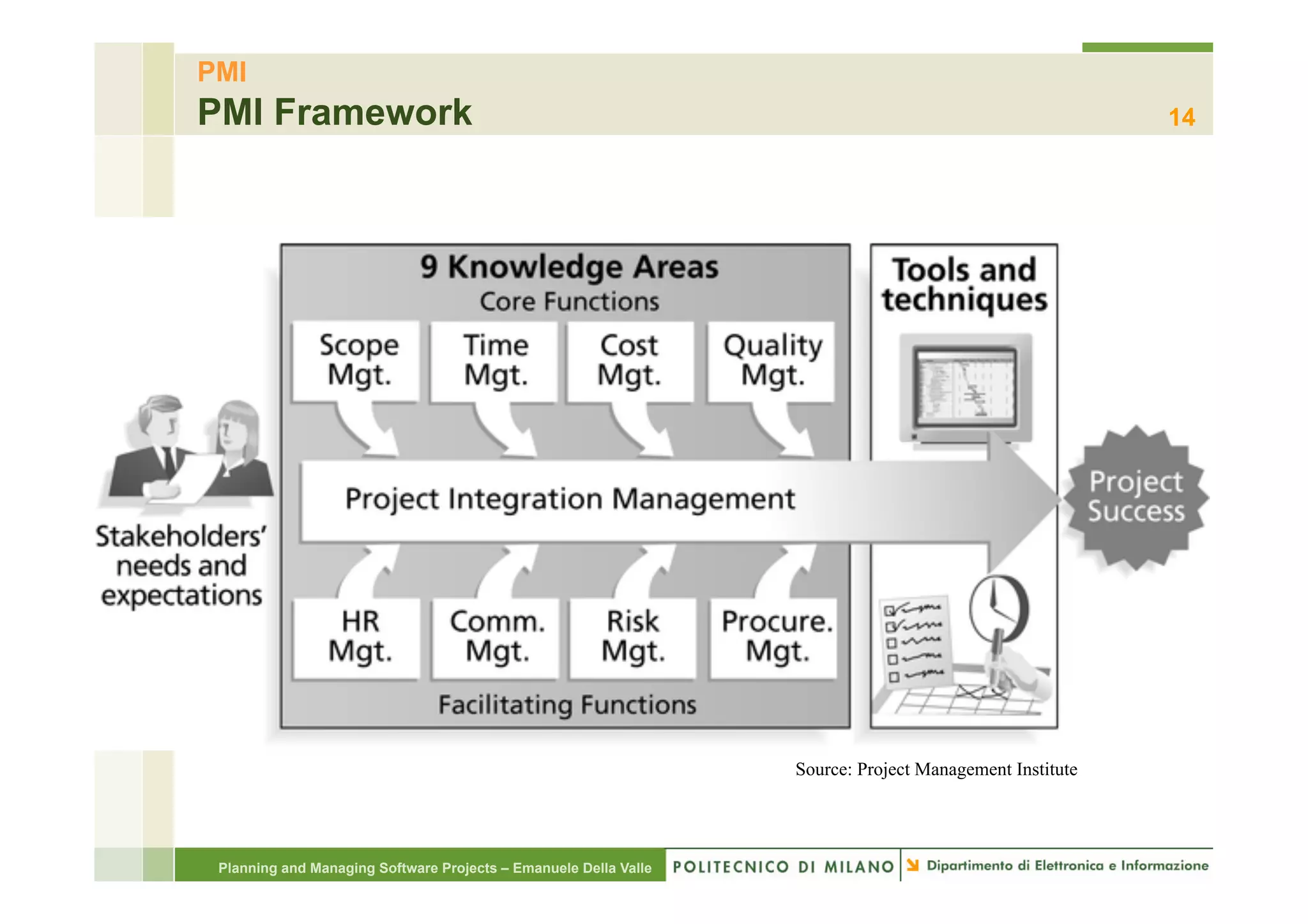
