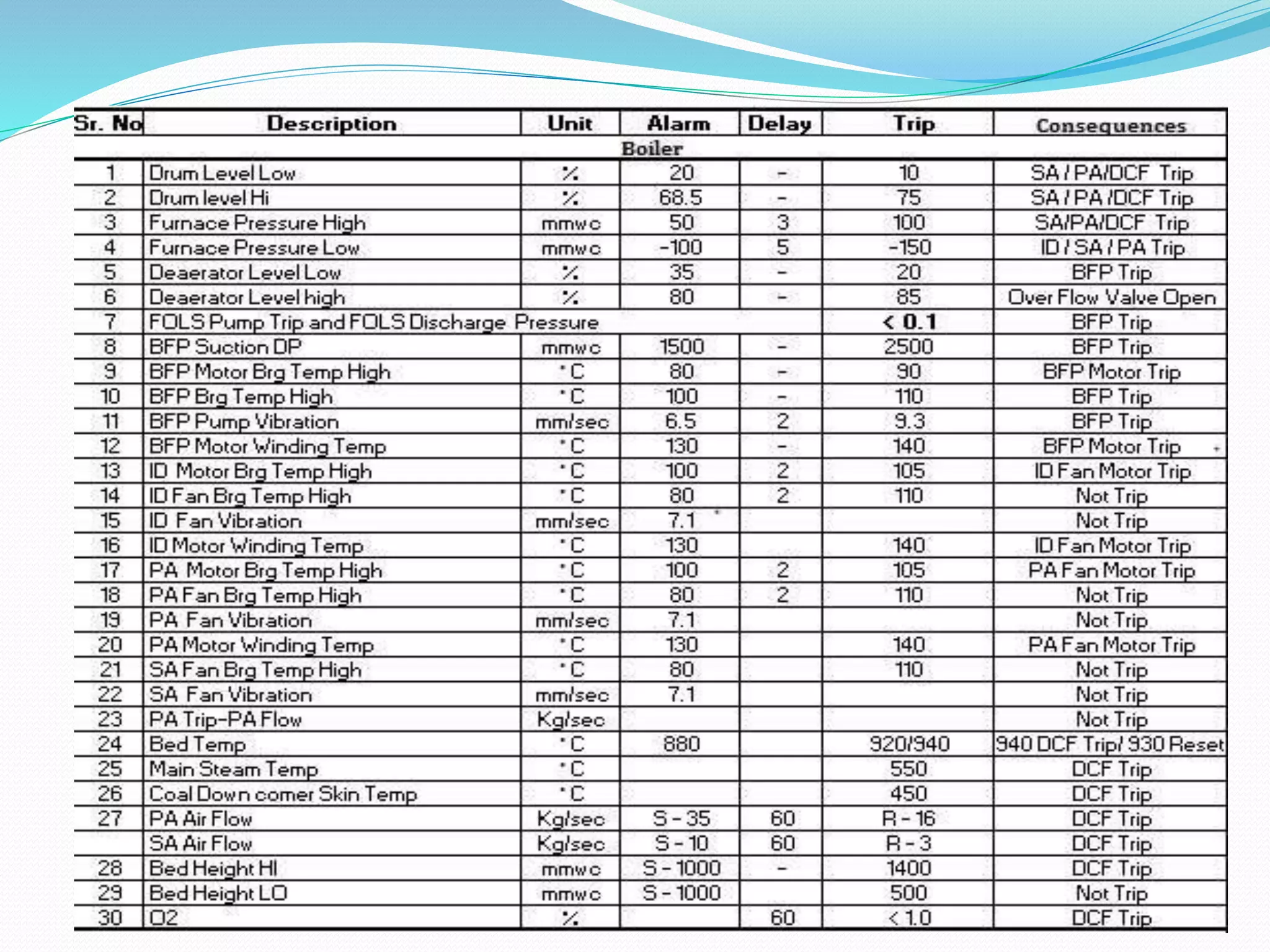
The document provides information on protection and interlocks in modern power plants. It discusses various boiler safety protections that detect abnormal conditions like high or low drum level, high steam pressure or temperature. It also describes interlocks that isolate faulty equipment to prevent damage and switch on backup equipment. Specific causes, effects and actions are outlined for issues like drum level high/low, flame failure, boiler feed pump failure, and loss of fans. The protections and interlocks are designed to trip the boiler or isolate equipment in emergencies to maintain continuous and reliable plant operation.