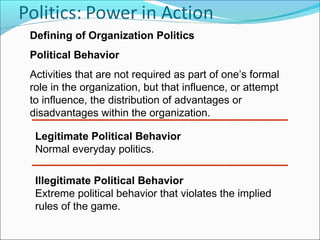
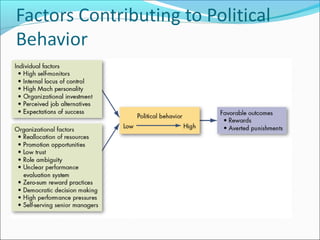
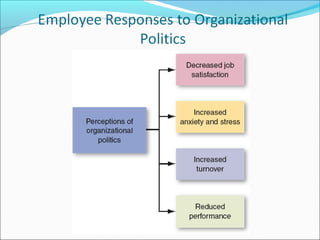
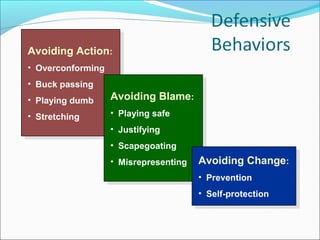
This document summarizes key concepts around power and politics from a presentation. It defines power as one's ability to influence another's behavior, and notes that dependency is important for gaining power over others. It contrasts leadership, which focuses on goals and downward influence, with power, which is used to gain compliance through dependency. Different bases of power are described, as well as tactics for gaining influence upward, downward, and laterally. Political behavior in organizations and impression management techniques are also outlined.