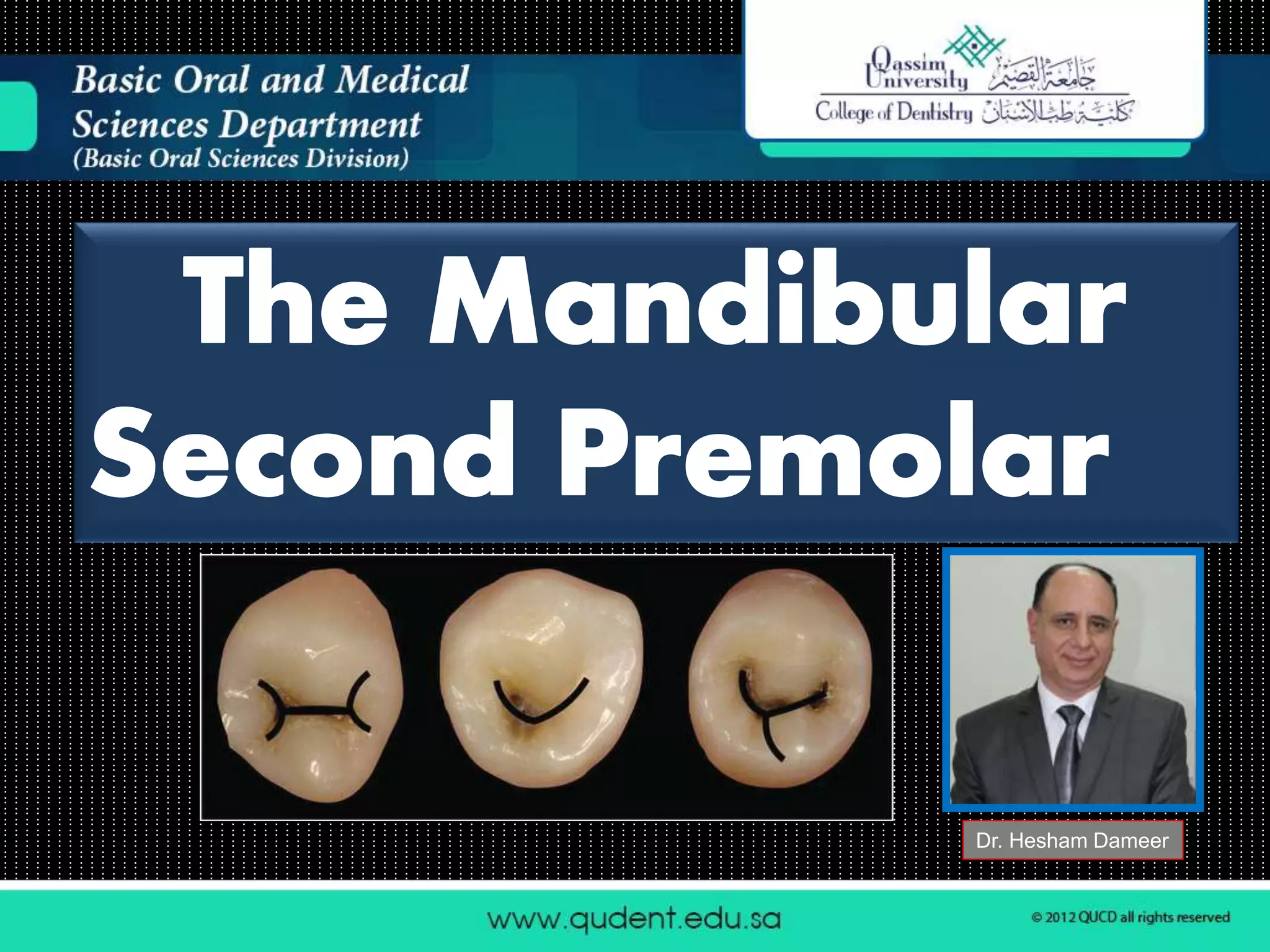
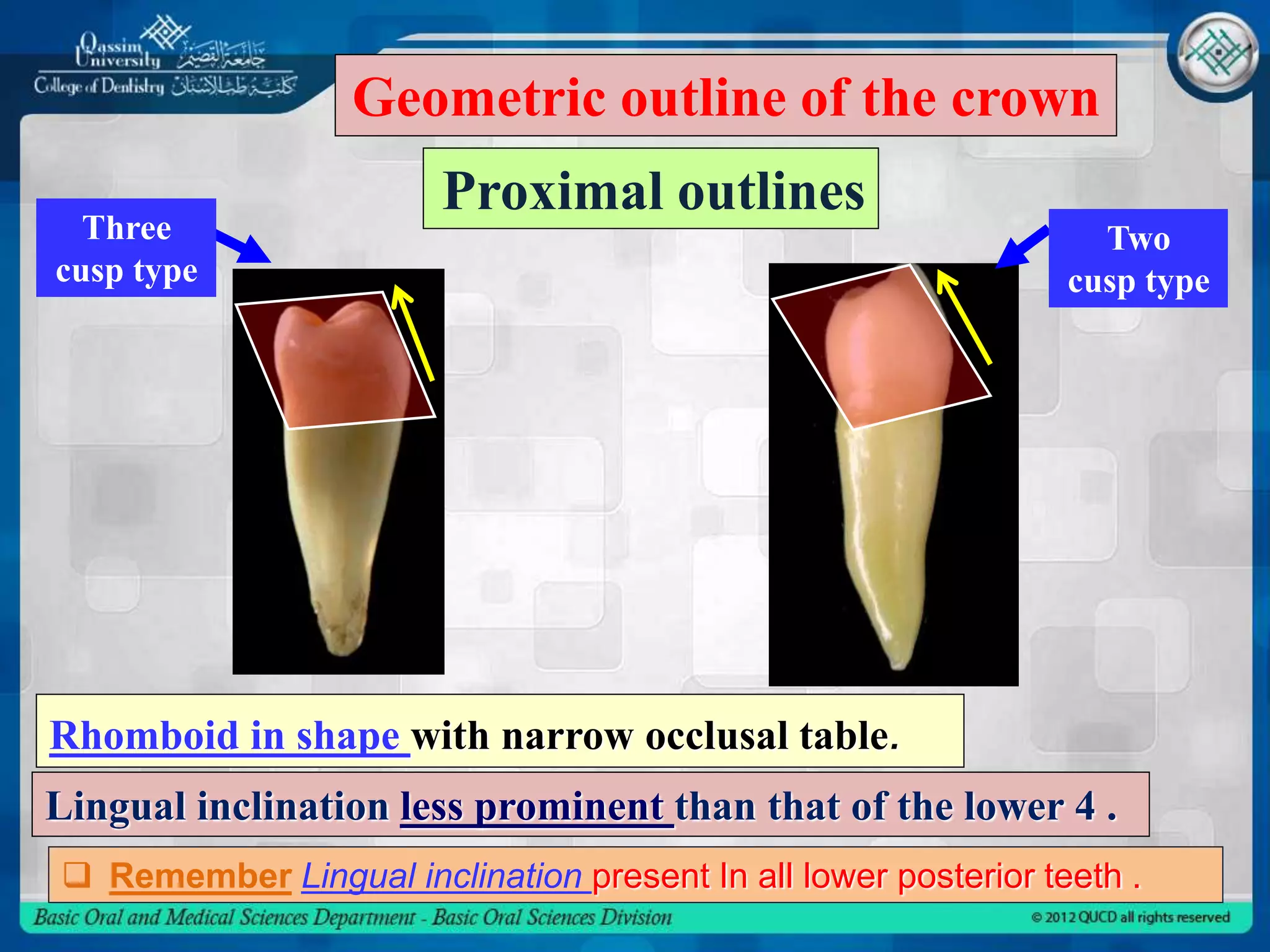
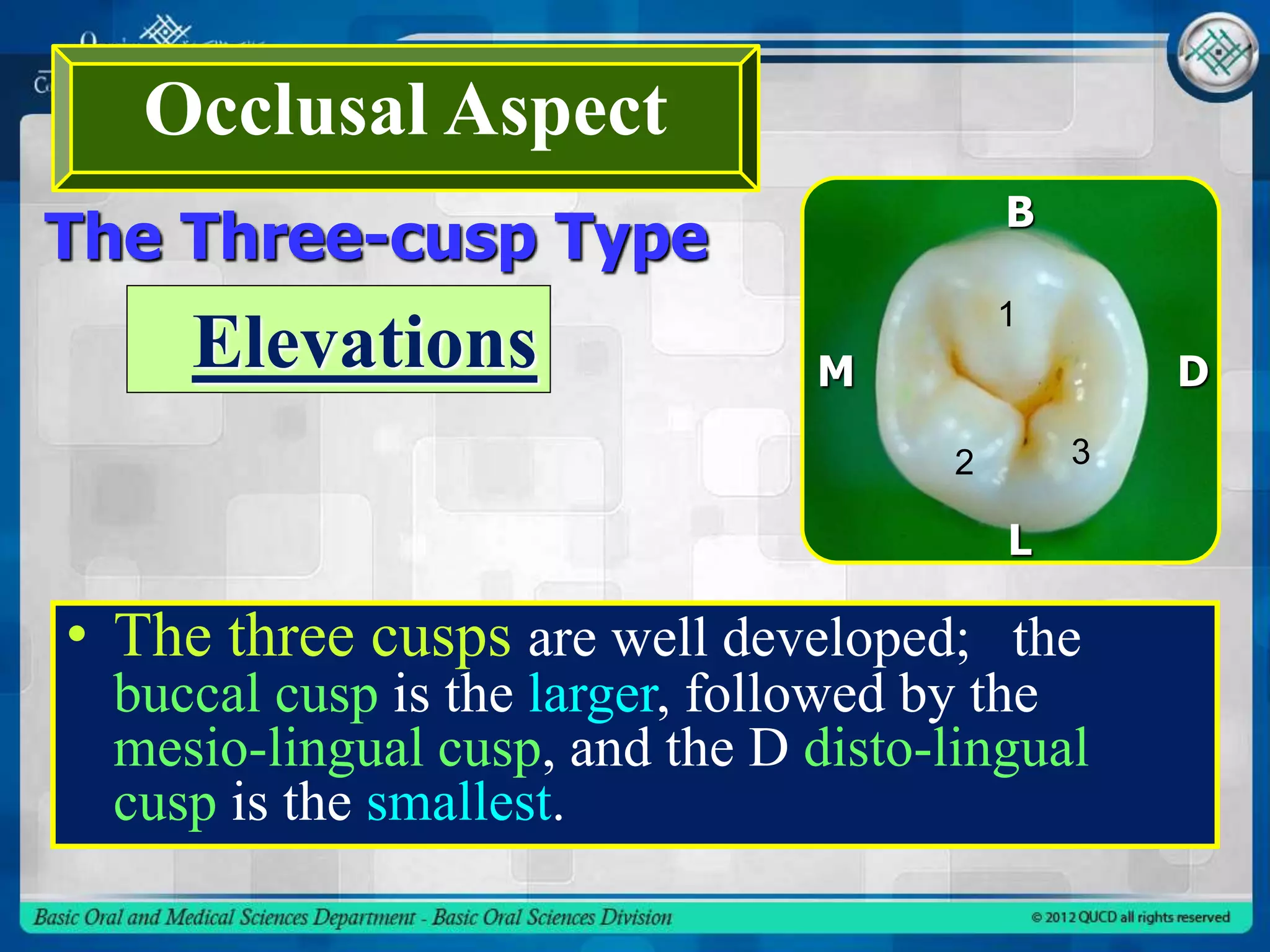
