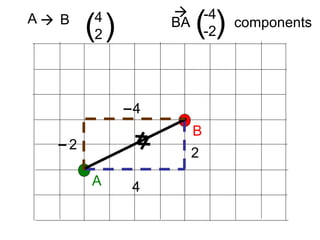
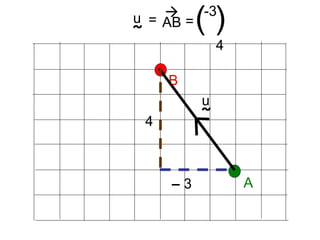
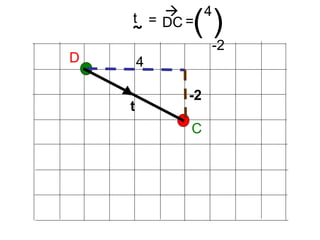
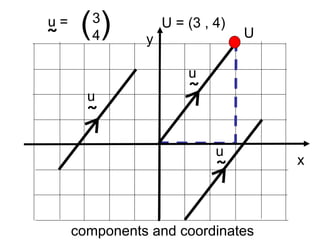
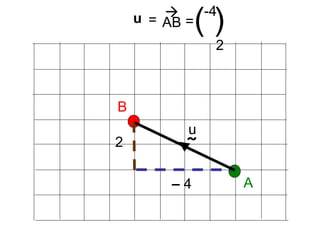
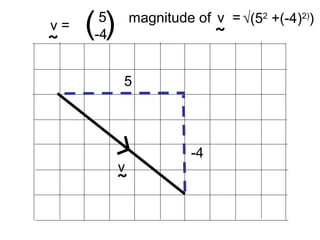
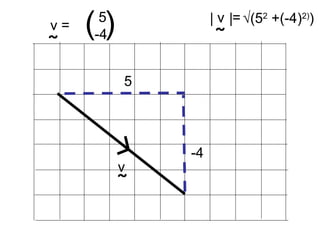
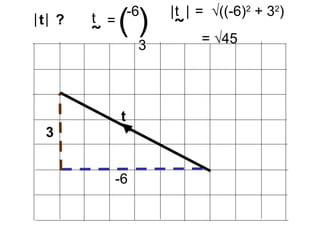
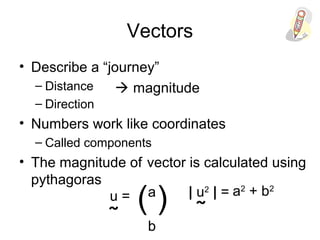
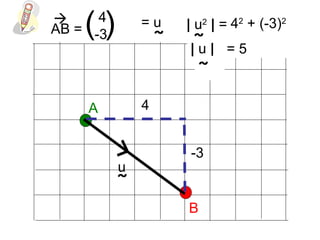
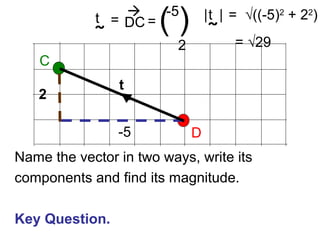
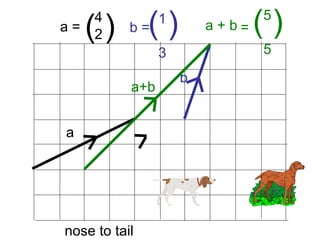
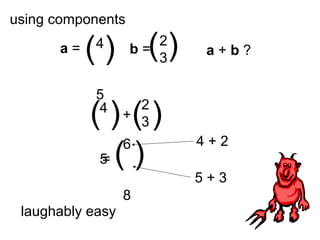
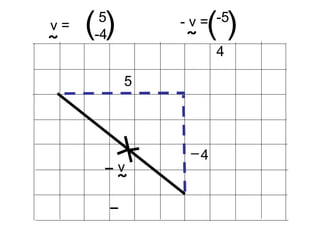
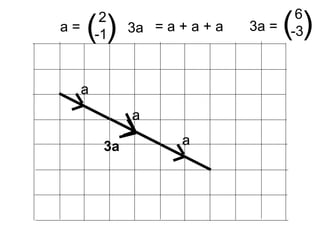
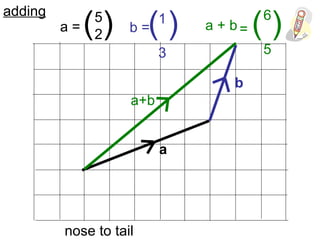
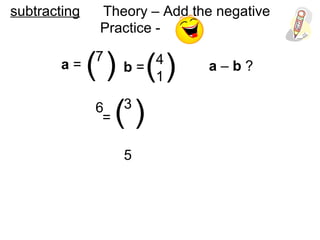
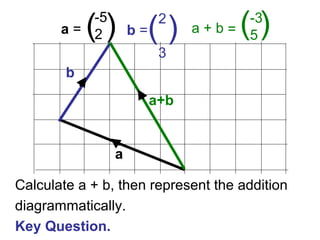
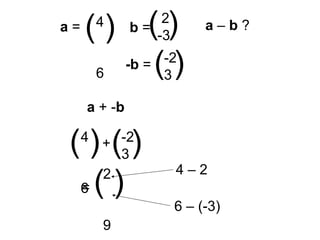Vectors can represent journeys with distance and direction. They have components that work like coordinates and magnitude that is calculated using Pythagoras. Vectors can be added by placing them nose to tail and adding corresponding components, subtracted by adding the negative vector, and multiplied by a scalar by multiplying each component.