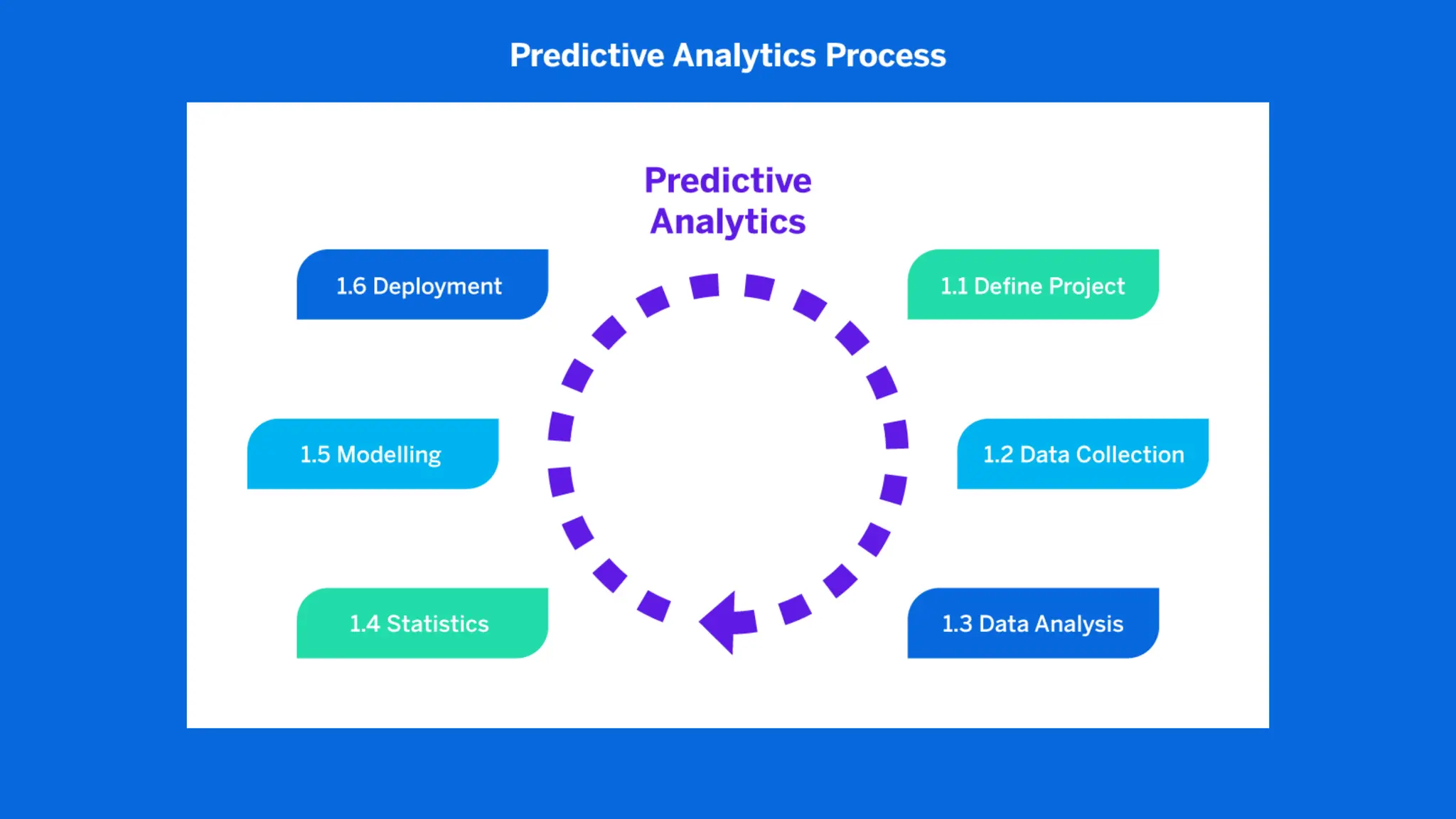
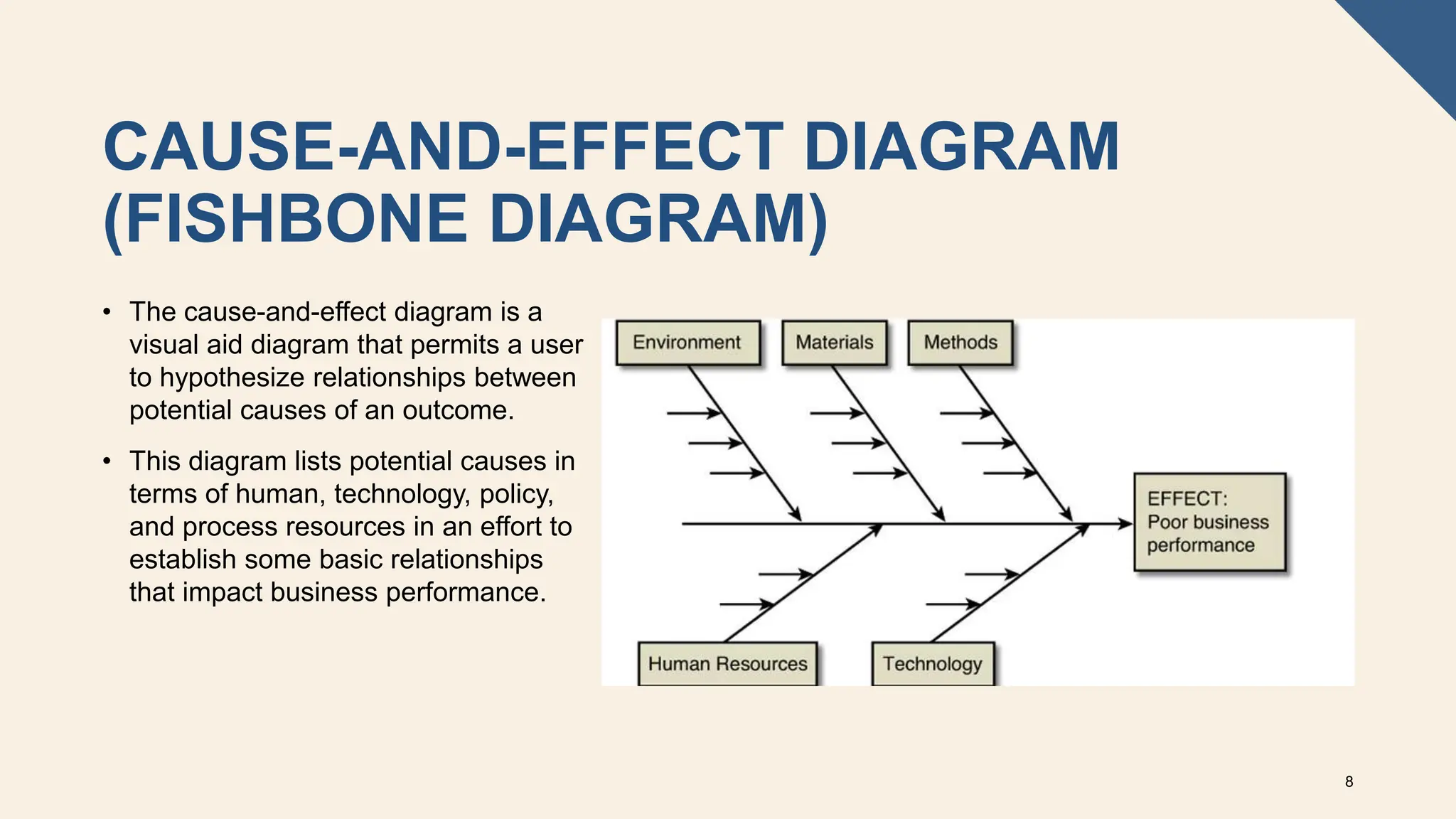
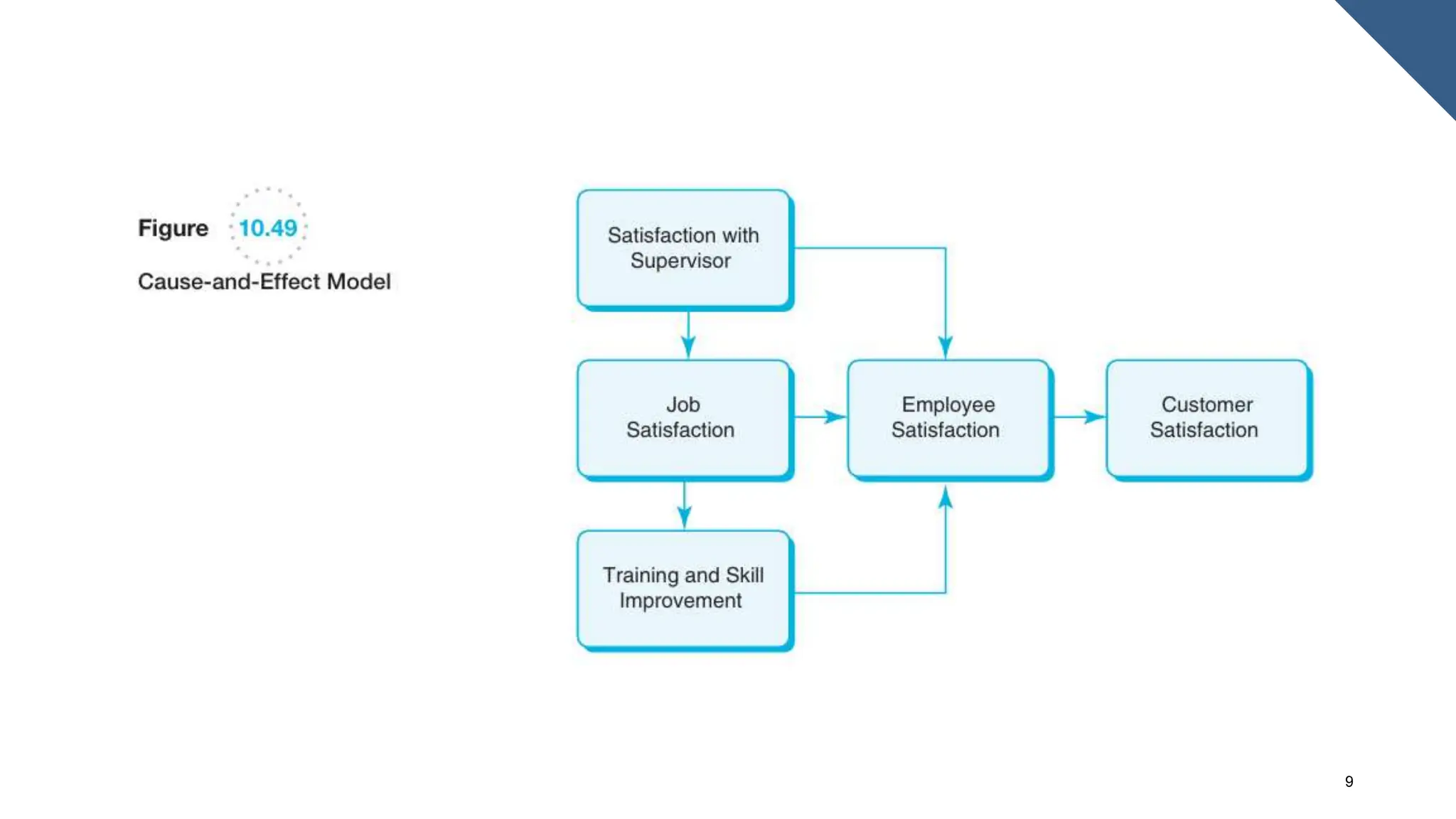
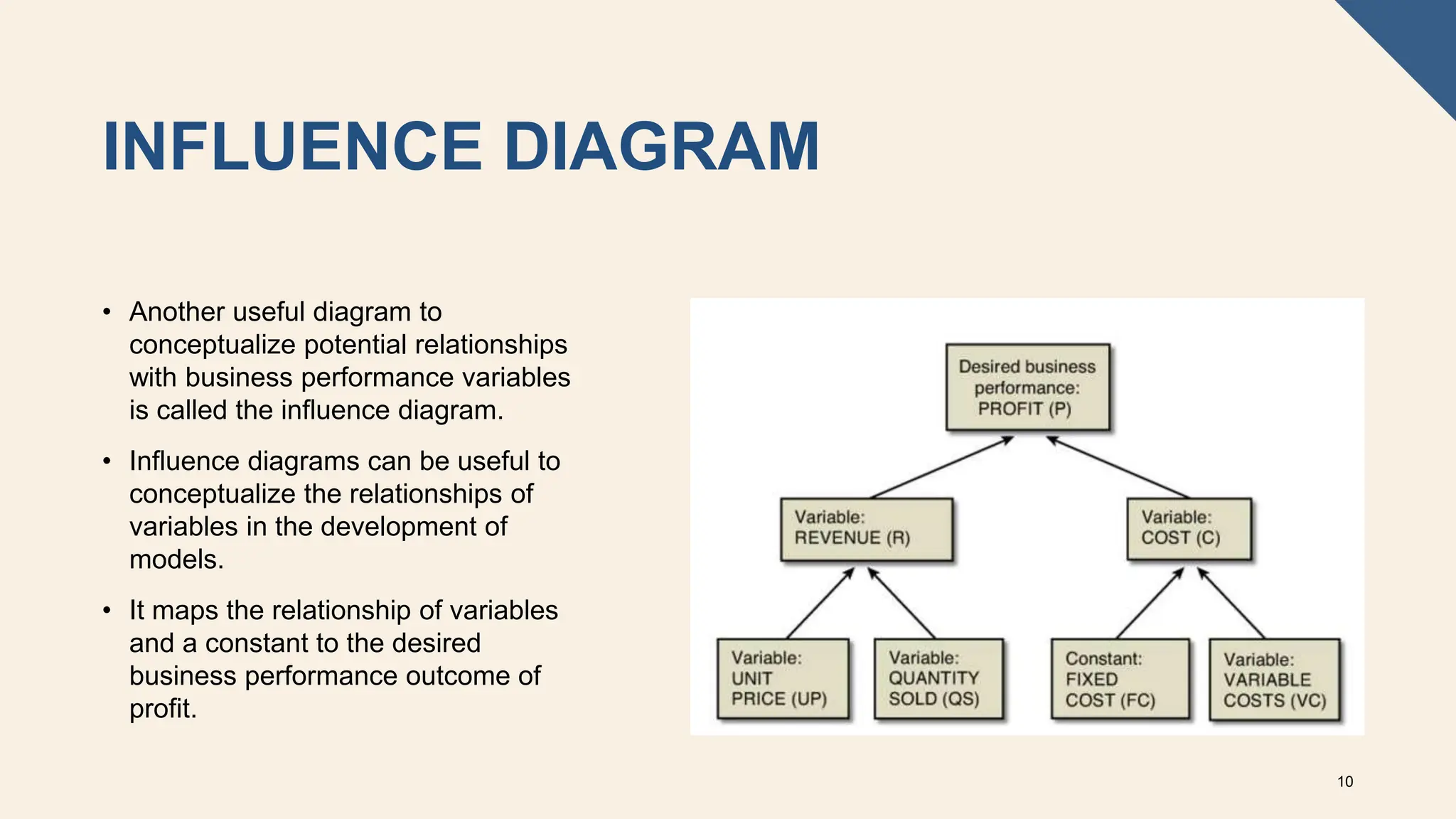
