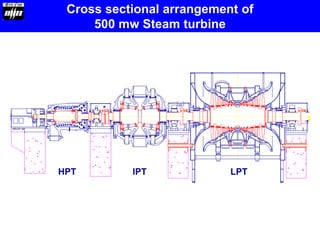
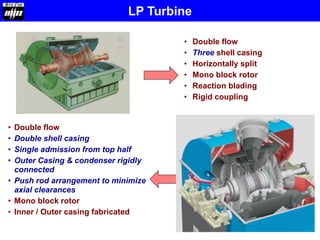
Large capacity supercritical steam turbines can improve overall efficiency through increasing steam parameters like pressure and temperature. The document discusses 660MW supercritical steam turbines, which have higher steam inlet pressures up to 300 bar and temperatures above 374°C. This allows significant efficiency gains over subcritical units and lowers emissions. Details are provided on the construction and configuration of the high, intermediate, and low pressure turbine modules, materials used, governing systems, lubrication systems, and other components of 660MW supercritical steam turbines.