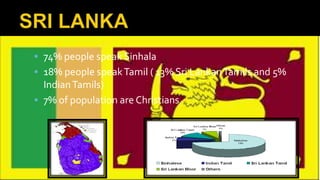
Belgium uses power-sharing as a model of governance to accommodate its ethnically divided population. It shares power vertically between the central and state governments, horizontally among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, and through community governments that represent French and Dutch groups. Power-sharing aims to reduce conflicts, provide stability, engage people, and give diverse groups a voice in administration to prevent alienation. Sri Lanka experienced ethnic tensions that led to civil war due to the dominance of the Sinhala community and lack of power-sharing with Tamils over language, regional autonomy, education, jobs, and an independent Tamil state.