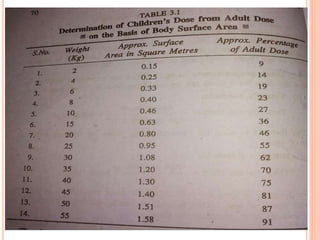
This document discusses posology, which is the science of calculating drug doses. It defines posology and explains that many factors can influence the appropriate dose of a drug for a patient, including age, sex, body weight, route of administration, and medical conditions. The document provides details on calculating doses for children, adjusting for body weight, and determining veterinary doses for animals based on surface area and weight. Overall, the document outlines the key principles of posology and the various considerations involved in accurately prescribing medication doses for both human and animal patients.