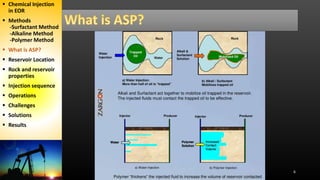
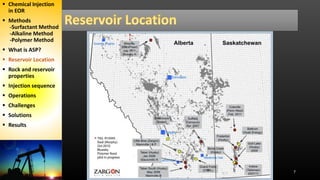
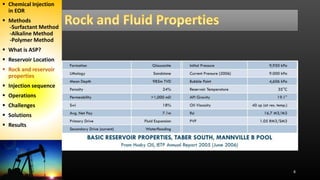
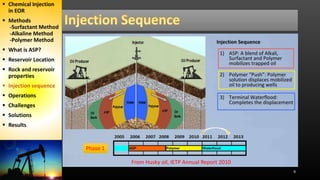
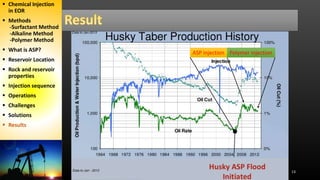
The document discusses an alkaline-surfactant-polymer (ASP) flood at an oil reservoir. Surfactants reduce oil-water tension to mobilize trapped oil while alkalis make the reservoir more water-wet. Initial ASP injection targeted 34% of the pore volume across 45 production and 18 injection wells. Major challenges included silicate scale buildup, which decreased injectivity and production over time. Later phases increased polymer injection and used improved scale inhibitors to partially address production declines, but ultimate recovery estimates were still reduced.