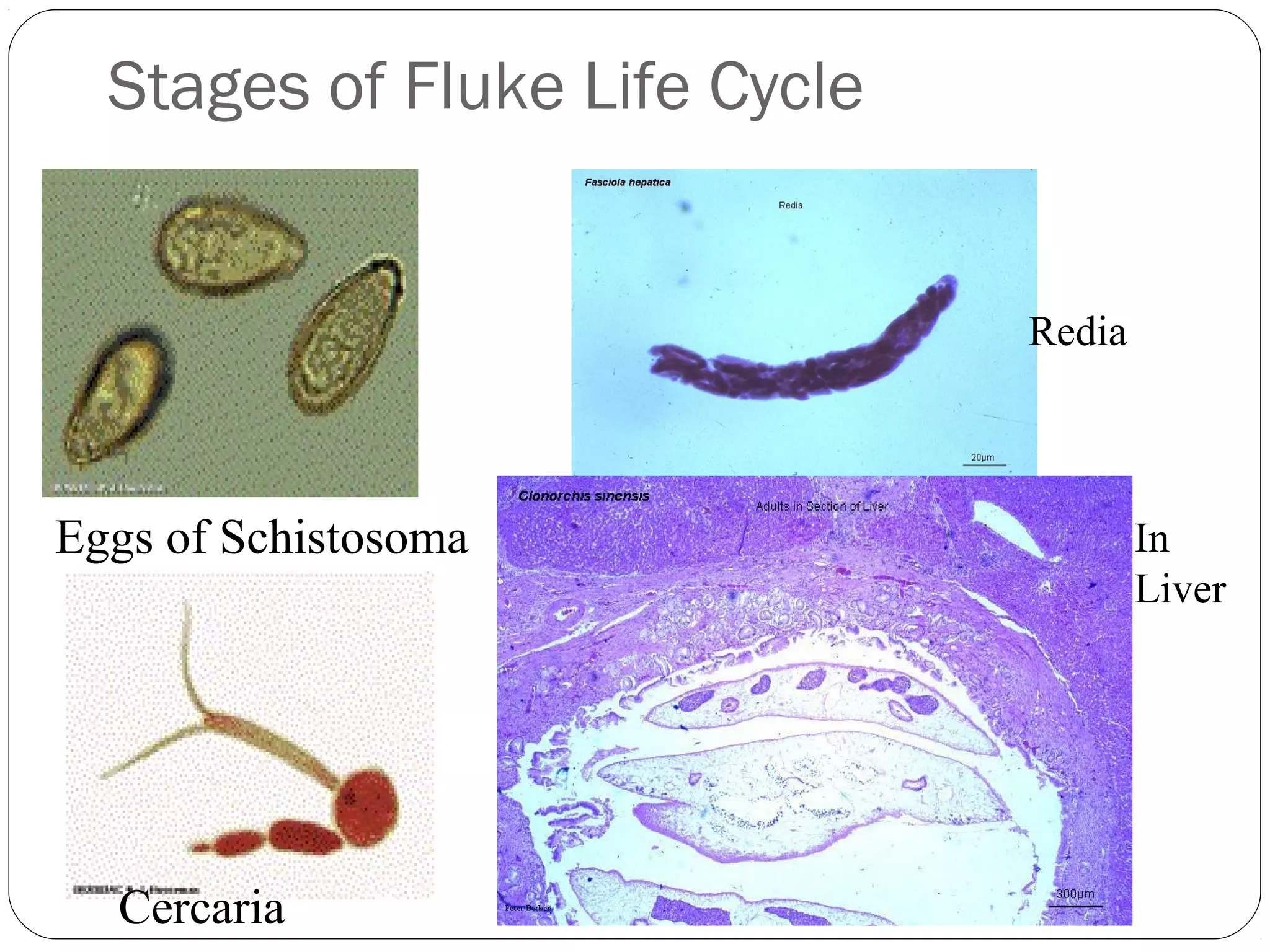
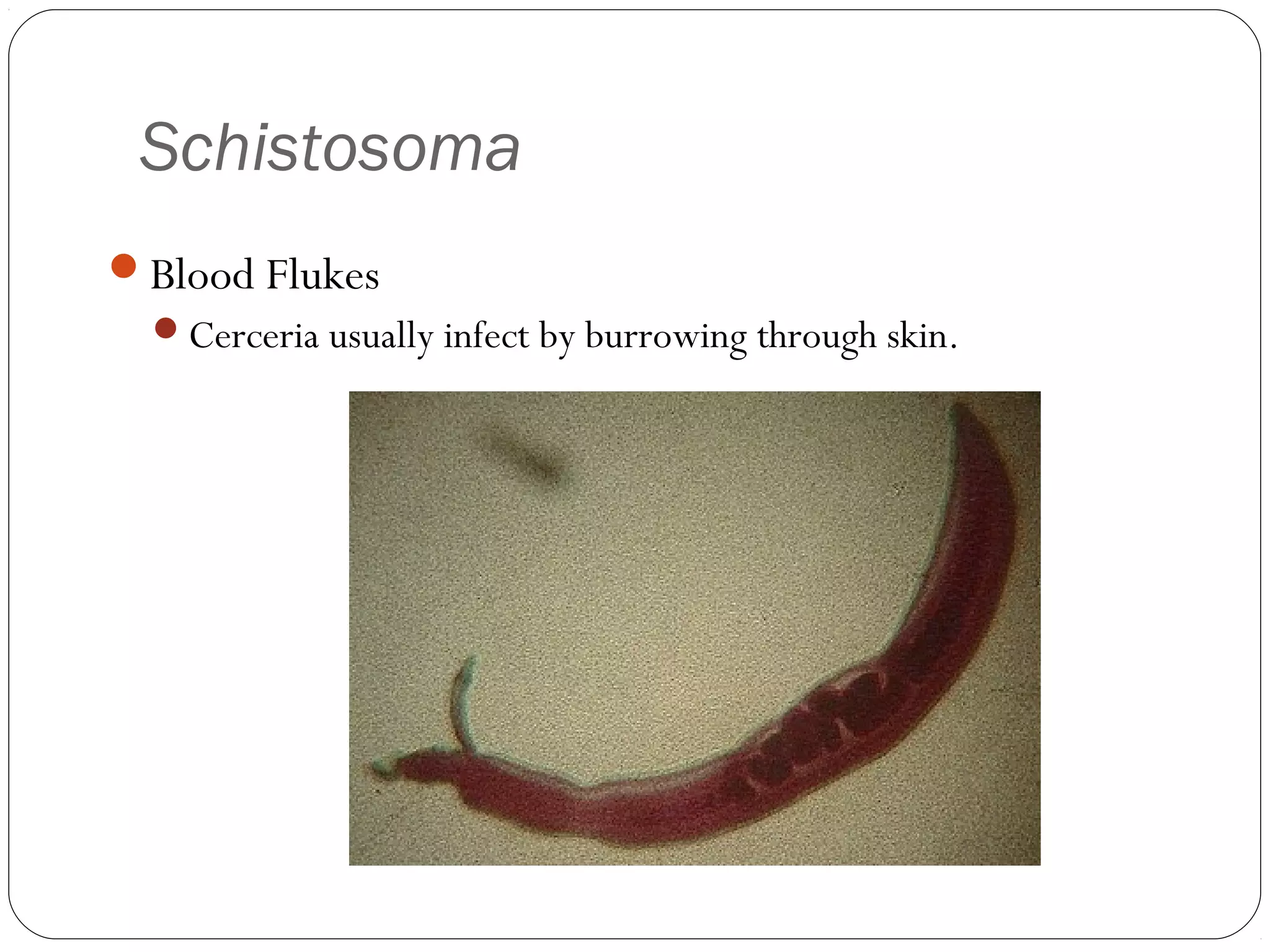
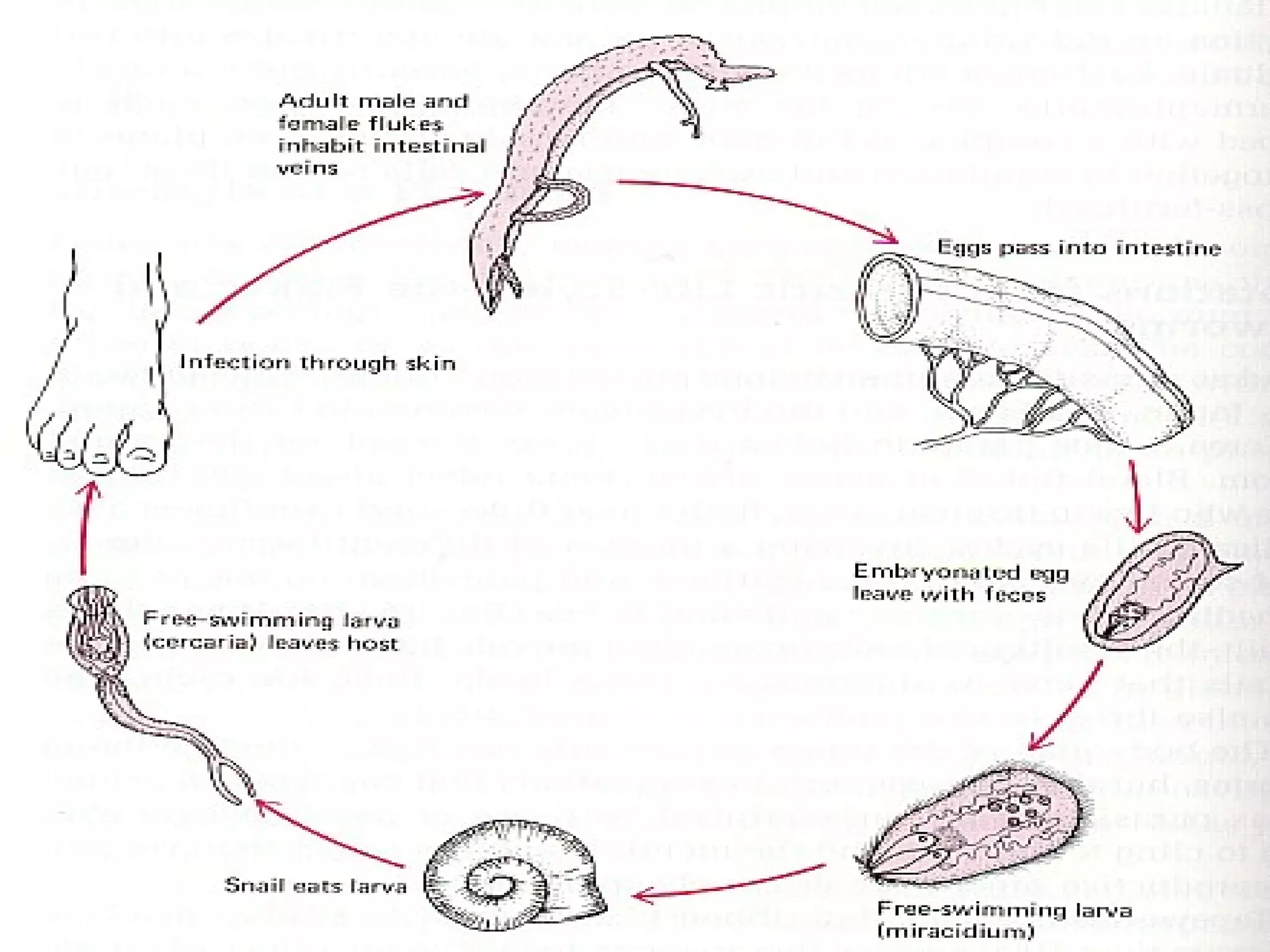
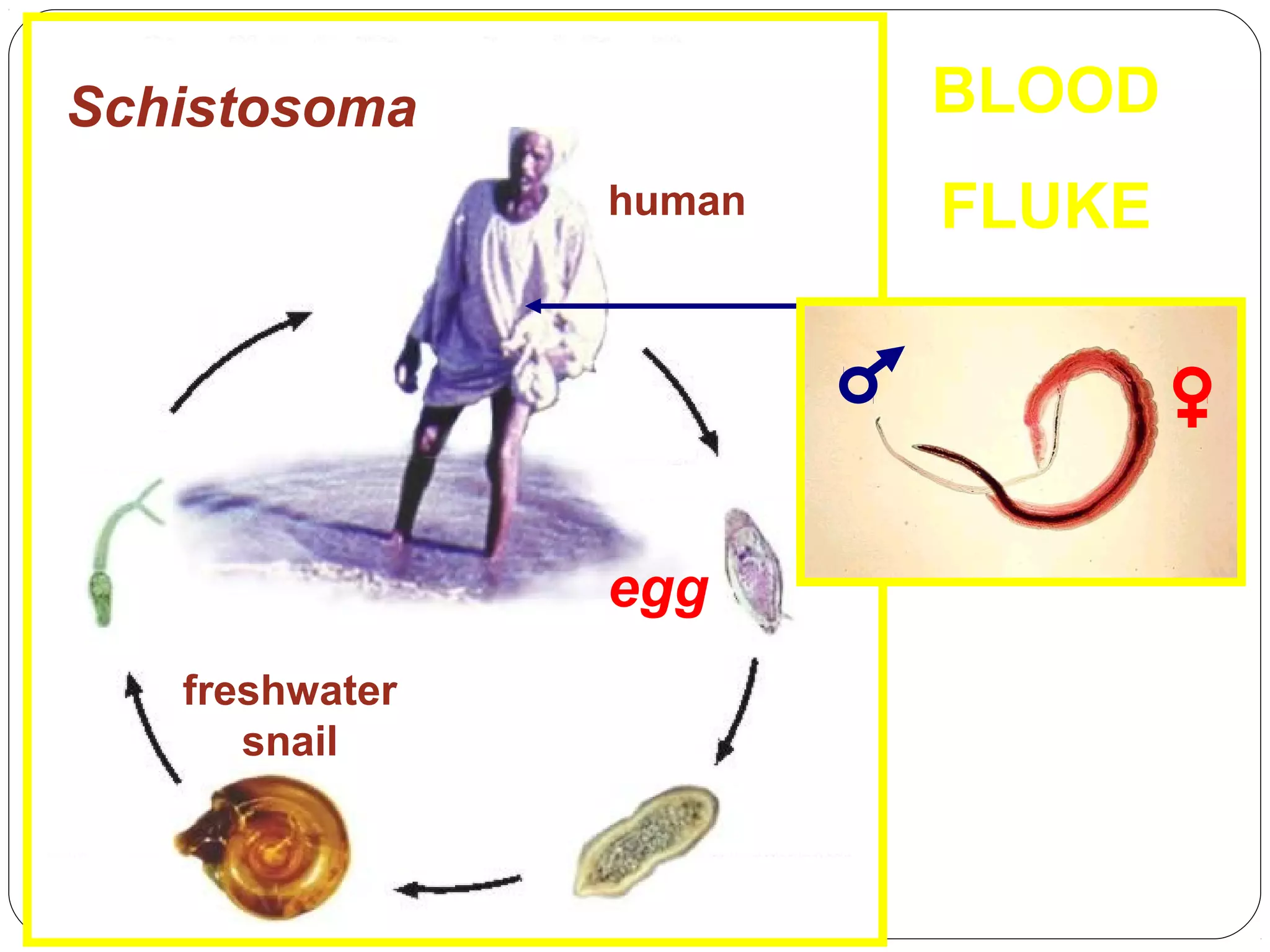
