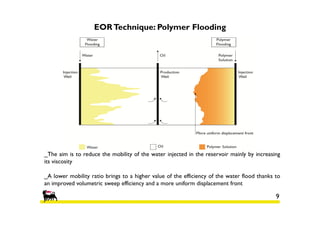
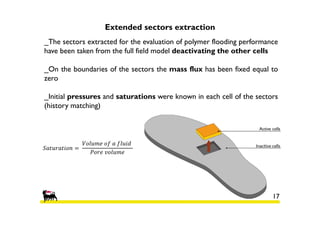
This document provides information about an oil reservoir in West Africa and enhanced oil recovery techniques being considered to increase production. It summarizes:
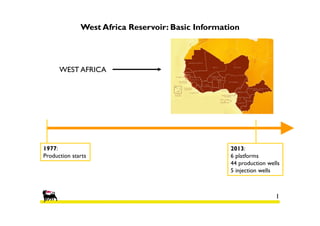
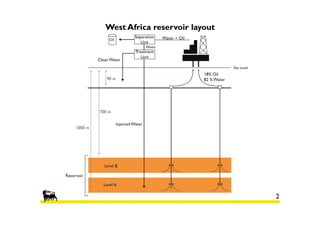
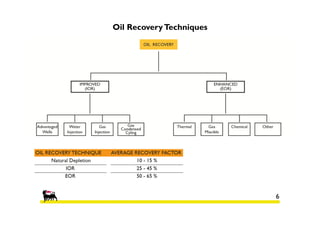
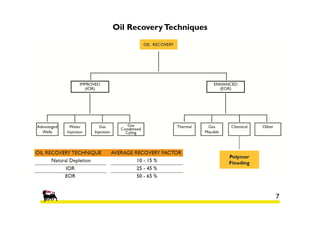
1) The reservoir began production in 1977 with 6 platforms and 49 wells currently. Polymer flooding is being evaluated as an enhanced oil recovery method.
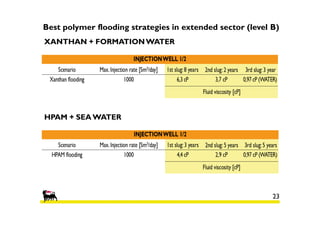
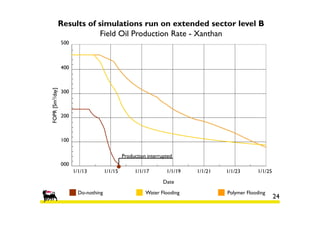
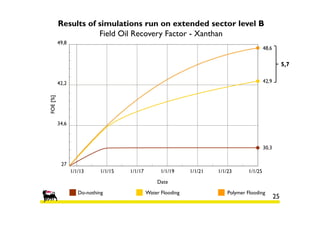
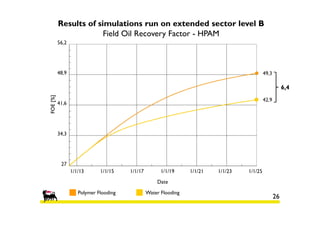
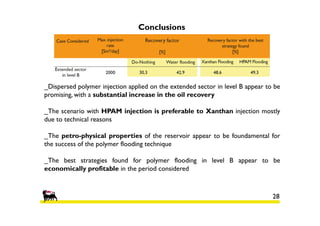
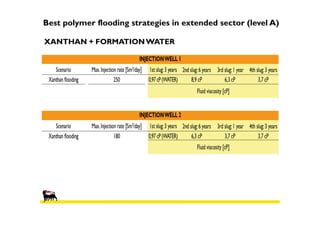
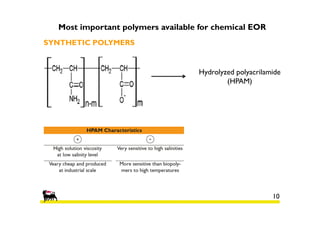
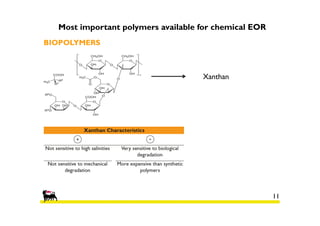
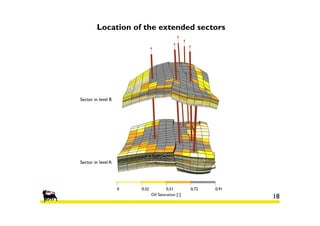
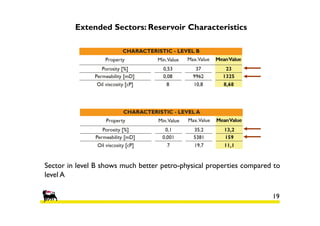
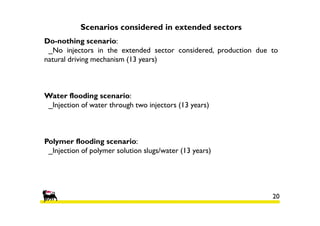
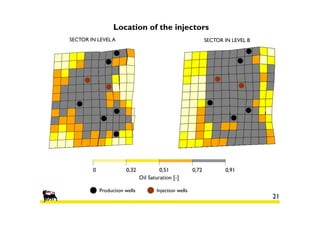
2) Simulations of polymer flooding were run on two extended sectors, with better results in Sector B. The best strategies were HPAM injection and xanthan polymer injection.