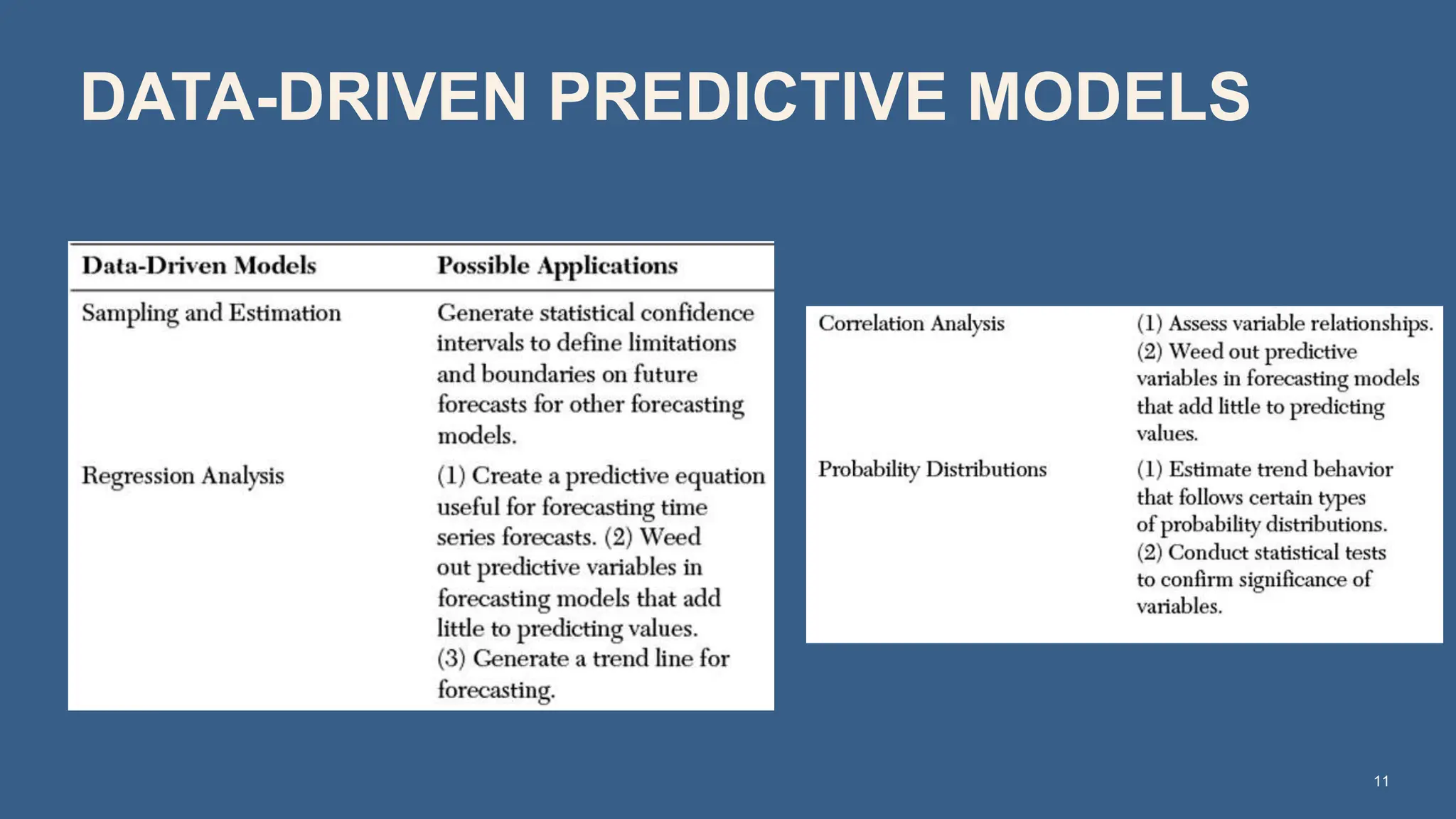
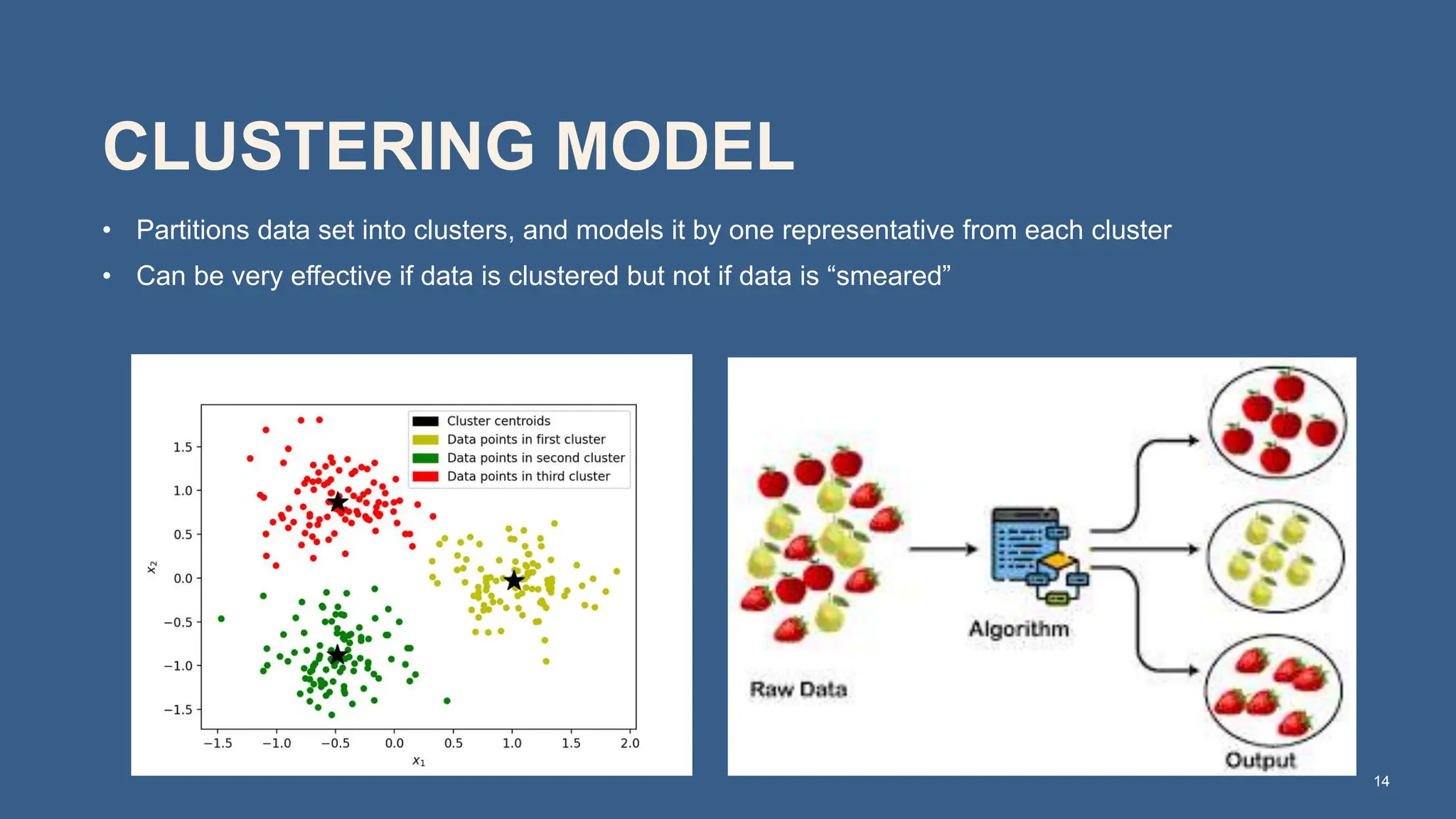
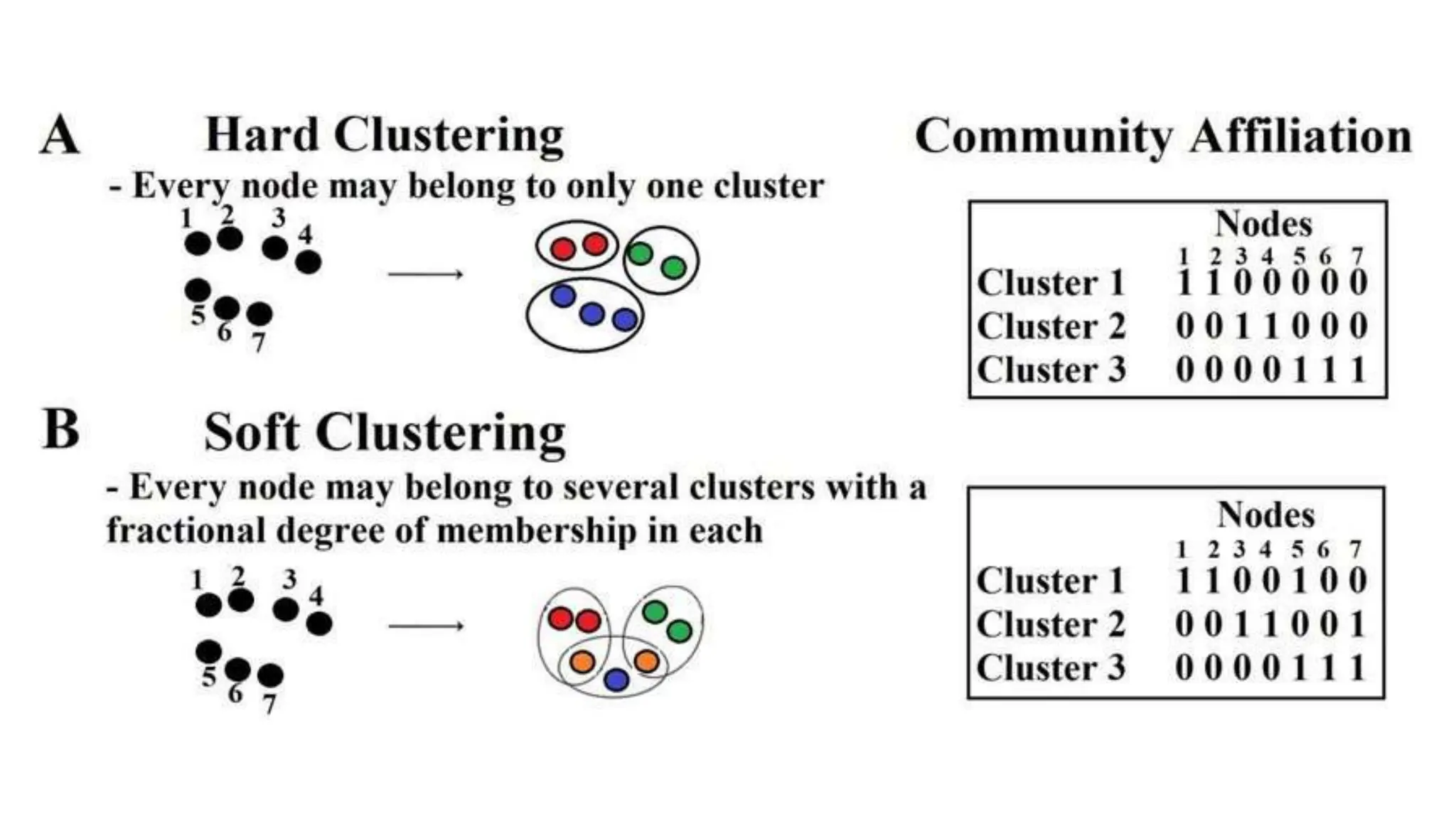
