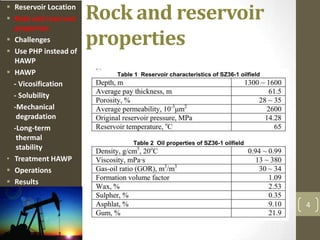
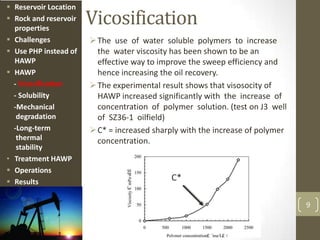
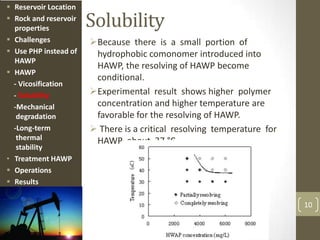
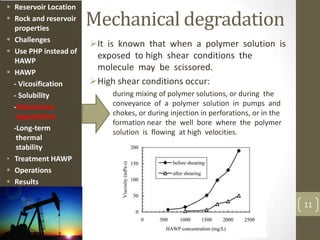
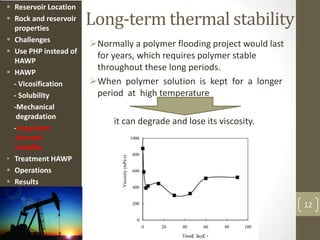
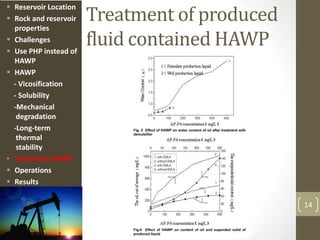
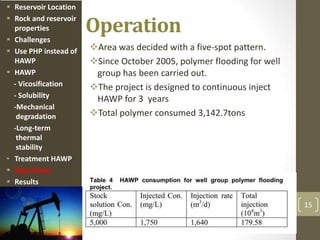
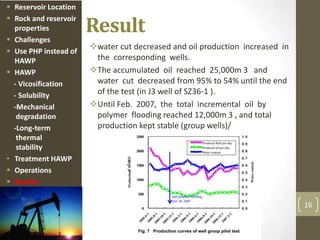
The document discusses a polymer flooding project in the Bohai Bay offshore oilfield in China. It summarizes that the project used a hydrophobically associating water-soluble polymer (HAWP) for polymer flooding due to challenges of high salinity water and highly viscous oil. The HAWP demonstrated good viscosification, solubility even at high salinity, resistance to mechanical degradation, long-term thermal stability, and could be treated from produced fluids. The polymer flooding project using HAWP achieved a decrease in water cut and increase in oil production for the wells.