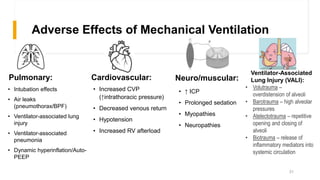
Mechanical ventilation involves using a machine to breathe for patients who cannot breathe effectively on their own. It works by delivering pressurized air into the lungs via a tube in the airway. Physiotherapists help optimize ventilation, clear secretions, prevent complications, and facilitate weaning patients off the ventilator using techniques like suctioning, drainage positions, percussion, and vibrations. The ventilator settings control aspects of breathing like tidal volume, oxygen levels, and respiratory rate. Modes include mandatory breaths or assisting patients' own breaths. Weaning gradually reduces support as the patient recovers lung function and the ability to breathe independently.










![2. Respiratory Rate[RR]
• Spontaneous breaths taken by
the patient
• 10-20 breaths per minute
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalventilation-210903183606/85/Mechanical-ventilation-and-physiotherapy-management-Dr-Muskan-Rastogi-PT-BPT-MPT-OBG-12-320.jpg)


![5. Peak Flow Rate[PFR]
• Maximum flow delivered by ventilator during inspiration
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalventilation-210903183606/85/Mechanical-ventilation-and-physiotherapy-management-Dr-Muskan-Rastogi-PT-BPT-MPT-OBG-15-320.jpg)



![10. Tidal Volume {VT}
• Volume of gas
exchanged with each
breath
• 6-8mL/kg of ideal body
weight [IBW] to prevent
barotrauma
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalventilation-210903183606/85/Mechanical-ventilation-and-physiotherapy-management-Dr-Muskan-Rastogi-PT-BPT-MPT-OBG-20-320.jpg)