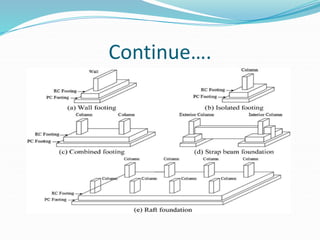
This document discusses foundations for structures. It defines foundations as the lowest part of a structure that transfers loads to the soil below ground level. Foundation engineering involves evaluating soil bearing capacity and determining the proper type, size, and depth of footings. The purpose of foundations is to transfer structural loads to the underlying soil without causing failure or excessive settlement. Shallow foundations spread loads laterally near the surface, while deep foundations distribute loads vertically to deeper soil layers using piles, piers or caissons when the upper soil cannot support the loads. Different types of shallow and deep foundations are described, along with their uses in different soil and load conditions.