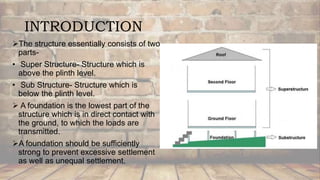
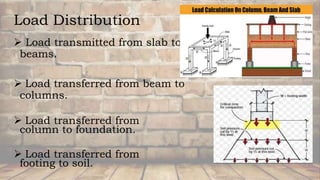
The document outlines the fundamentals of building foundations, detailing the elements of superstructure and substructure, and the purposes and requirements of a good foundation. It describes factors affecting foundation selection, such as soil conditions and structural loads, while classifying foundations into shallow and deep types with various examples and their applications. The conclusion emphasizes the ability to select appropriate foundation types based on soil bearing capacity and structural loads.