The document discusses various aspects of engine design and operation, including:
1. It classifies engines based on their stroke cycle, combustion type, cooling method, valve arrangement, cylinder arrangement, and lists the requirements for proper combustion.
2. The main components of an engine like the cylinder block, crankshaft assembly, piston assembly, cylinder head, valves, and lubrication system are described.
3. The four stroke cycle and engine specifications such as bore and stroke, compression ratio, and displacement are explained.
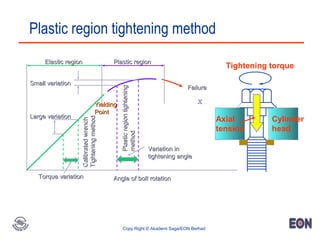
4. The document provides details on engine timing diagrams, cooling and lubrication system operation, and discusses tightening procedures and measurement techniques.






























![ENGINE SPECIFICATION
HOW TO MEASURE TOTAL
DISPLACEMENT
TOTAL DISPLACEMENT
33..1144
44 FF//mm :: p == xx DD² xx LL xx 44
Copy Right © Akademi Saga/EON Berhad
[B
ore
]Stroke
0.7854 x Bore²(cm) x Stroke(cm) x No.Cyl.
Example : 0.7854 x 7.6 x 7.6 x 8.73 x 4
=1584 cc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engine4g1-141116234201-conversion-gate01/85/Engine-4G15-31-320.jpg)