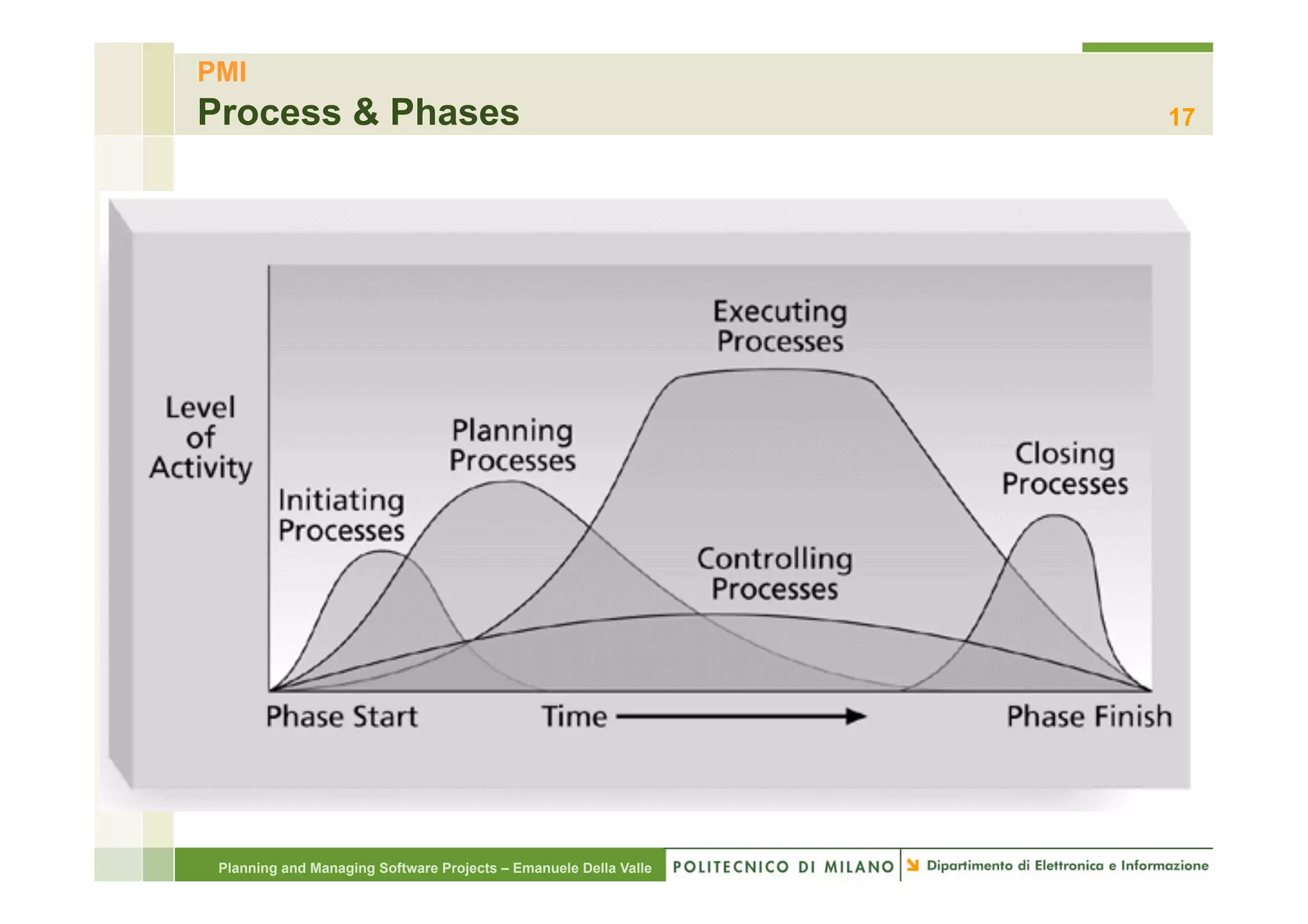