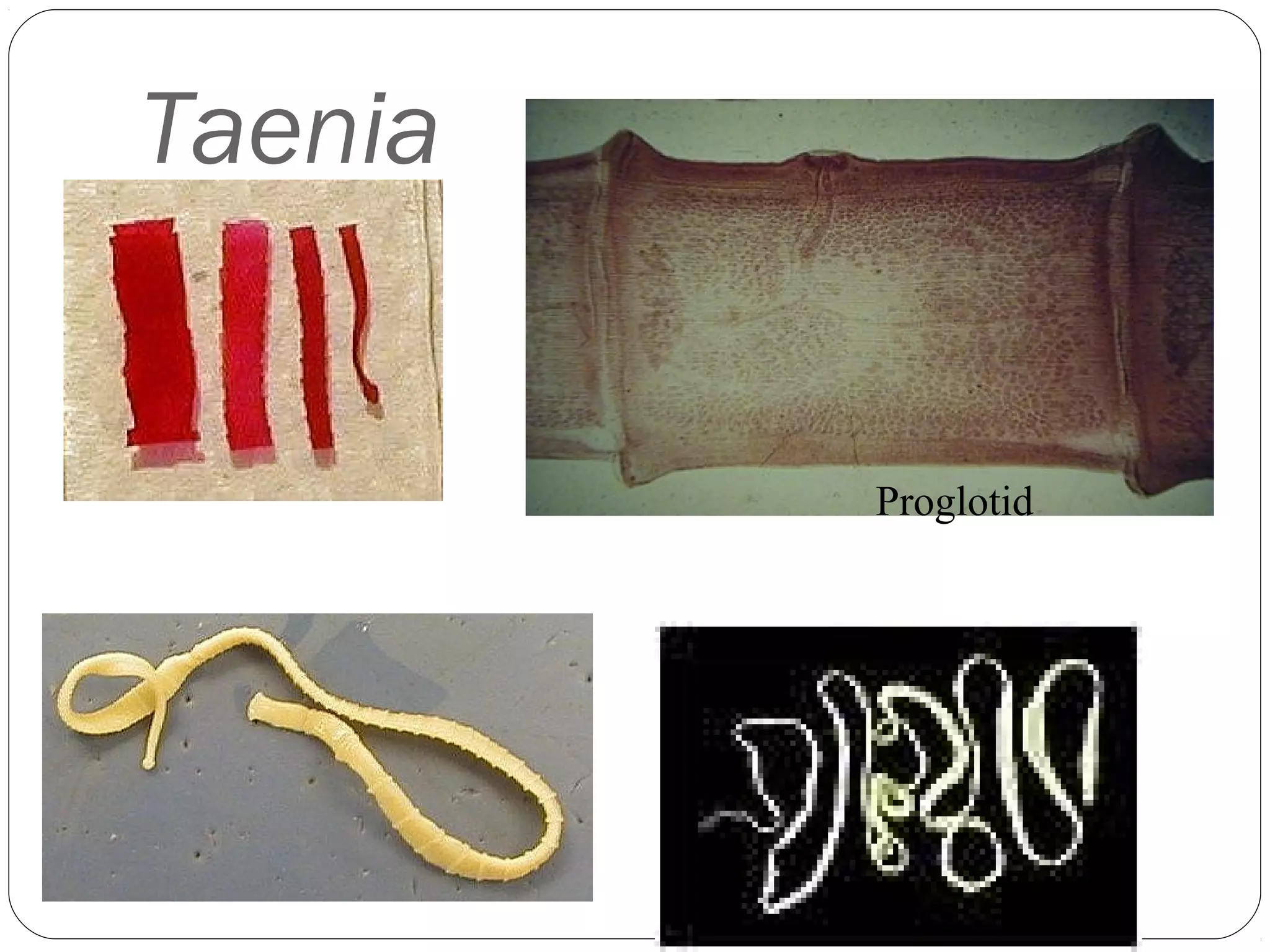
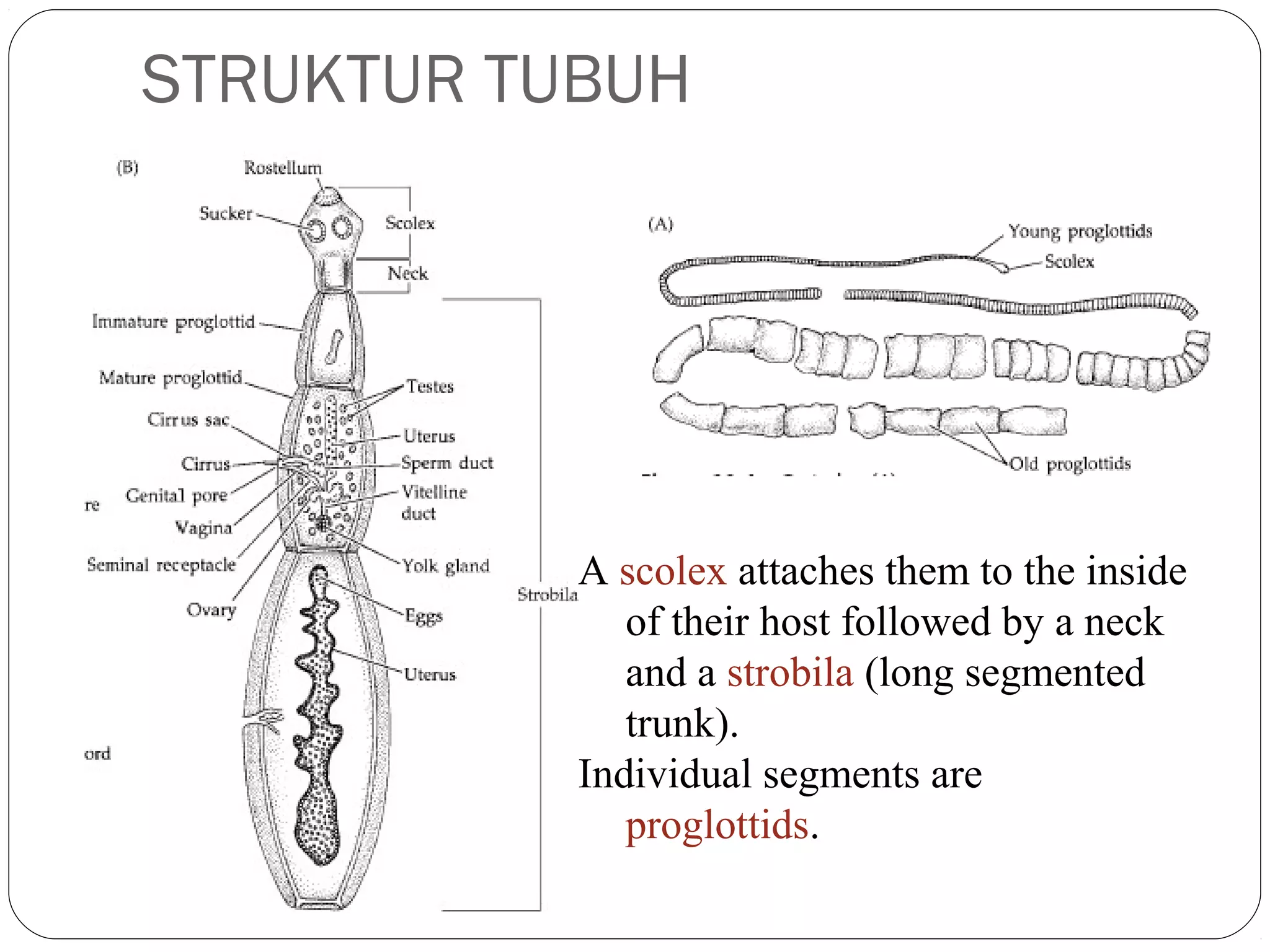
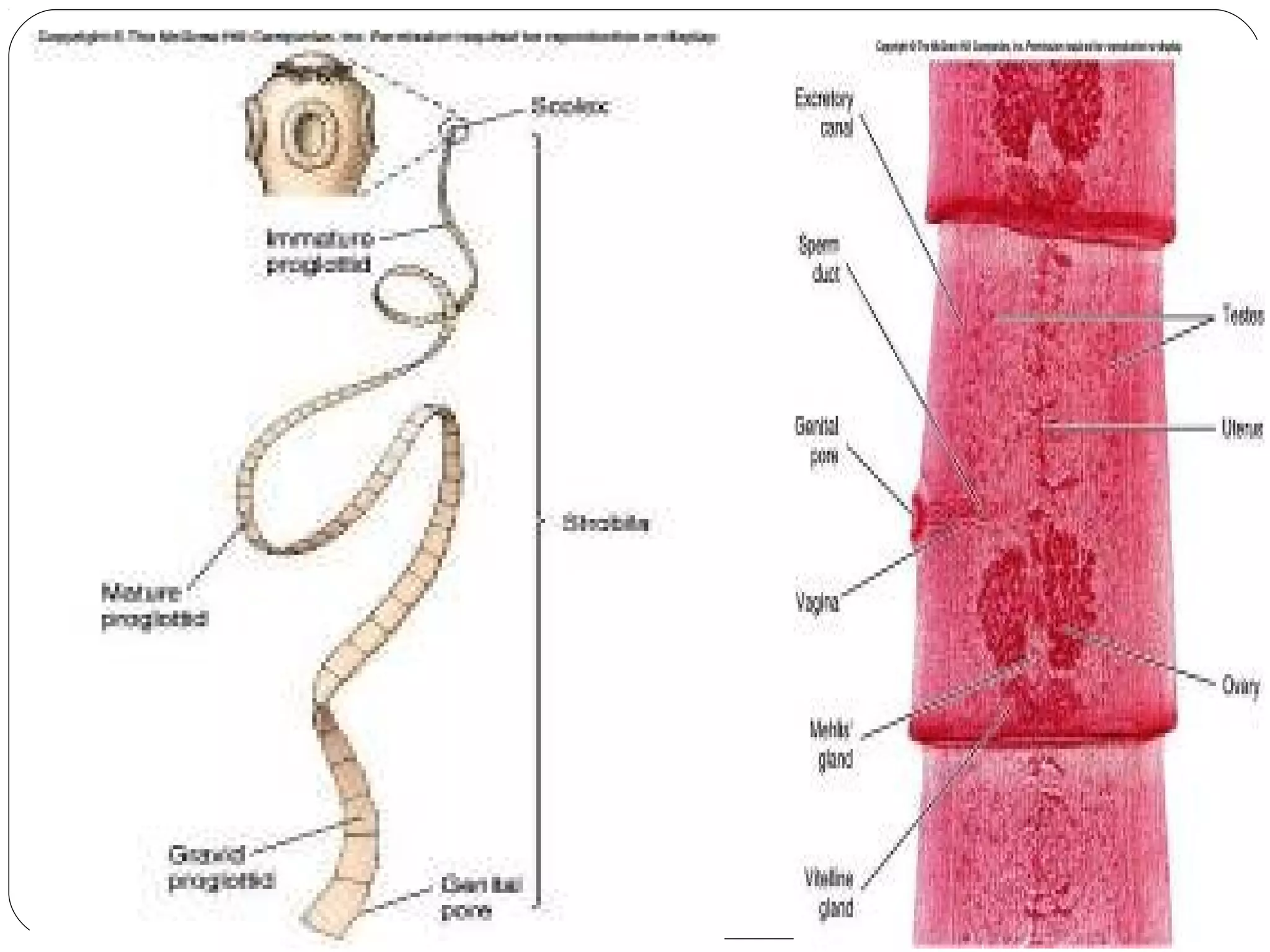
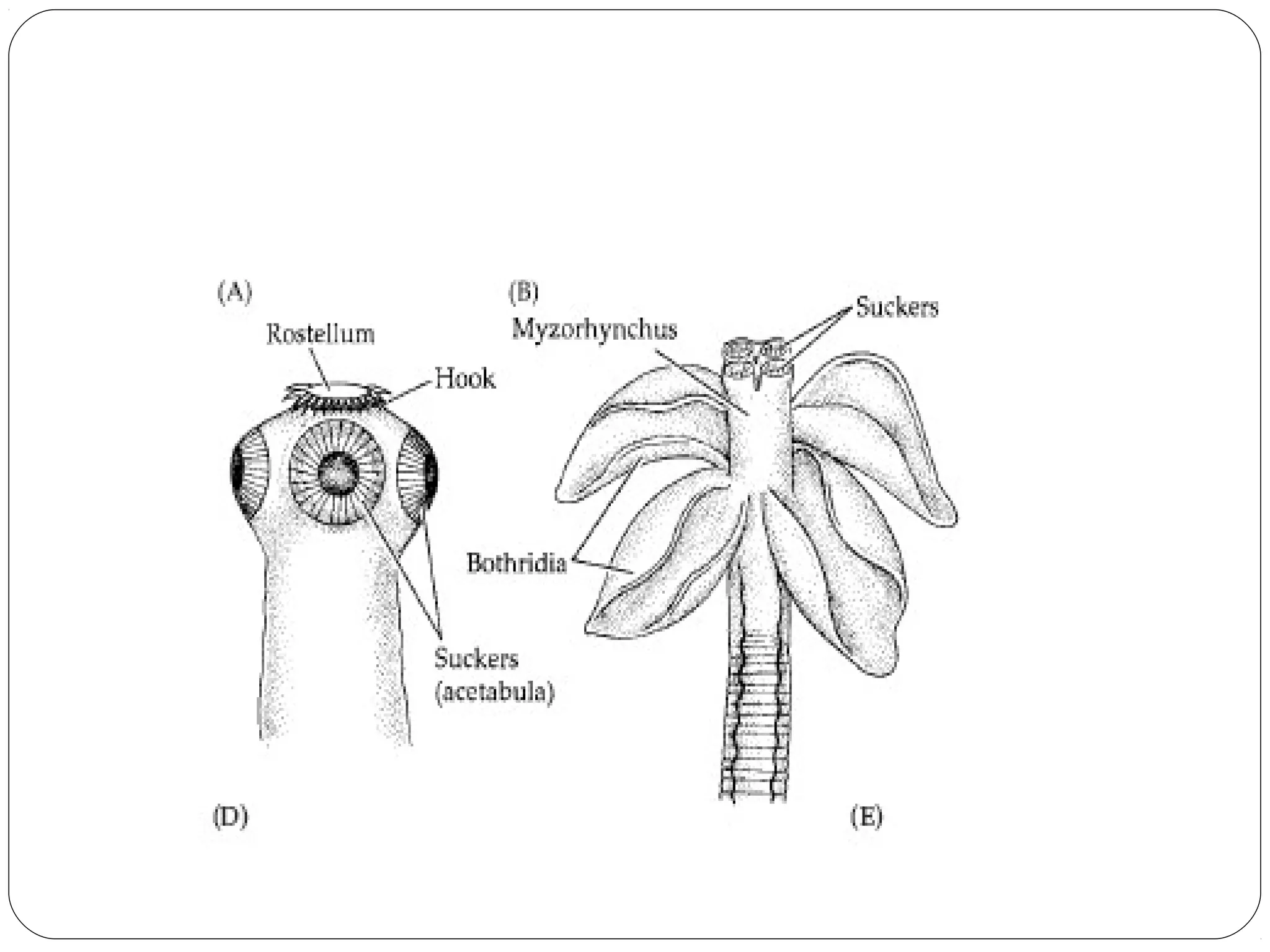
