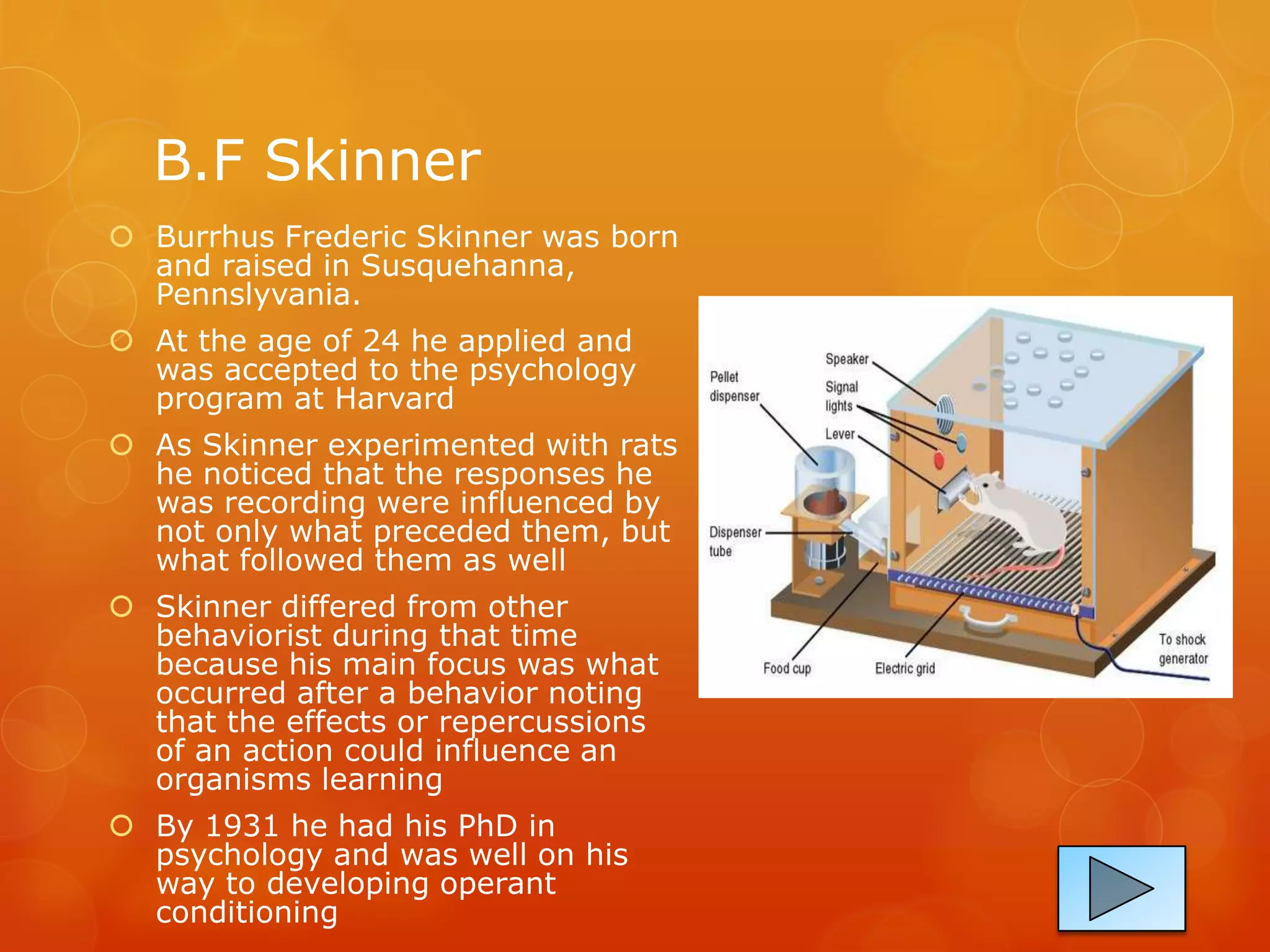
Behaviorism is a learning theory introduced by B.F. Skinner that focuses on observable behaviors and responses to stimuli. Learning is viewed as the acquisition of new behaviors through conditioning, whether classical conditioning of innate reflexes or operant conditioning using reinforcement and punishment. In a classroom, behaviorism would shape student behavior quickly using positive or negative feedback, allow students to adapt to the environment, and allow teachers to measure behavior. The document provides examples of how behaviorism could be applied in a classroom through rewards, stickers, and tests.