The document provides an introduction to the phylum Platyhelminthes. Some key points:
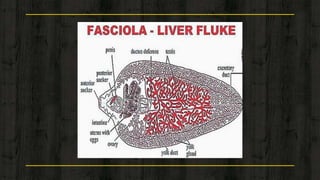
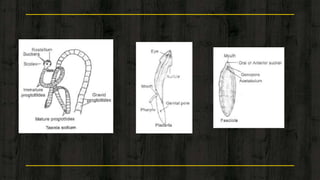
1) Platyhelminthes includes flatworms and are the most primitive bilateral animals, with some being free-living and others being parasites.
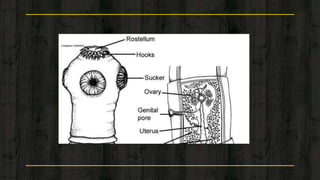
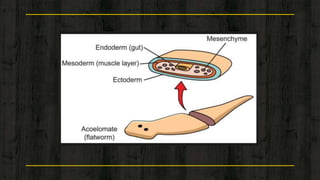
2) They have a triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical body without organs for locomotion but with adhesive organs like suckers.
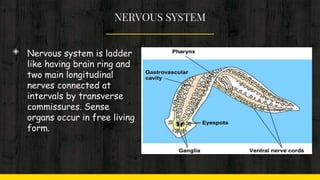
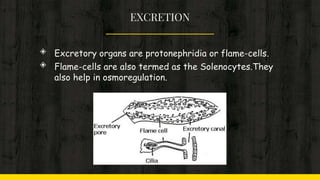
3) Their nervous system is ladder-like with a brain ring and longitudinal nerves connected by transverse commissures. They lack circulatory and respiratory systems.