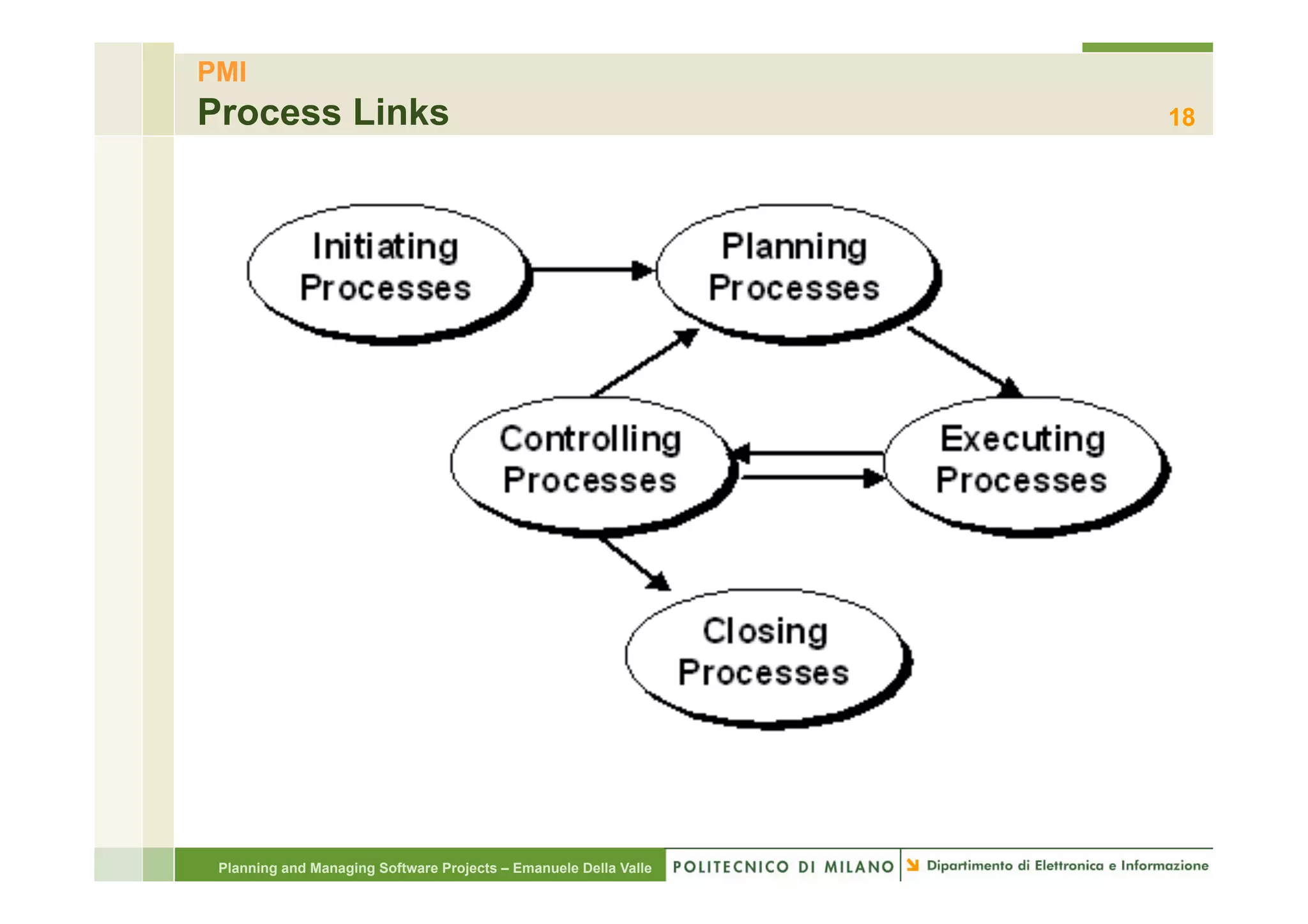
