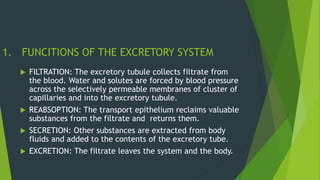
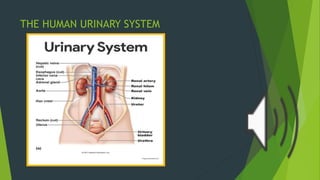
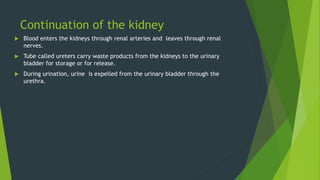
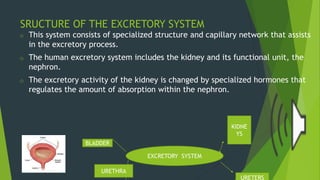
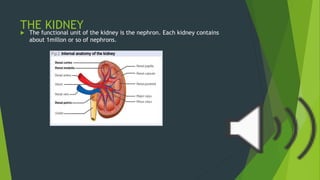
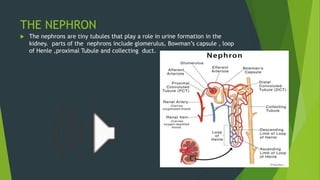
The human excretory system maintains homeostasis by removing metabolic waste from the body. The major organs involved are the kidneys, which filter blood to remove waste that is excreted in urine, and the bladder, which stores urine until excretion through the urethra. The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron, which contains a glomerulus that filters blood and tubules that reabsorb useful substances and remove waste to form urine. Together, these organs work to eliminate toxins from the bloodstream and regulate fluid balance in the body.