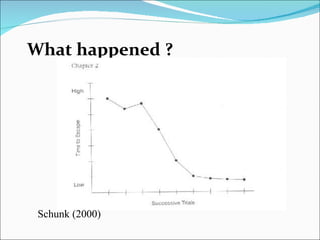
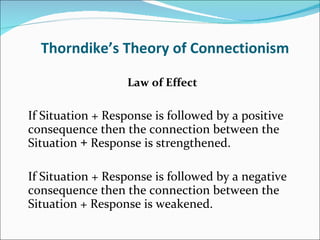
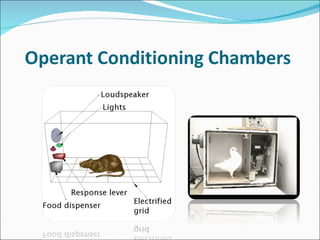
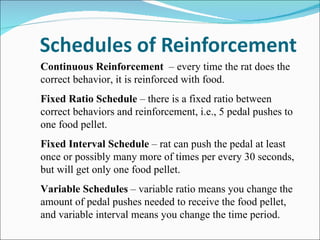
1. Behaviorism is a learning theory that focuses on observable behaviors and how they are shaped through interactions with the environment and consequences.
2. Key behaviorist theorists include John B. Watson, E.L. Thorndike, and B.F. Skinner. Their work established principles of classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and the use of reinforcement and punishment to modify behaviors.
3. Robert Gagne extended behaviorism by identifying different types of learning outcomes and proposing a hierarchy of learning. He also outlined nine instructional events teachers can follow to optimize learning conditions.