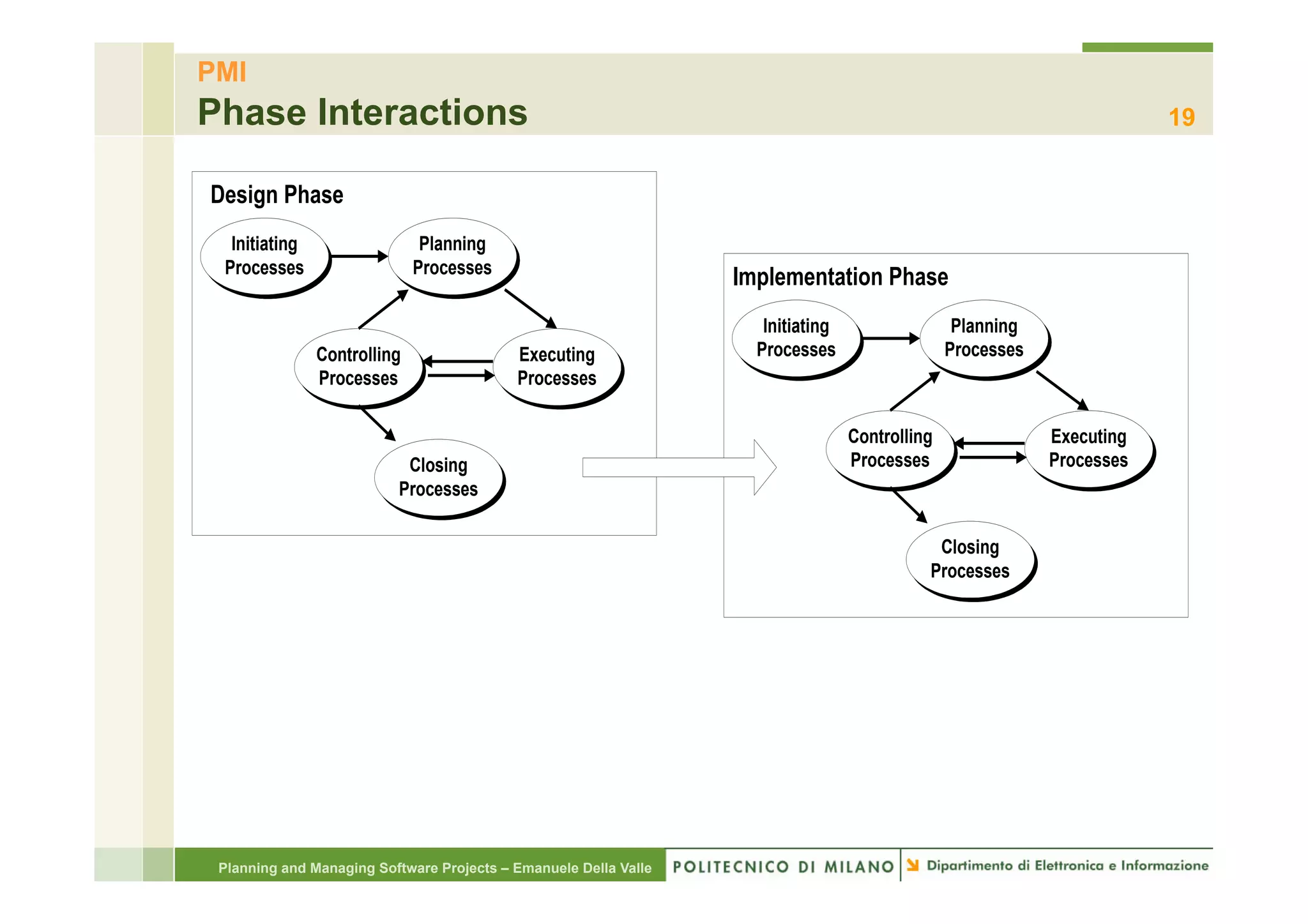