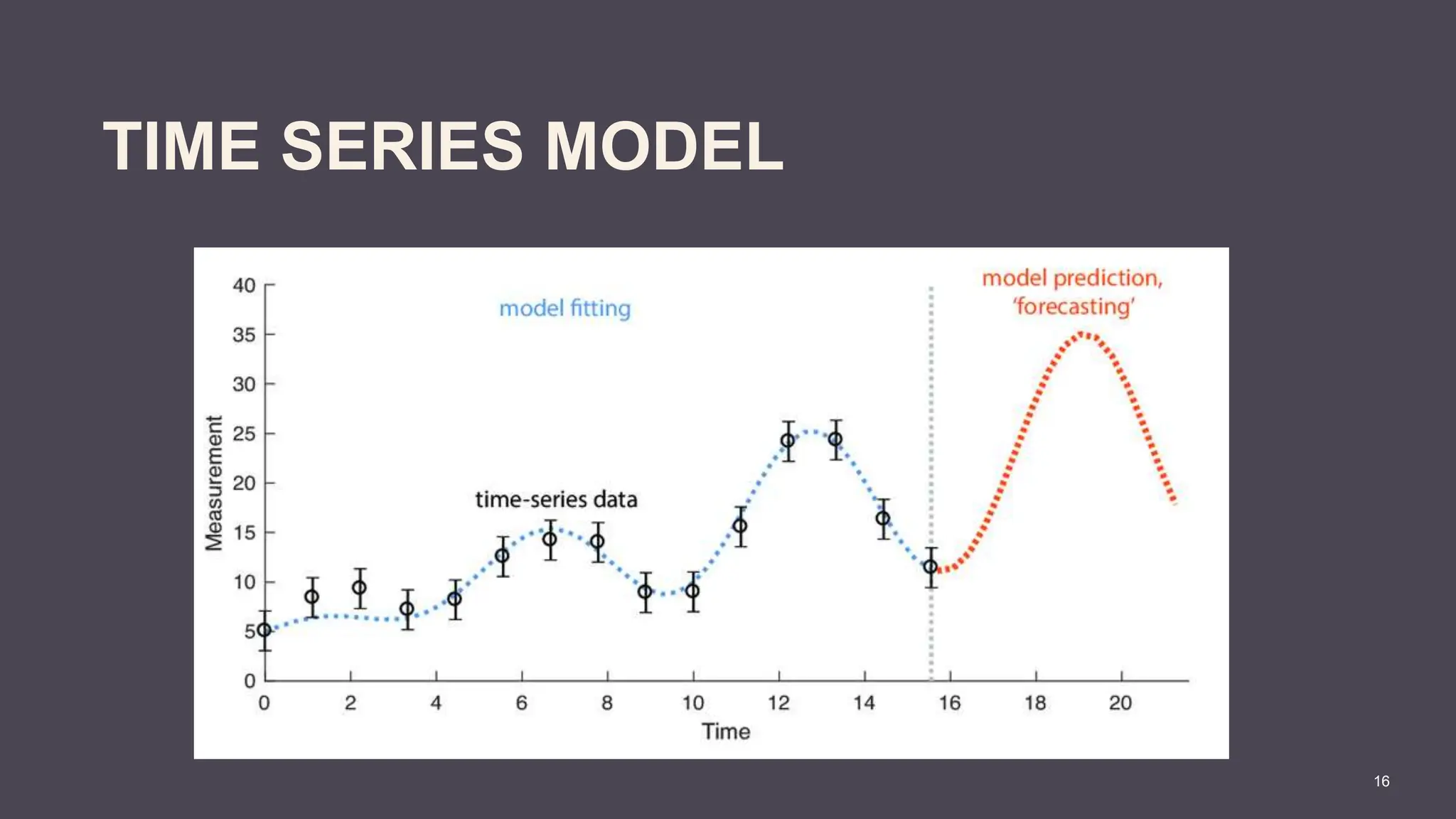
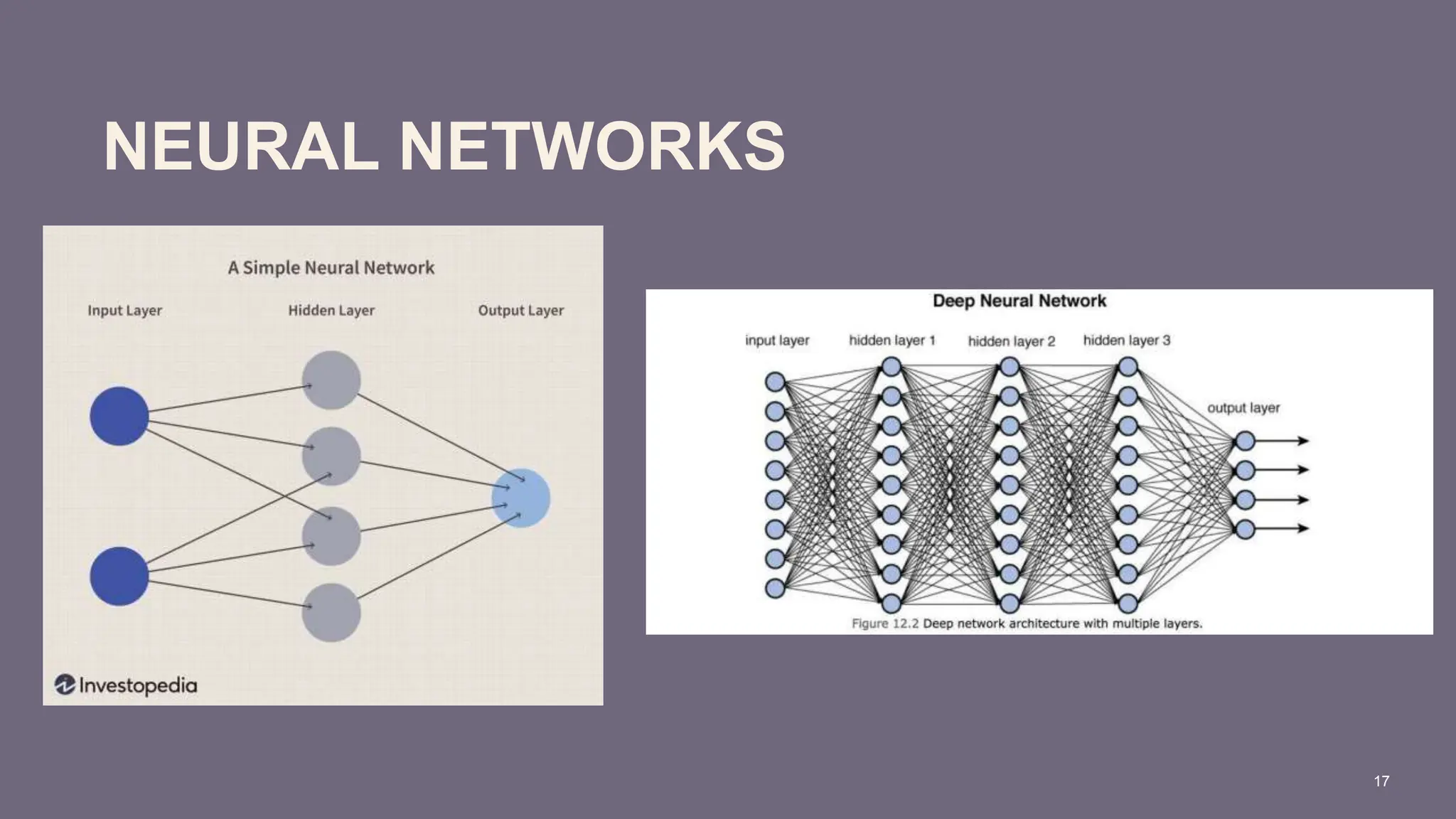
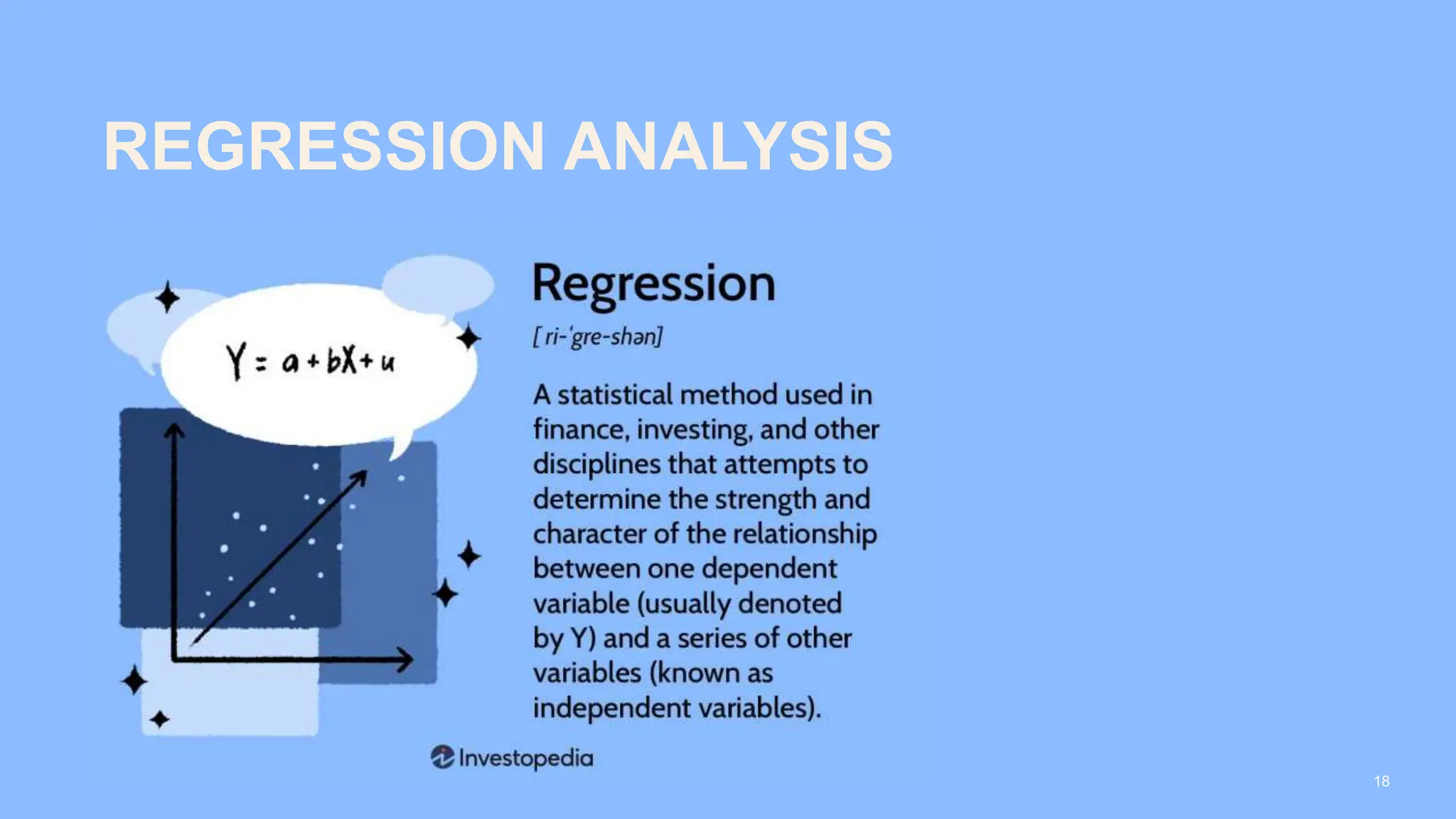
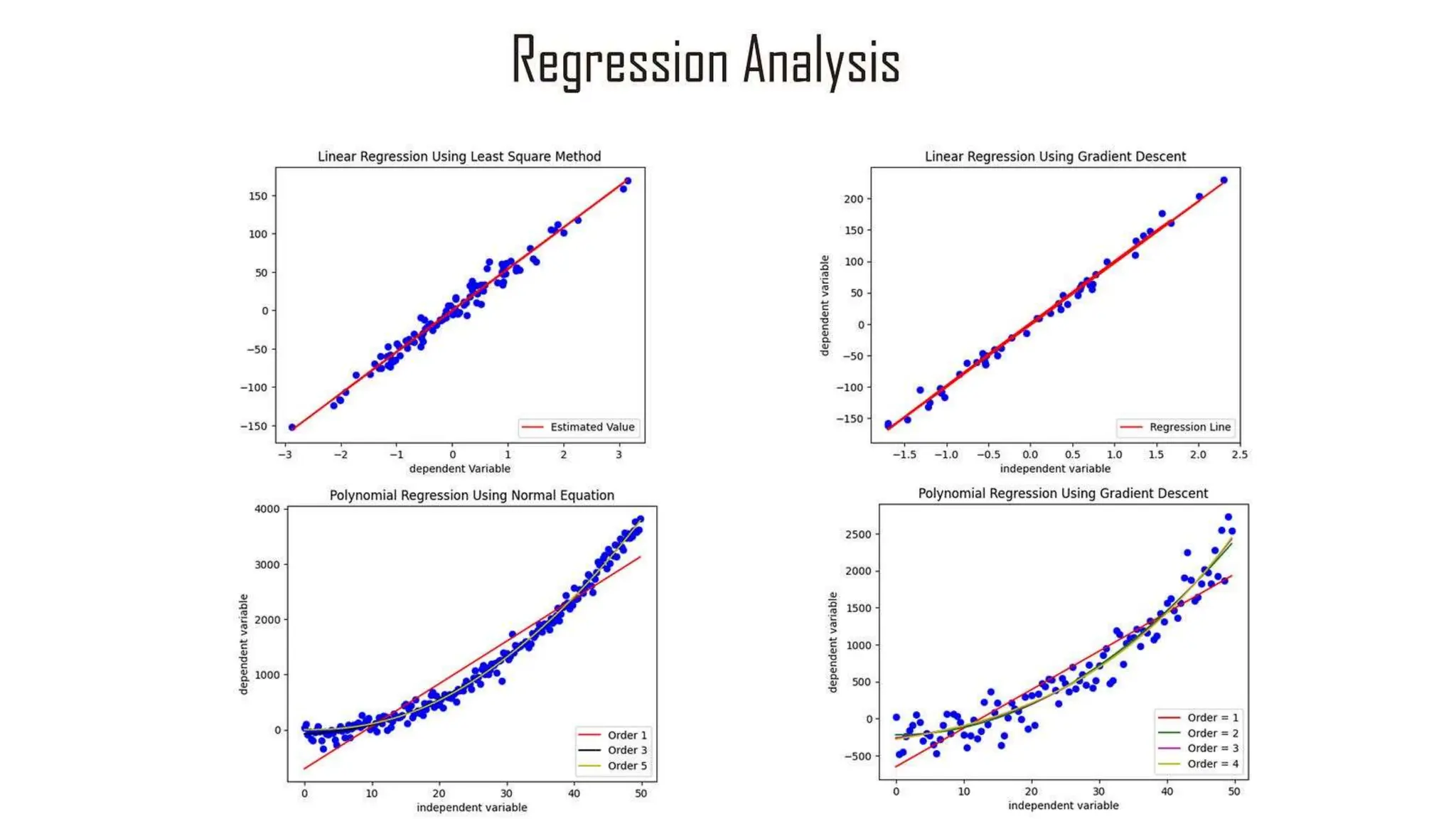
