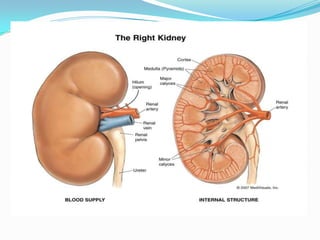
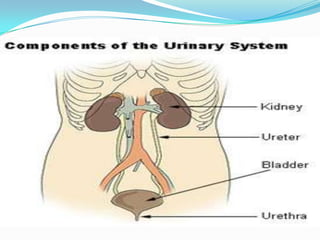
The excretory system removes waste from the body through the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys contain a renal cortex and medulla, which filter blood to produce urine. The renal artery brings blood to the kidneys and renal vein carries urine away. Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys that filter blood and regulate water and substances through filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Urine is then stored in the bladder and exits the body through the urethra.