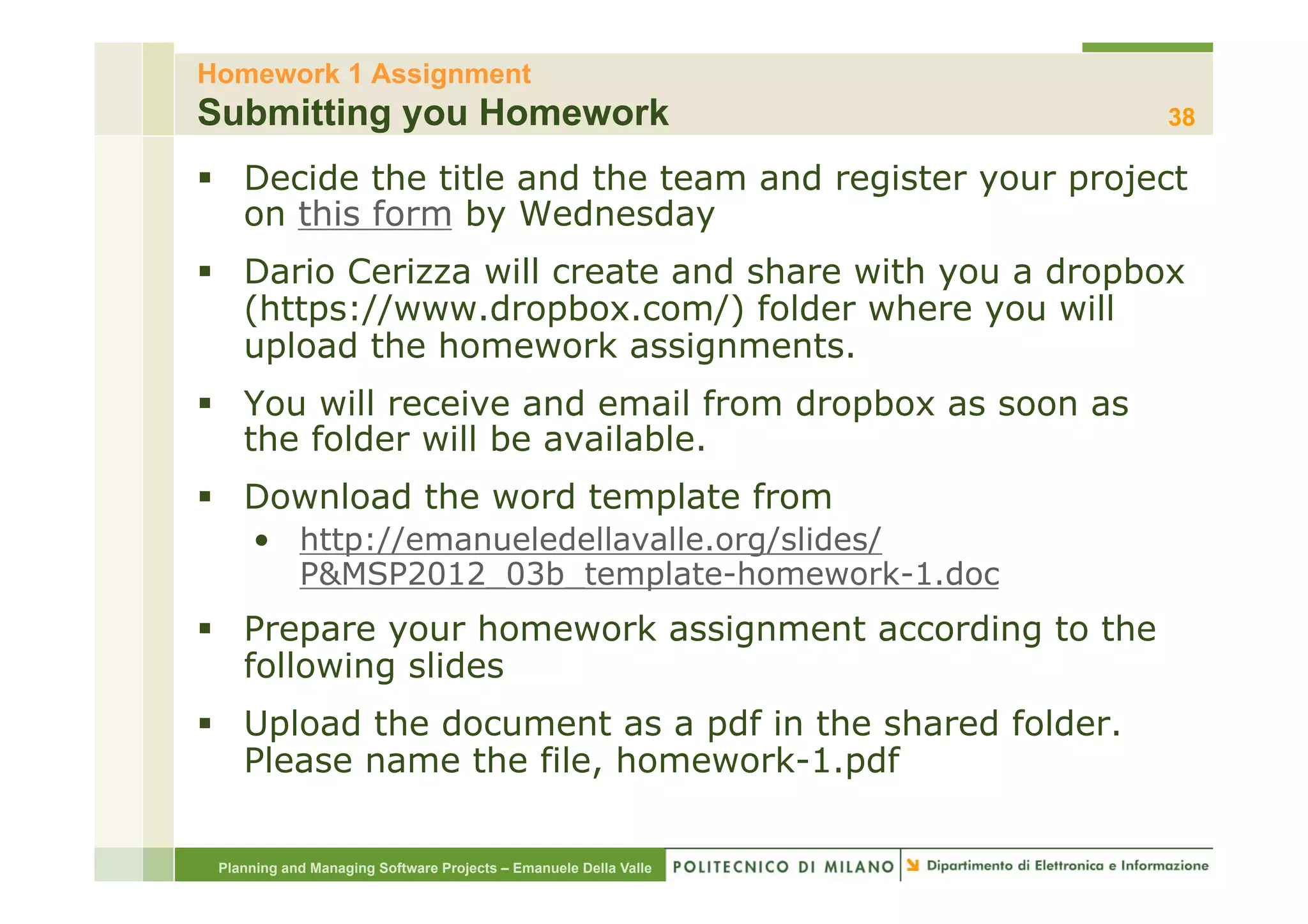