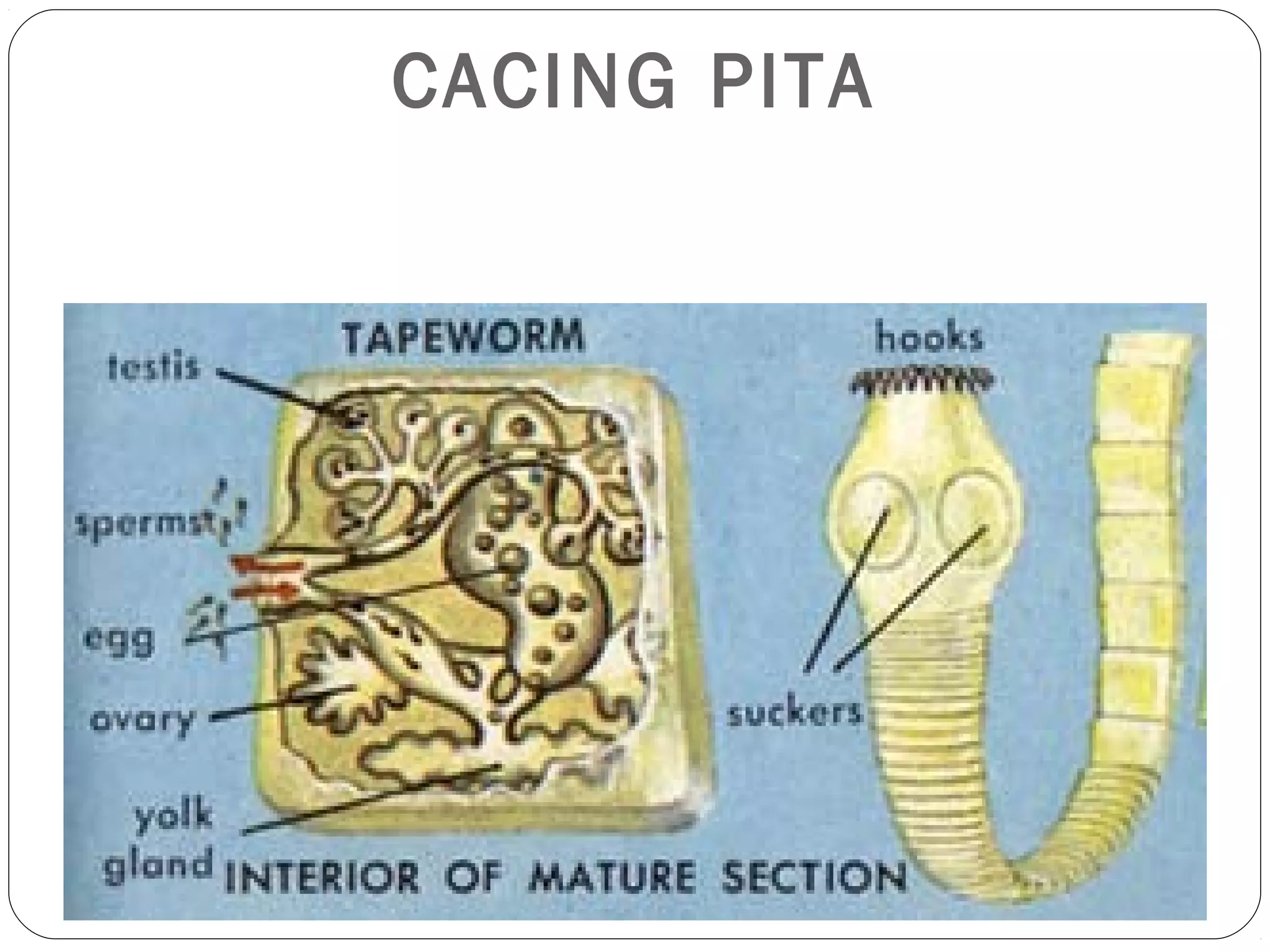
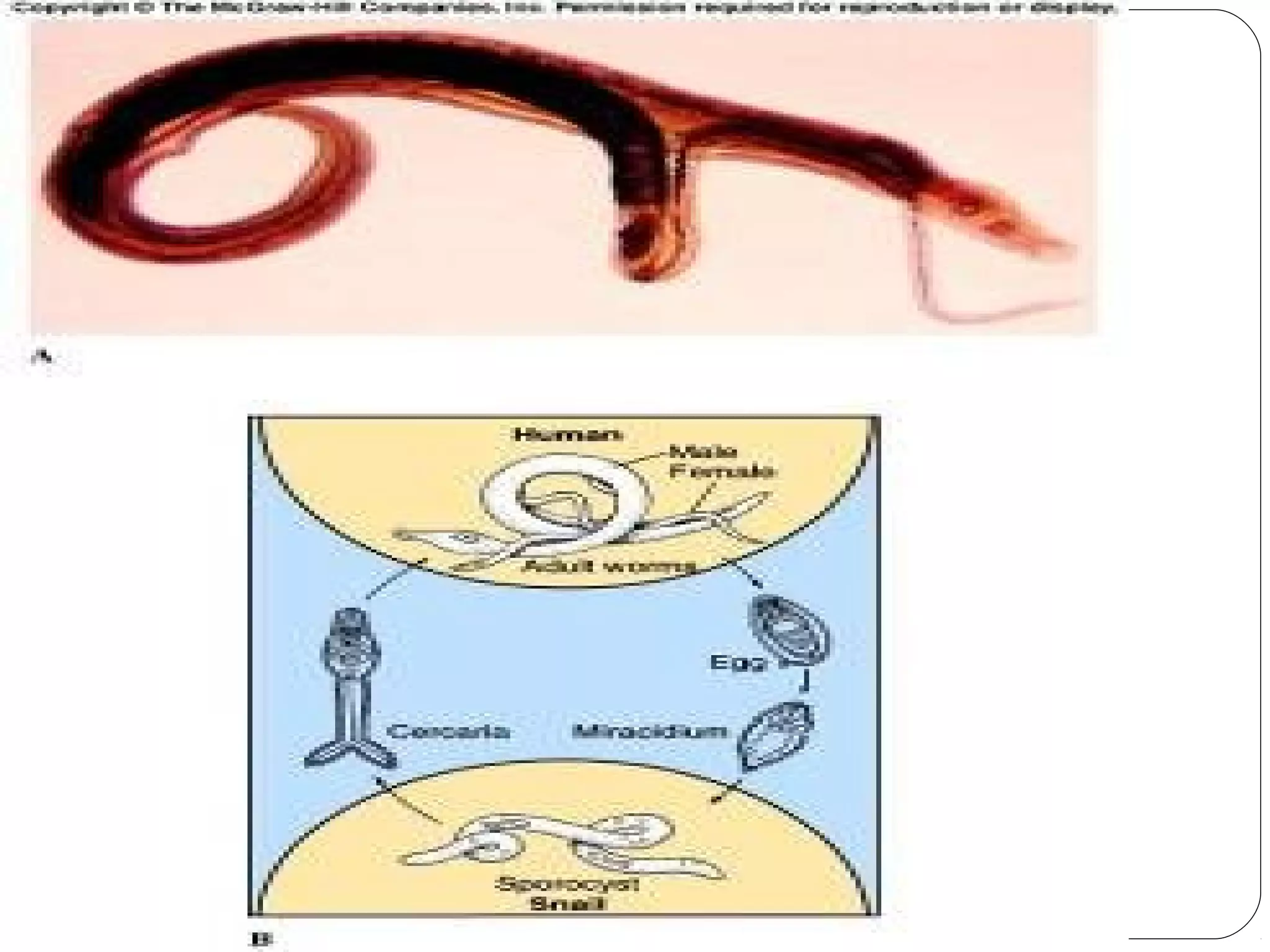
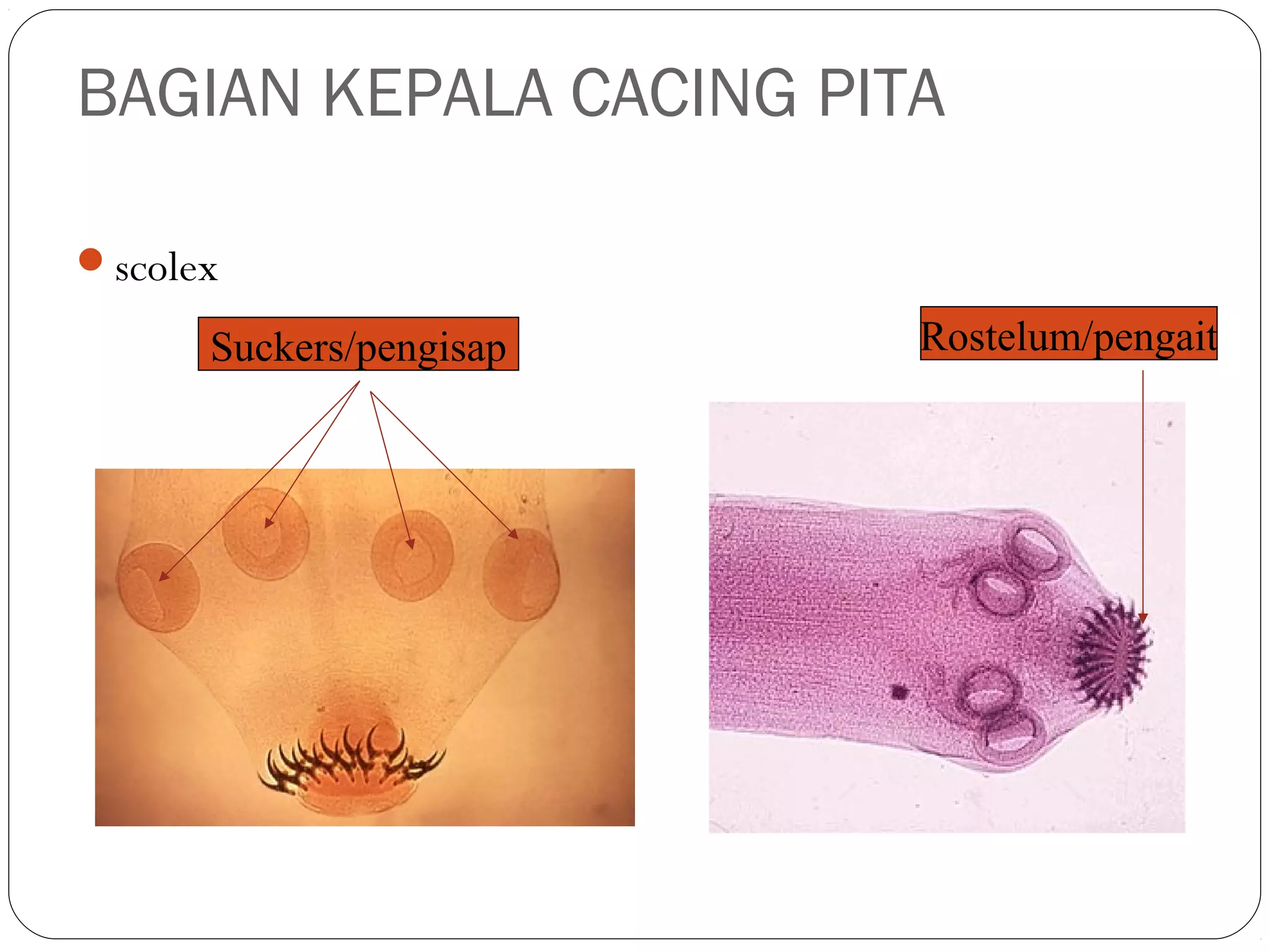
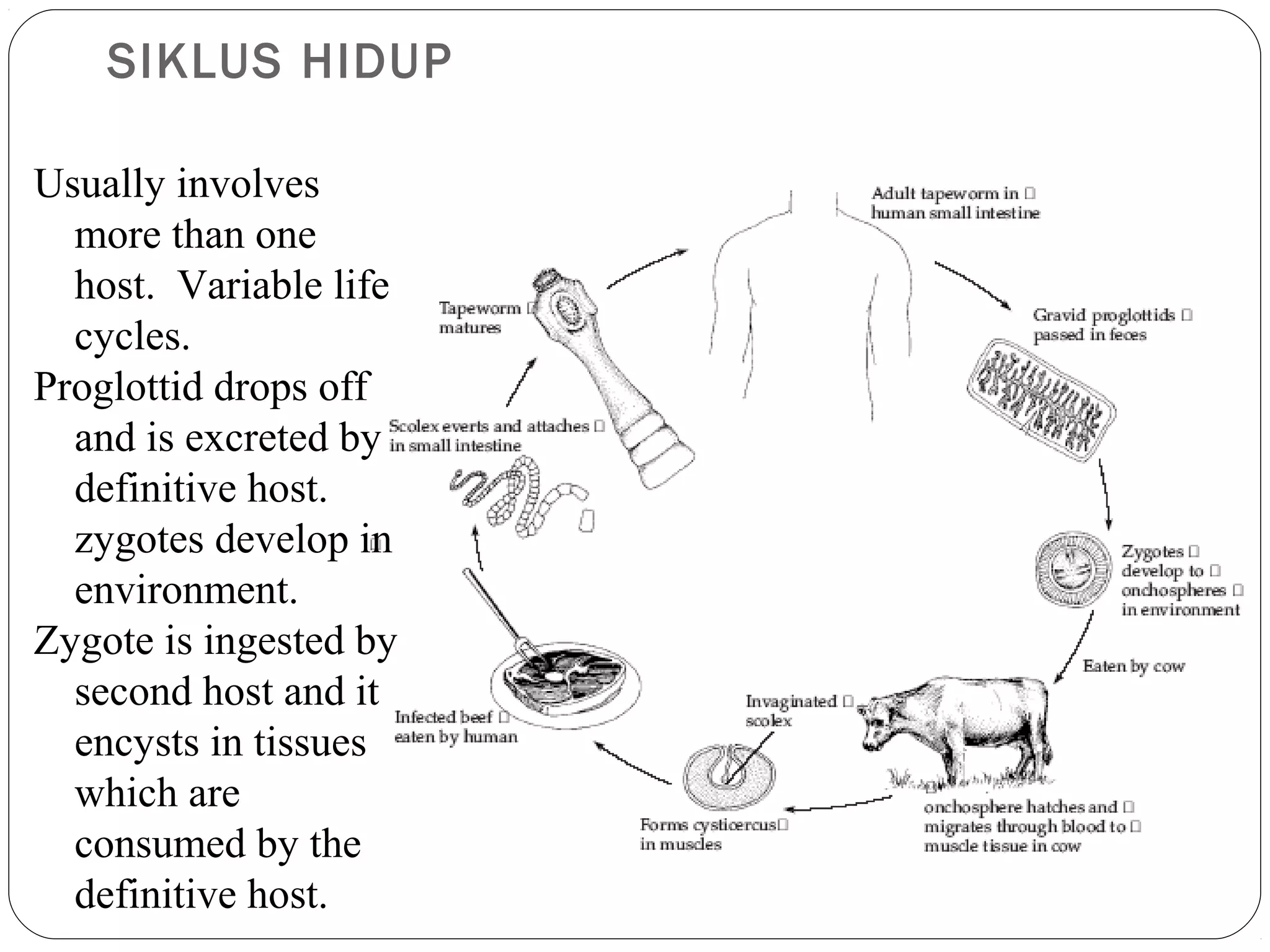
