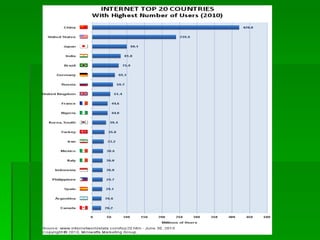
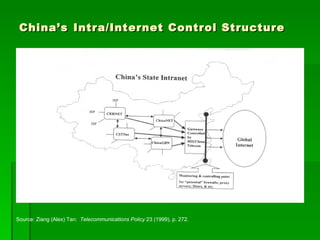
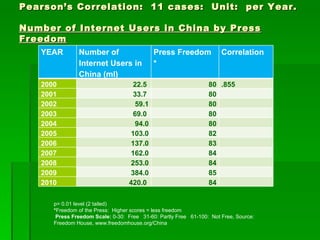
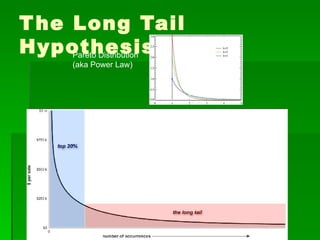
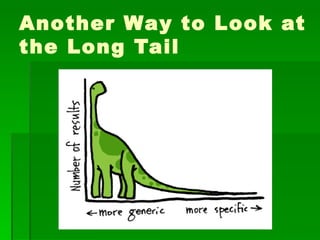
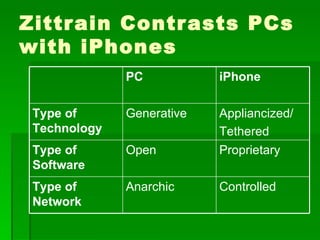
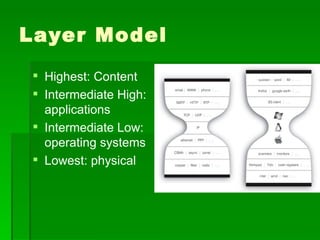
This document contains summaries of several topics related to politics and control of the internet. It discusses protests in Poland against the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement (ACTA), China's structure for controlling internet access, a correlation between internet users and press freedom in China, concerns about how the internet may impact diversity of political views and comparisons to traditional media, types of user-generated content on the internet, and questions about how certain groups may be helped or hurt by an open internet model.