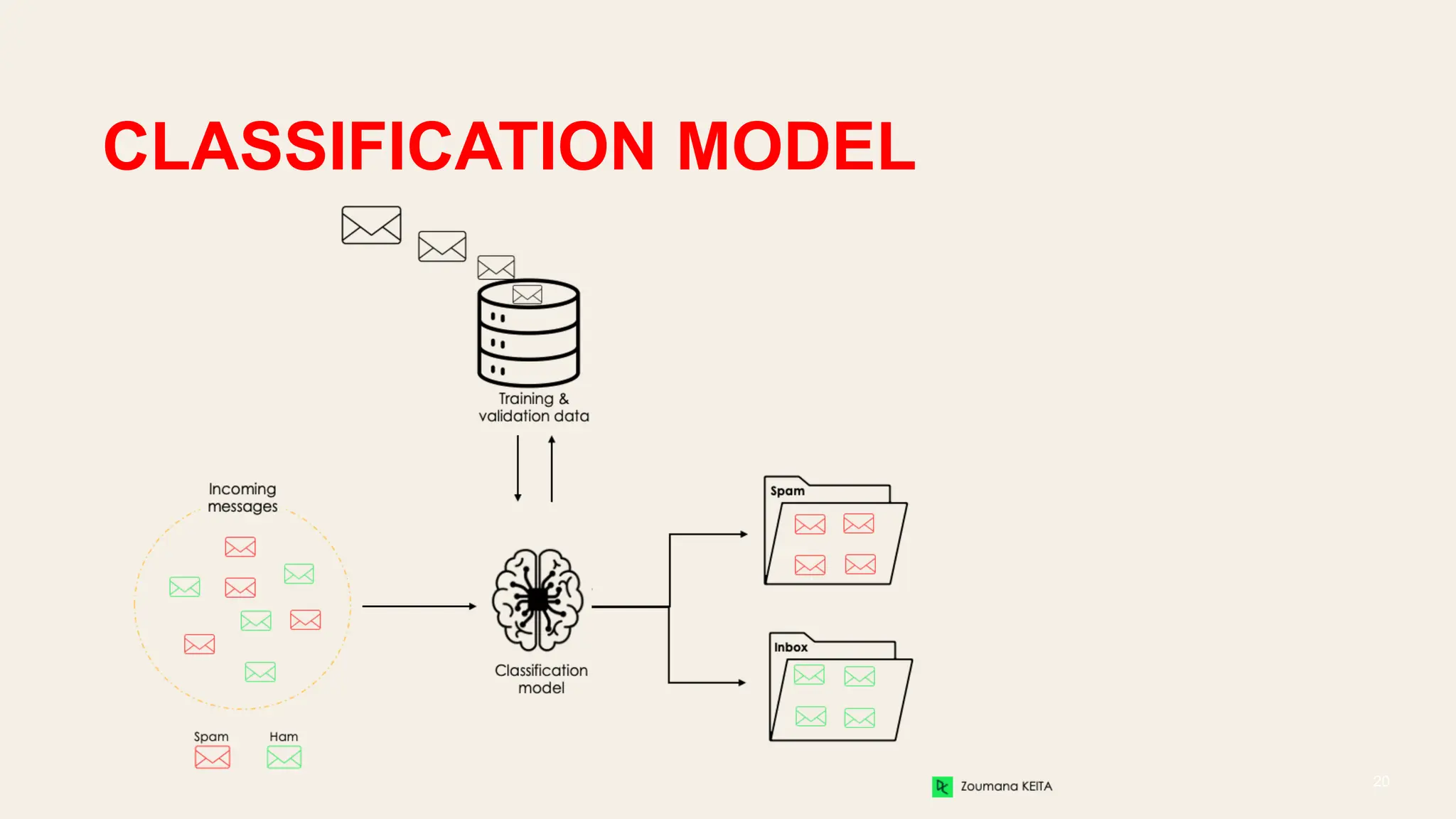
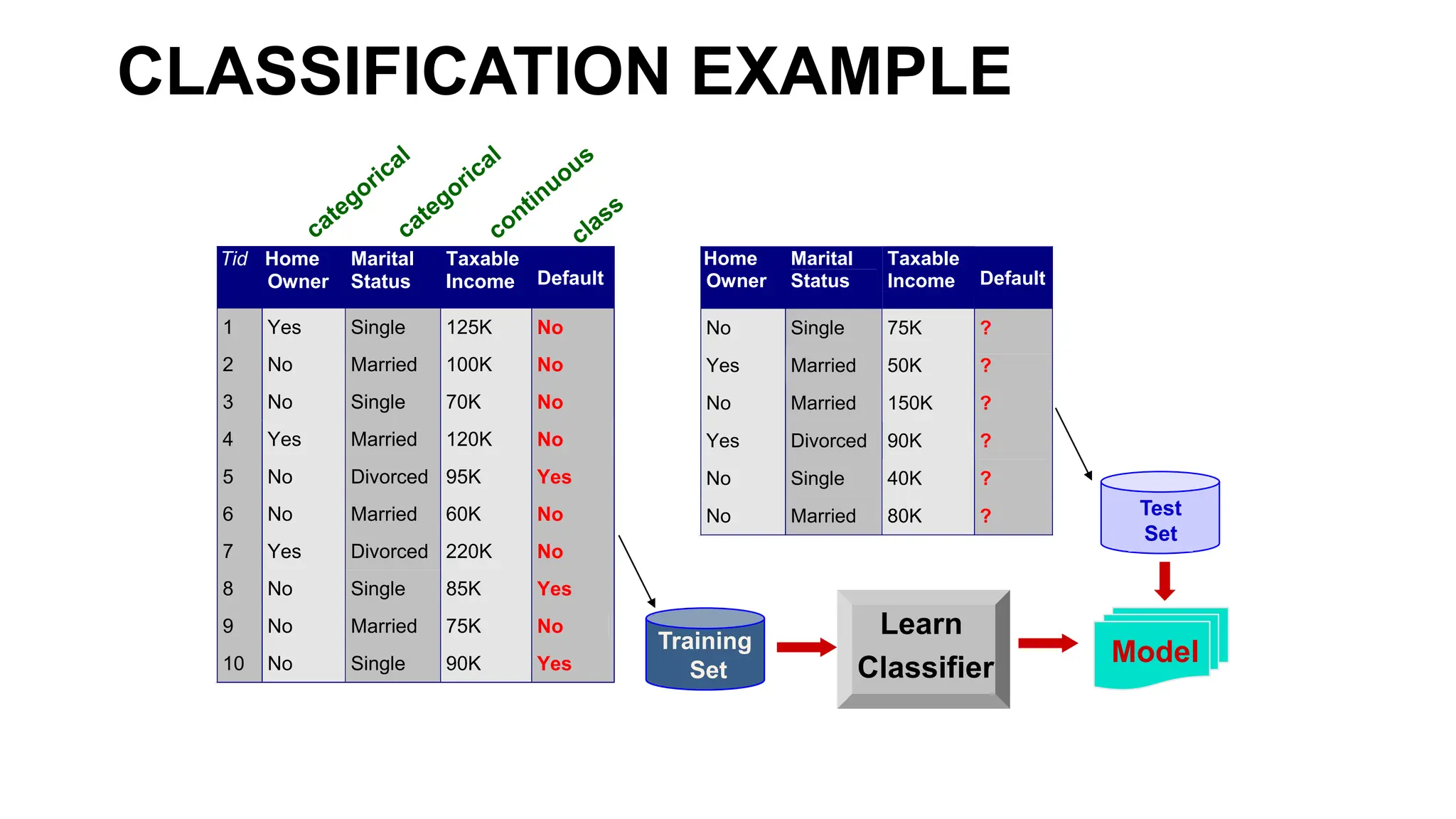
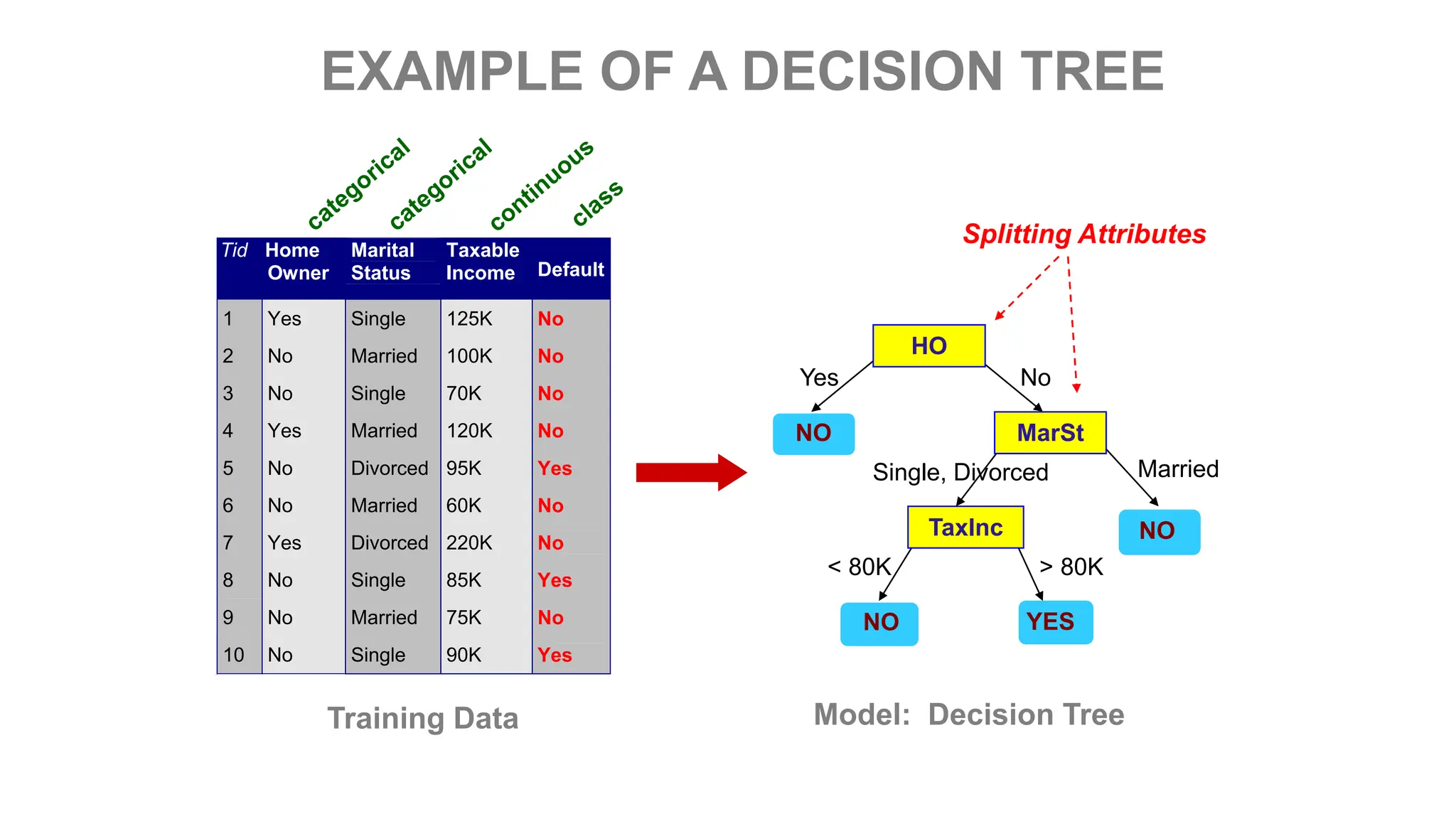
