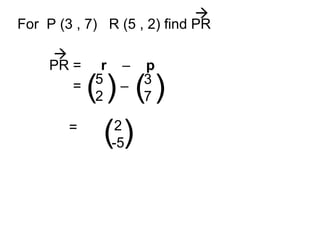Embed presentation
Download to read offline

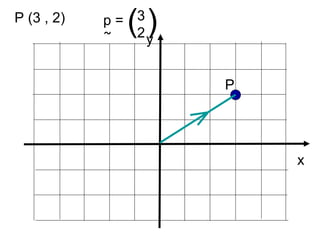
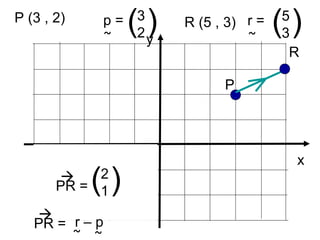
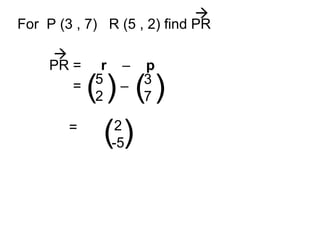
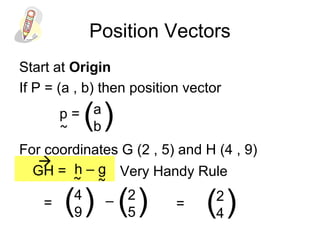
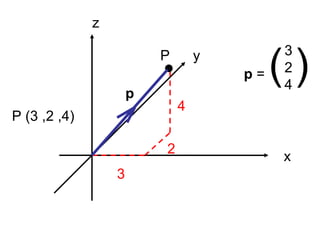




This document discusses position vectors in 2D and 3D coordinate systems. - A position vector starts at the origin and represents the displacement from the origin to a point P defined by its coordinates. - The position vector rule states that the position vector from point P to point R is equal to the vector from R's position vector subtracted by P's position vector. - Position vectors and their properties like magnitude, addition, subtraction, and scalar multiplication follow the same rules in 3D as in 2D. Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the position vector and magnitude between two points in 3D space.