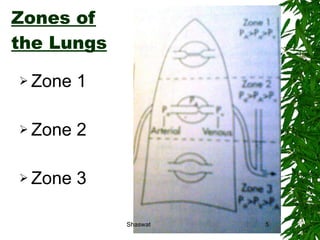
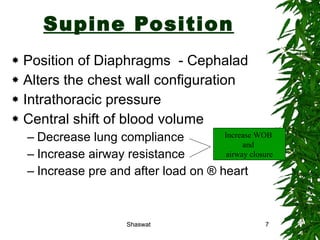
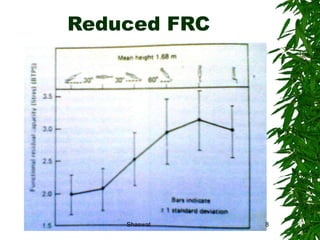
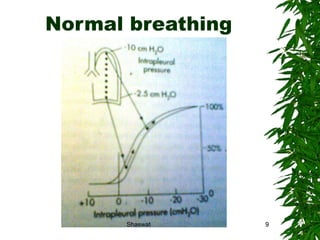
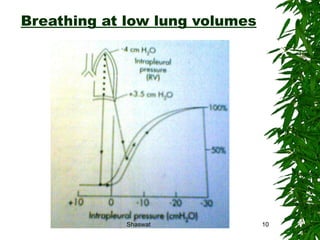
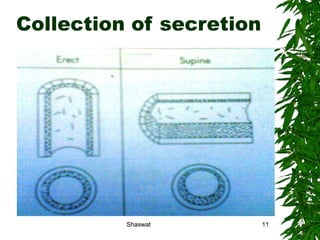
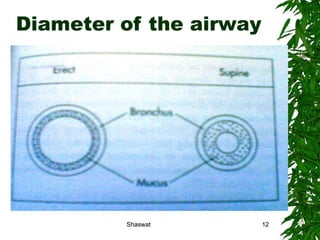
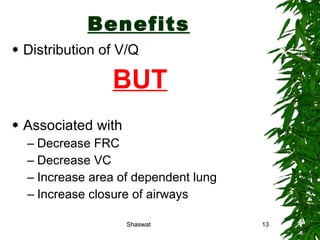
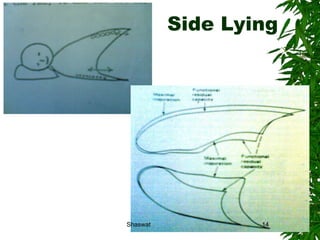
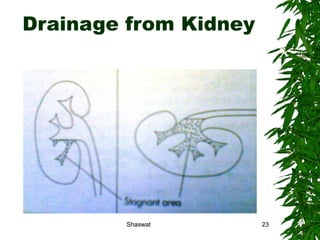
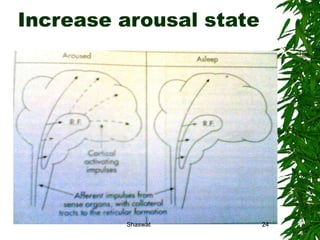
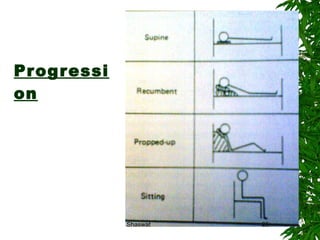
Positioning can improve oxygen transport and lung function in patients with cardiopulmonary dysfunction. Different positions like supine, side lying, and prone affect lung volumes and ventilation in different areas of the lungs. The supine position decreases lung capacity but improves ventilation distribution, while side lying improves ventilation in the dependent lung. Prone positioning increases lung capacity and decreases airway closure. Head down and forward leaning positions can relieve dyspnea. Upright positioning augments drug effects and improves ventilation-perfusion matching. Mobilization provides both acute benefits like increased ventilation and oxygen transport, as well as chronic benefits including increased exercise capacity and decreased cardiac workload.