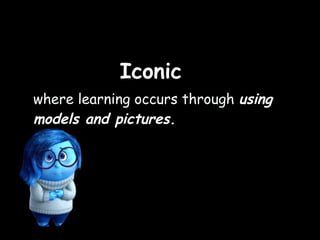
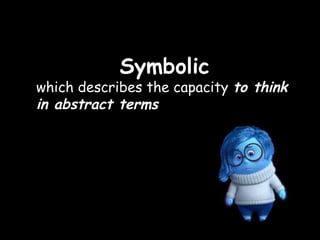
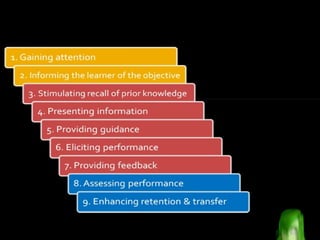
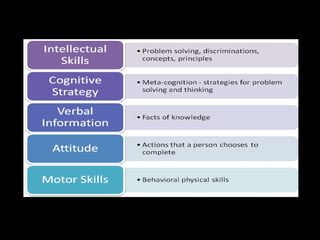
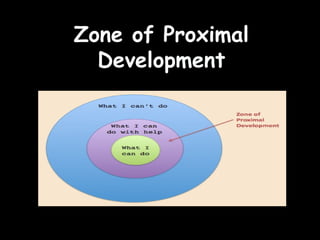
The document summarizes several cognitive learning theories including Bruner's theory of three stages of intellectual development (enactive, iconic, symbolic), Ausubel's meaningful learning theory which emphasizes relating new information to prior knowledge, constructivist theories which view learning as an active process of constructing new knowledge based on previous experiences including those proposed by Piaget and Vygotsky, and Dewey's progressive education which emphasizes learning through hands-on experiences. Gagne also proposed a hierarchy of skills building in complexity and nine events of instruction.