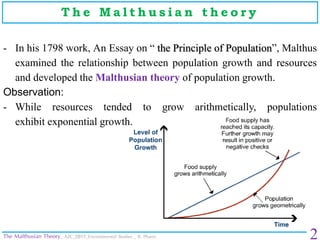
The document discusses Thomas Malthus' Malthusian theory of population growth. Malthus observed that while resources grew arithmetically, populations grew exponentially. He warned that unchecked population growth would eventually outpace food production, leading to a "Malthusian catastrophe" of famine, disease, and war. Malthus proposed two checks on population growth: preventative checks like abstinence and sterilization, and positive checks like famine that naturally limit population when it exceeds resources. While food production has since increased faster than population, overpopulation remains a threat combined with issues like global warming.