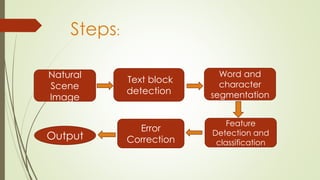
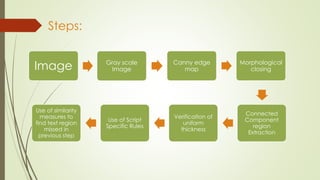
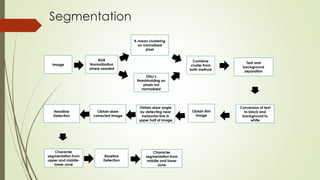
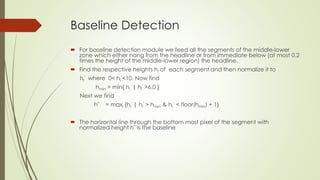
The document describes the steps for Hindi scene text recognition including:
1. Detecting text blocks in natural scene images using canny edge detection and morphological operations.
2. Segmenting words using vertical histogram analysis and character segmentation using region growing after removing headlines.
3. Recognizing characters using feature extraction and classification.
The goal is to create a system that can detect and recognize Devanagari characters from natural scene images to enable search of image texts.