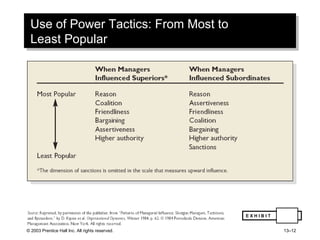
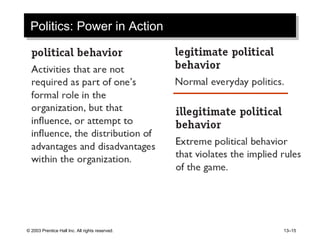
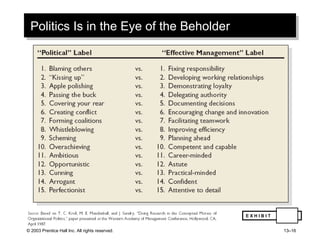
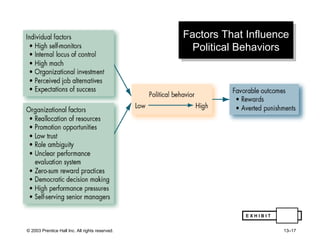
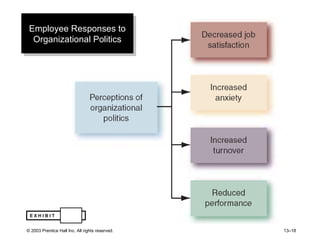
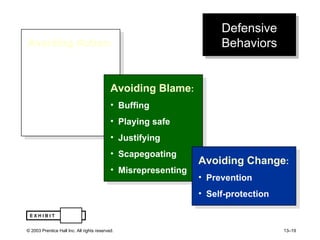
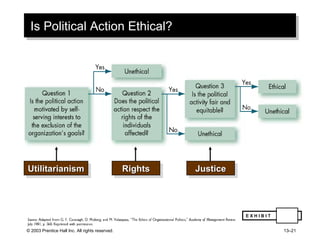
The document outlines learning objectives and key concepts around power and politics in organizational behavior. It defines power and leadership, discusses the four bases of power and how dependency influences power relationships. It also examines power tactics, sexual harassment as an abuse of power, and the importance of political perspectives at work.