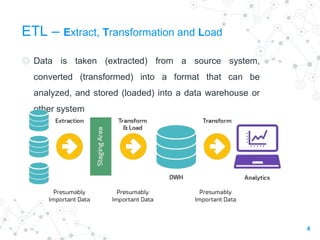
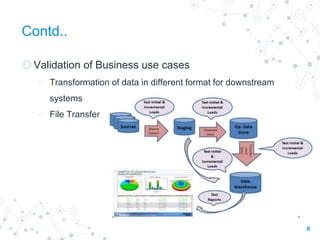
The document discusses ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) testing, covering its importance, types, strategies, and challenges. Key components include the architecture of data warehouses, various ETL jargons, and best practices to ensure data integrity during migration. Additionally, it outlines different types of slowly changing dimensions and testing methodologies to validate data transformations and ensure data completeness.