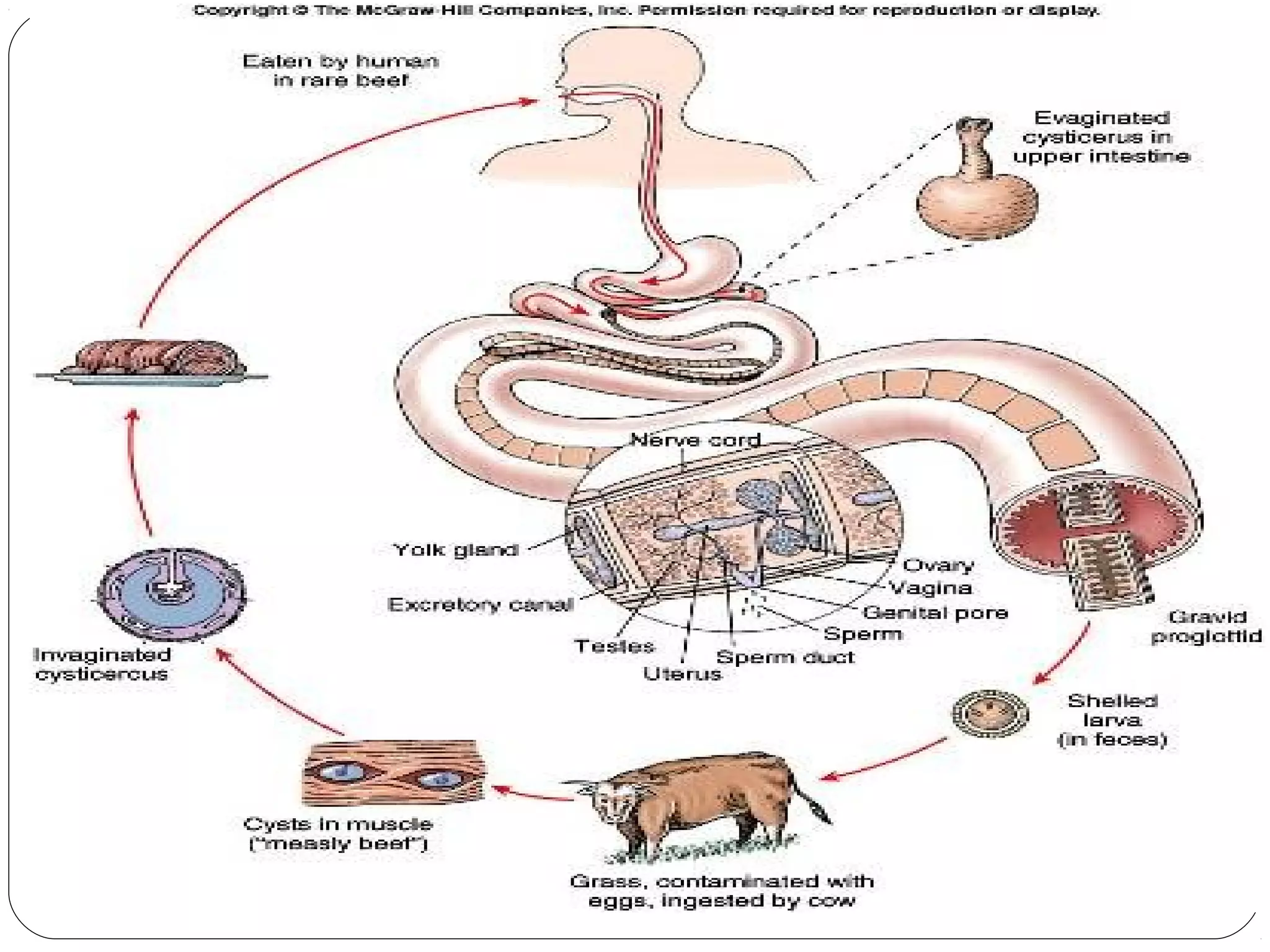
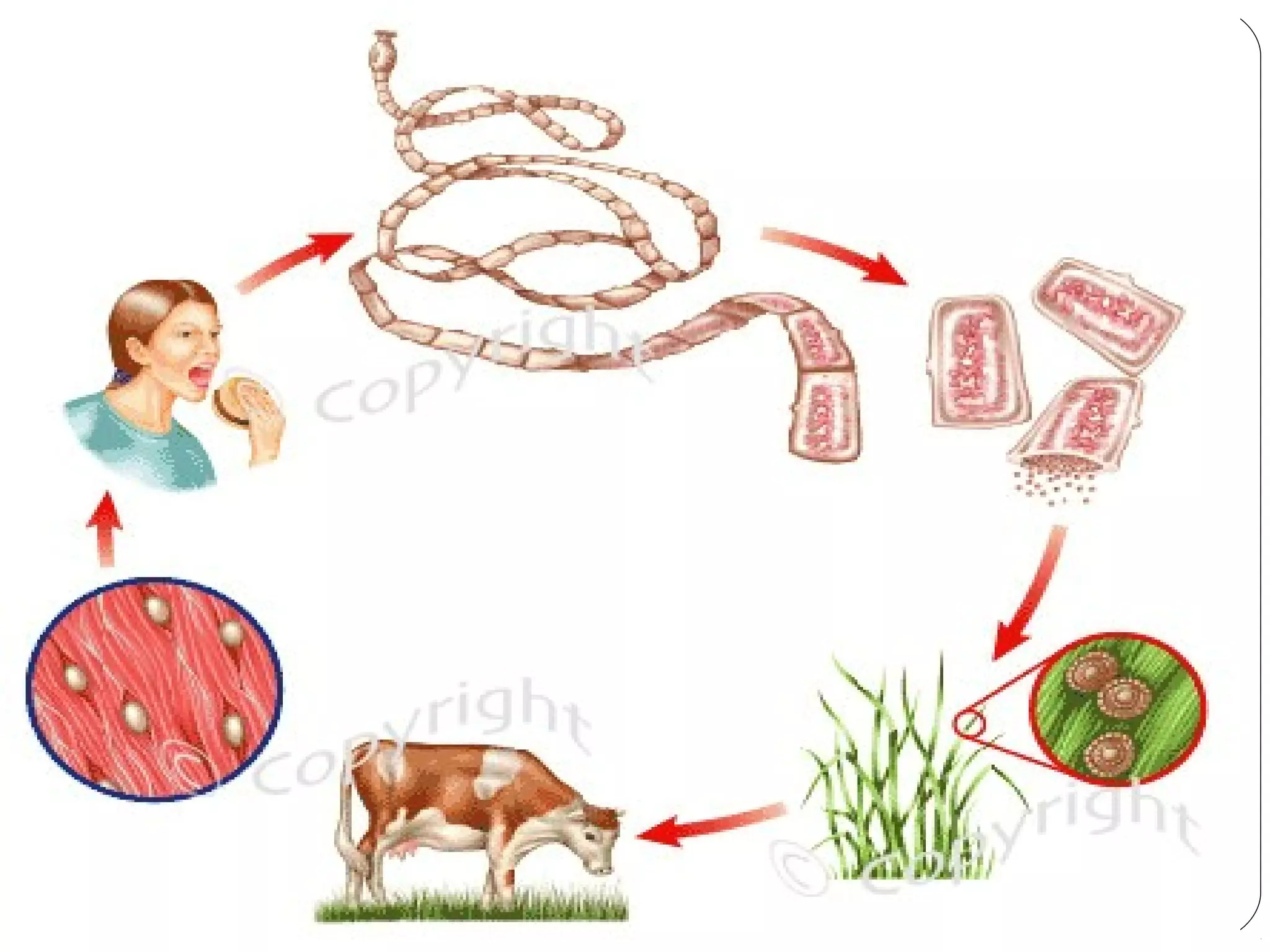
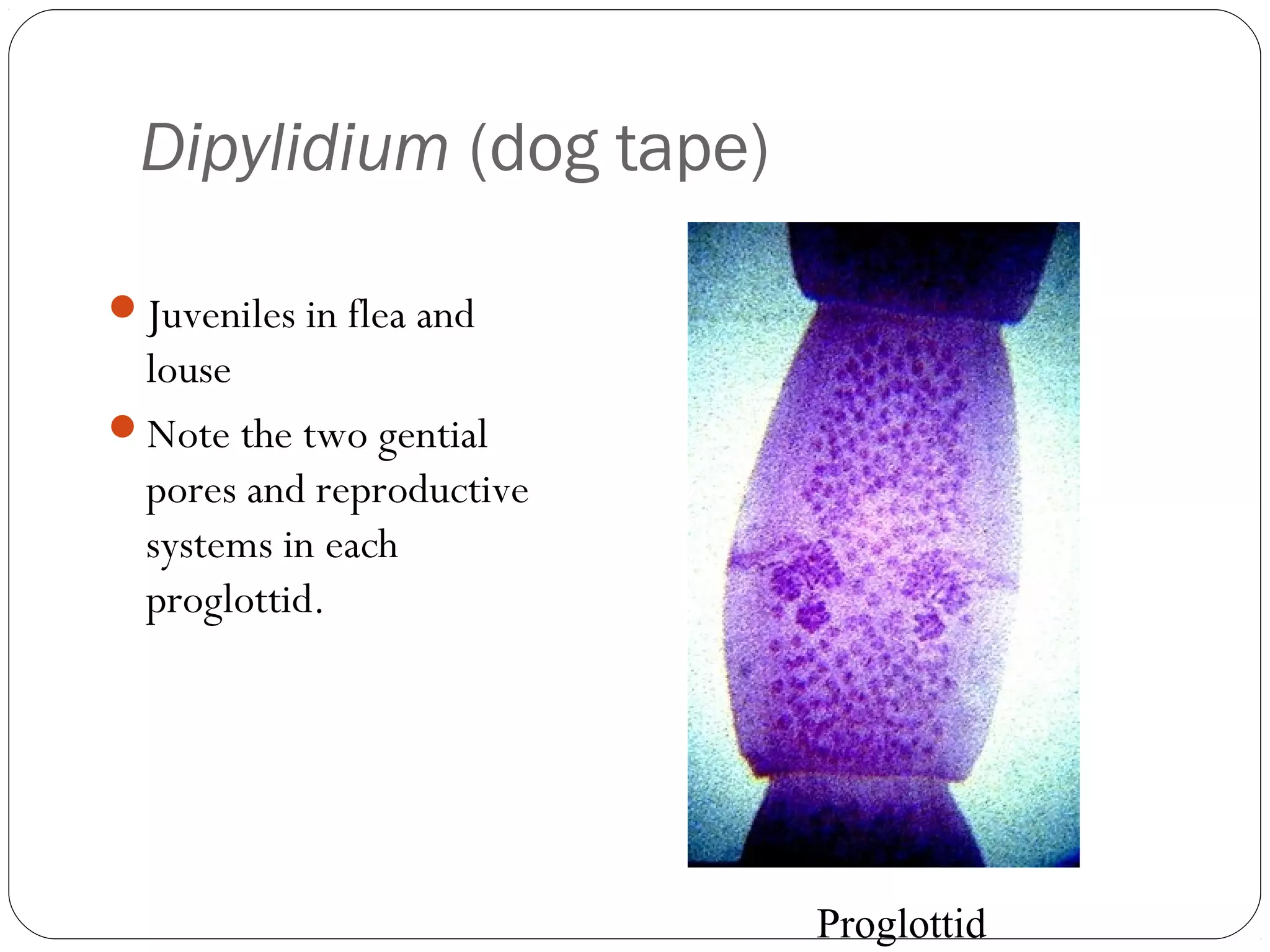
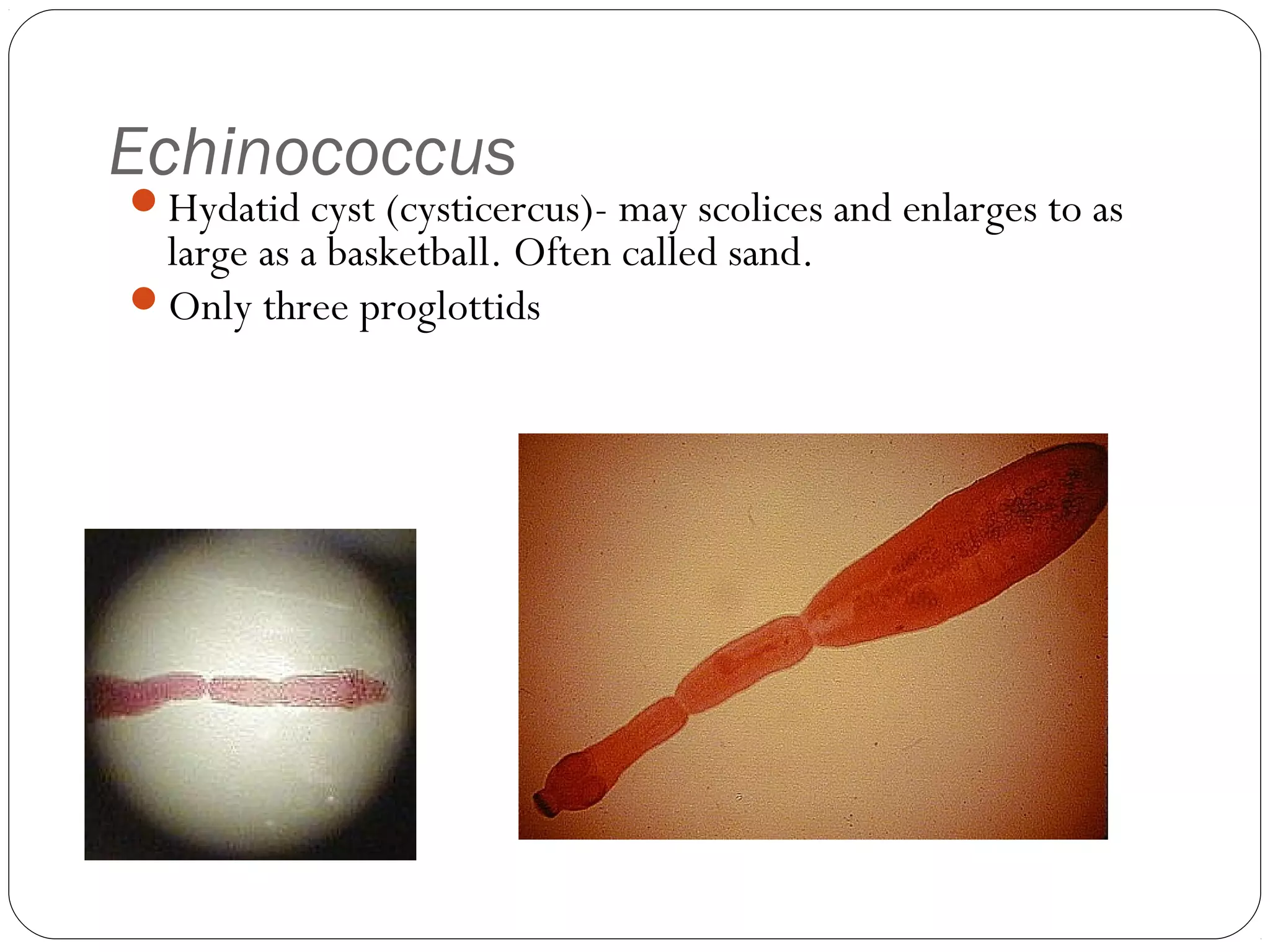
This document provides information about the phylum Platyhelminthes. It discusses their defining characteristics such as being triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, and lacking organs like a circulatory system. It describes the four classes - Turbellaria, Trematoda, Cestoda, and Monogenea. Key details are provided on representative genera for each class. Examples include the planarian Dugesia for Turbellaria, the flukes Clonorchis and Fasciola for Trematoda, and the tapeworms Taenia and Echinococcus for Cestoda. The document also examines anatomical structures, life cycles, and other biological systems and features of flatworms.