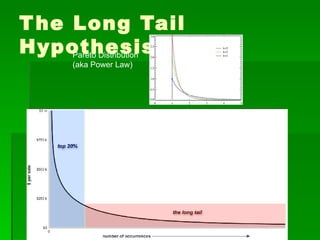
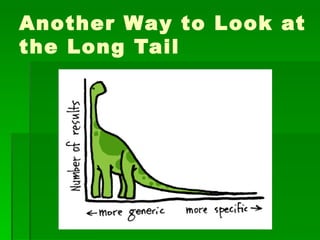
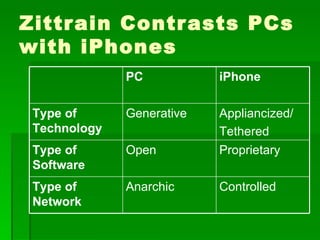
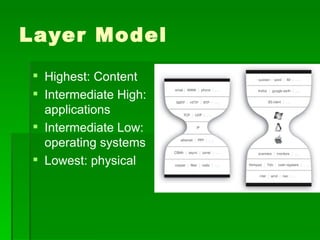
The document discusses some of the original concerns around how the internet impacts political views and democracy. It also discusses concepts like user-generated content, the long tail hypothesis, and generative vs. tethered technologies. Some risks of generative and anarchic networks mentioned include malware, incompatibilities, and use by criminals or for hate speech/censorship. Tethered networks can also enable censorship and monitoring of private information.