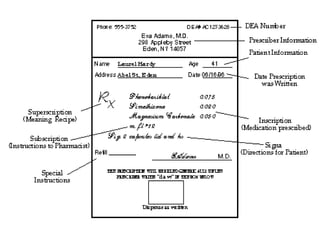
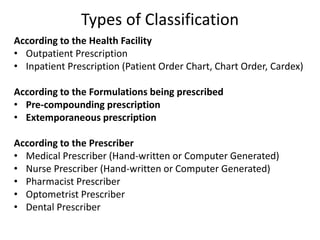
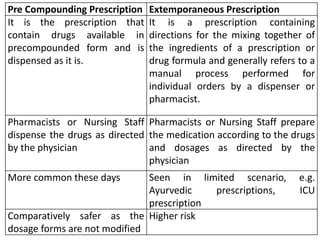
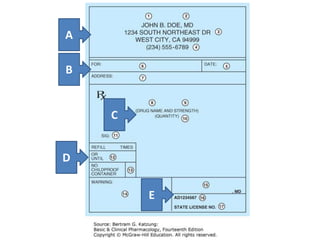
A prescription is a written order from a physician directing a pharmacist to dispense medication. It contains 4 main components: superscription with the Rx symbol, inscription with drug name and dosage, subscription with instructions for the pharmacist, and signature with instructions for the patient. Prescriptions can be classified as outpatient or inpatient, pre-compounded or extemporaneous, and by the type of prescriber. Key elements of a prescription include prescriber information, patient information, drug name and strength, quantity, directions for use, refill information, and prescriber identification. Prescribing errors can occur due to omission of information, poor handwriting, inappropriate drug selection, or failure to consider patient history or interactions