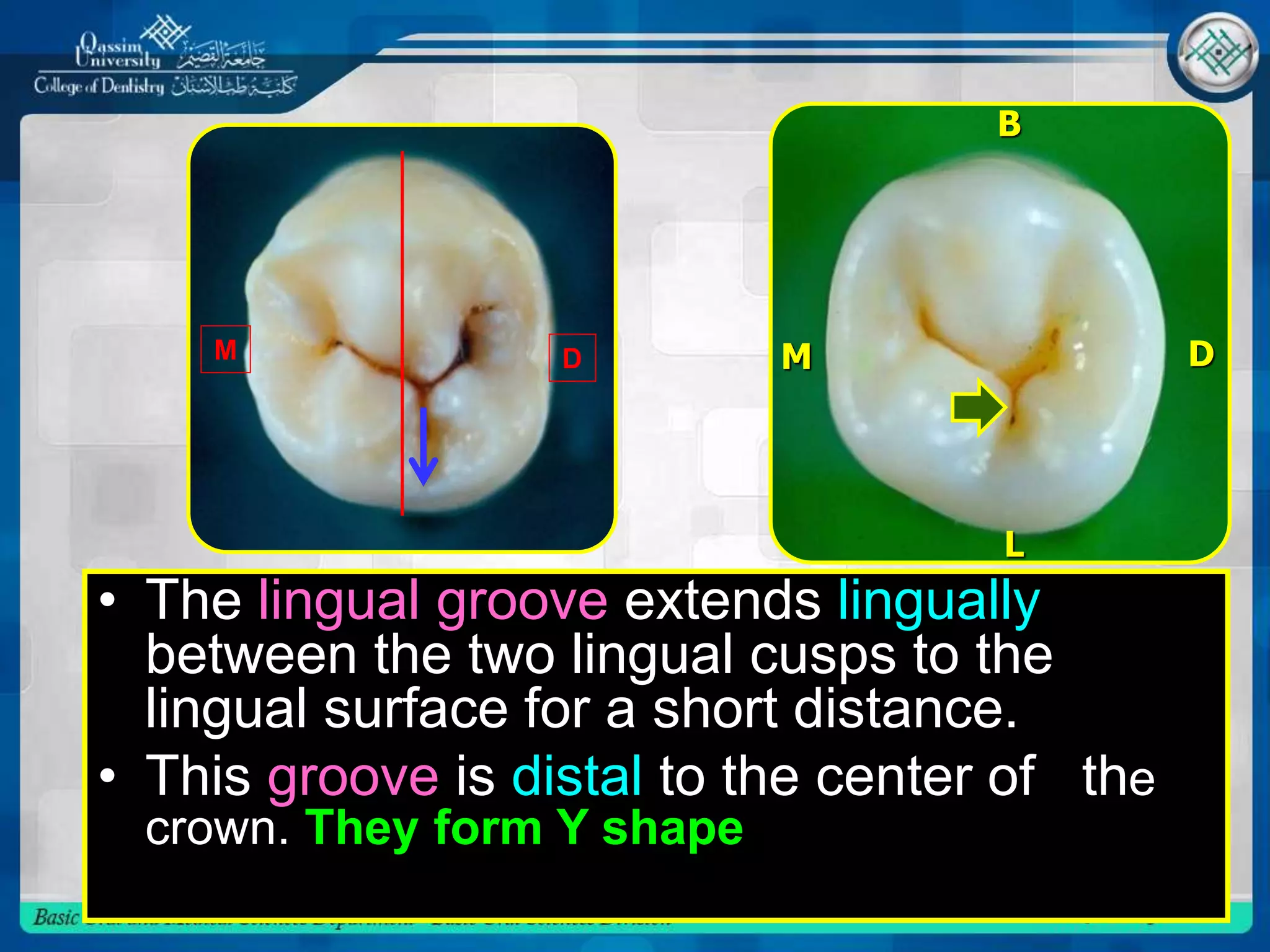
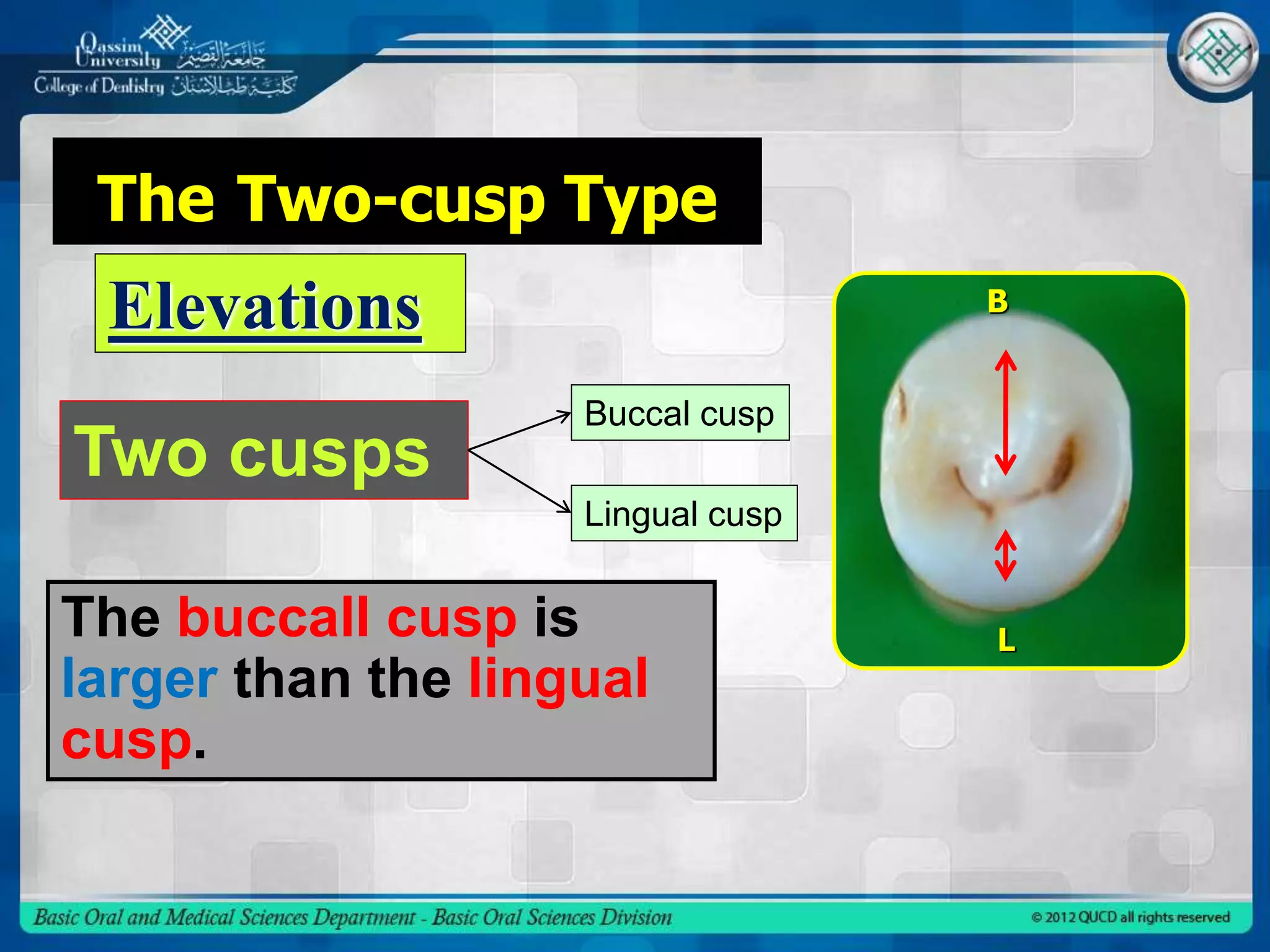
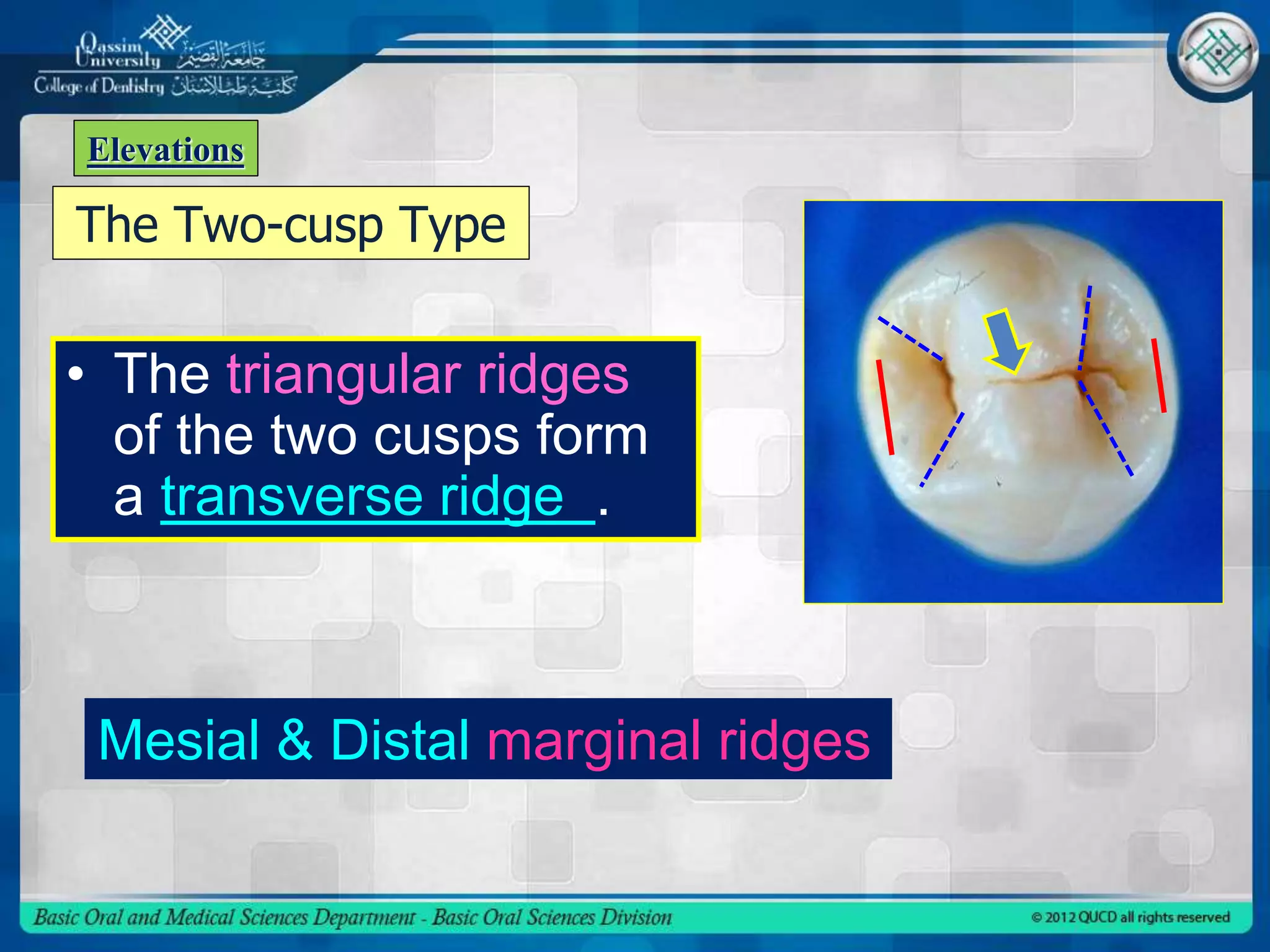
This document describes the anatomy and morphology of the mandibular second premolar tooth. It discusses the chronology of development, outlines and surfaces of the crown from different aspects, comparisons between the two types of second premolars and comparisons to the first premolar. There are typically two types - a three cusp type and a two cusp type that differ in their occlusal and lingual aspects. Details are provided on geometric outlines, cusp patterns, ridges, grooves and fossae for each tooth type and surface.