Embed presentation
Download to read offline

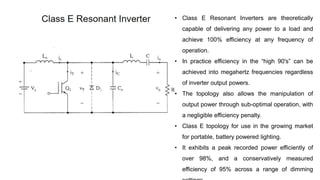
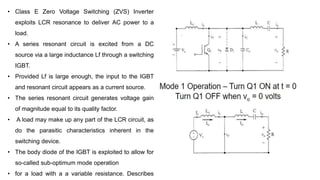
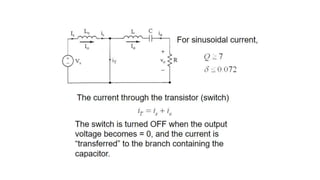
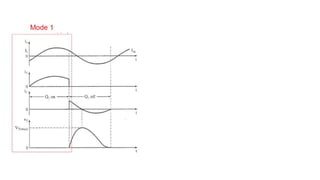
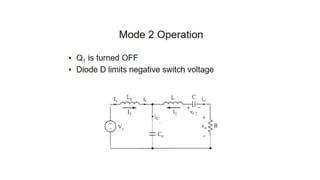
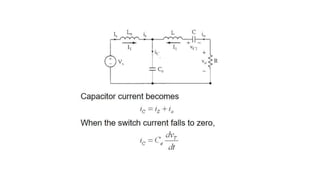





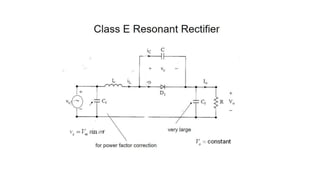
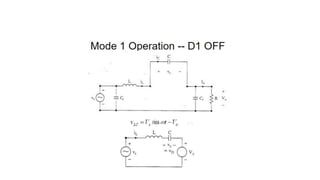
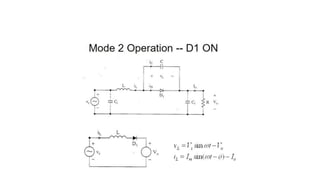

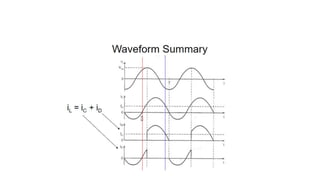




Class E resonant inverters can deliver any power with nearly 100% efficiency at high frequencies, achieving over 95% practical efficiency, particularly useful in portable lighting applications. They utilize zero voltage switching to exploit LCR resonance for AC power delivery, allowing for flexible load configurations. The design incorporates sub-optimal operation without significant efficiency loss, harnessing the characteristics of the switching device.



