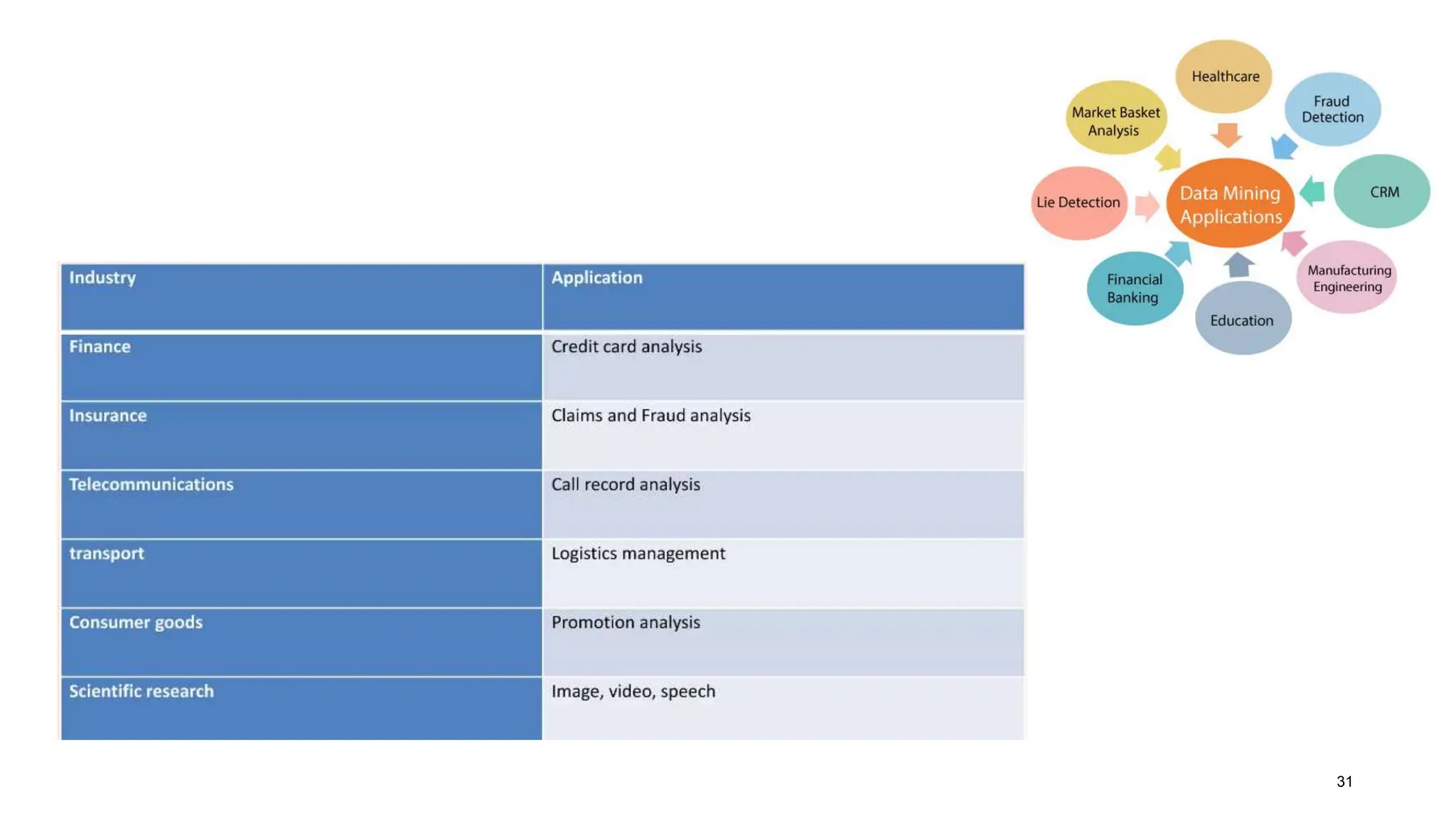
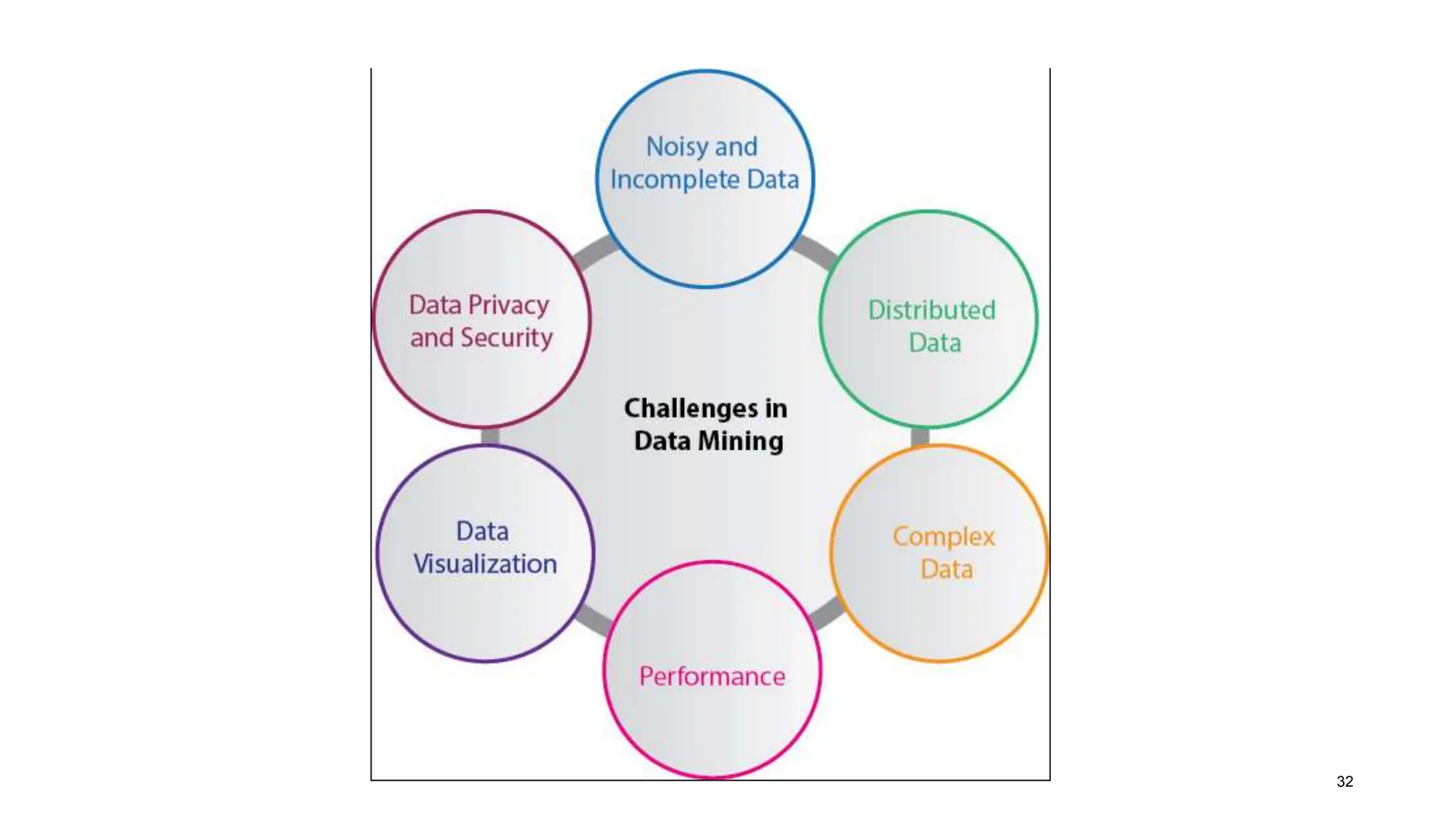
The document covers the fundamentals of predictive analytics, focusing on how data and statistical algorithms are used to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. It describes various modeling techniques, including logic-driven and data-driven models, as well as methods such as data mining and time series analysis. Additionally, it outlines the advantages and limitations of predictive models and emphasizes the importance of effective communication in conveying insights from predictive analytics.