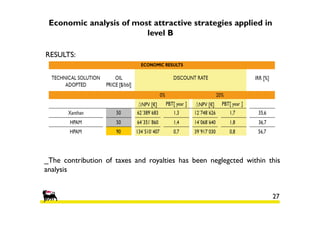
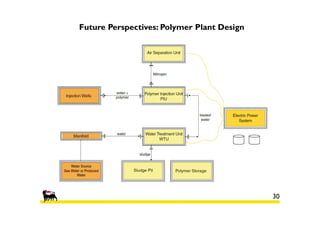
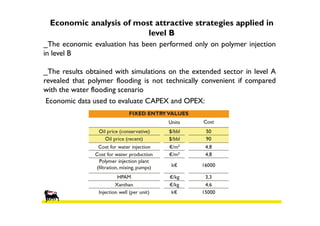
3) An economic analysis found polymer flooding in Sector B could be profitable over the evaluation period, while polymer flooding was not advantageous compared to water flooding in Sector A. Future work may include laboratory tests and full field implementation in Sector B




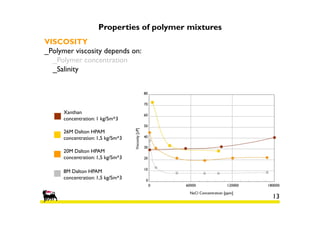
![Properties of polymer mixtures
VISCOSITY
_Polymer viscosity depends on:
_Polymer concentration
ܭൌ
ܸ݅݊݅ݐݑ݈ݏ ݎ݁݉ݕ݈ ݂ ݕݐ݅ݏܿݏ
ܸ݅ݎ݁ݐܽݓ ݂ ݕݐ݅ݏܿݏ
Viscosity coefficient (K)
40
35
30
K [-]
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
1
2
3
4
Polymer concentration [kg/Sm^3]
5
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymerinjectioneor-140201054339-phpapp01/85/Polymer-injection-eor-13-320.jpg)
![Properties of polymer mixtures
VISCOSITY
_Polymer viscosity depends on:
_Polymer concentration
_Salinity
_Shear rate
Shear rate ≈ Velocity of propagation of the mixture
HPAM
concentration 1 kg/Sm^3
HPAM
concentration 1,5 kg/Sm^3
HPAM
concentration 2 kg/Sm^3
Polymer solution viscosity [cP]
HPAM solution Viscosity vs.Velocity
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
Velocity of propagation of the mixture
[m/day]
1
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymerinjectioneor-140201054339-phpapp01/85/Polymer-injection-eor-15-320.jpg)
![Properties of polymer mixtures
ADSORPTION
_Adsorption refers to the interaction, through physical adsorption, Van
Der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding, between polymer molecules and
porous media surfaces
_Adsorption causes a reduction in rock permeability
Polymer adsorption [g/grock]
HPAM adsorption curve
0,00003
0,000025
0,00002
0,000015
0,00001
0,000005
0
0
1
2
3
4
Polymer concentration [kg/Sm^3]
5
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymerinjectioneor-140201054339-phpapp01/85/Polymer-injection-eor-16-320.jpg)

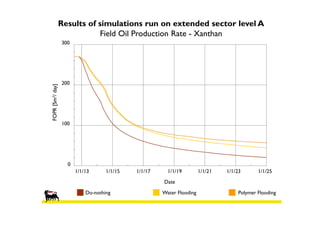
![Results of simulations run on extended sector level A
1/1/2025
FOE = RECOVERY FACTOR
0,4
Do-nothing
Water Flooding
Polymer Flooding
0
0,08
0,16
0,24
0,32
0,4
Polymer Concentration
[kg/Sm^3]
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymerinjectioneor-140201054339-phpapp01/85/Polymer-injection-eor-23-320.jpg)