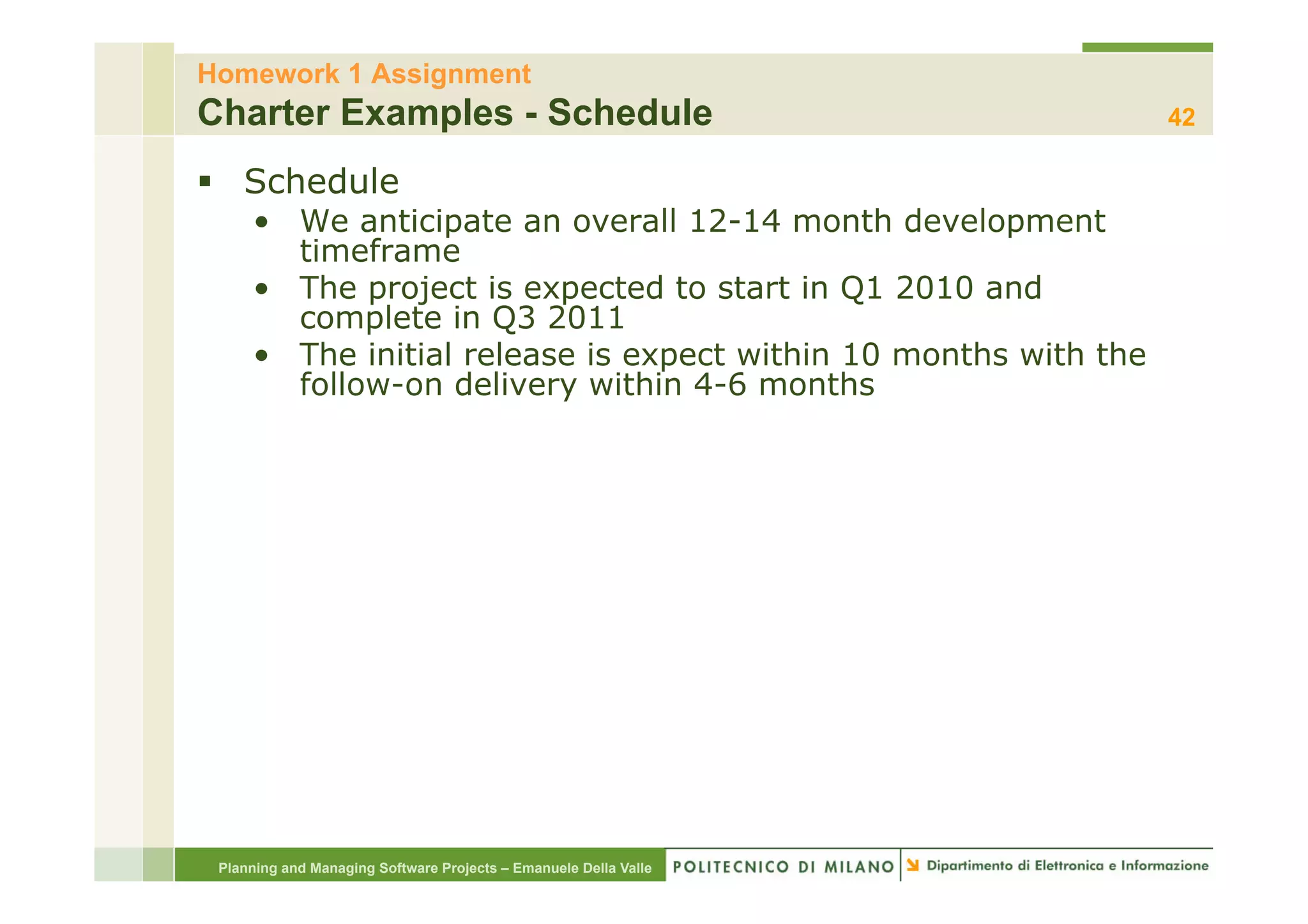
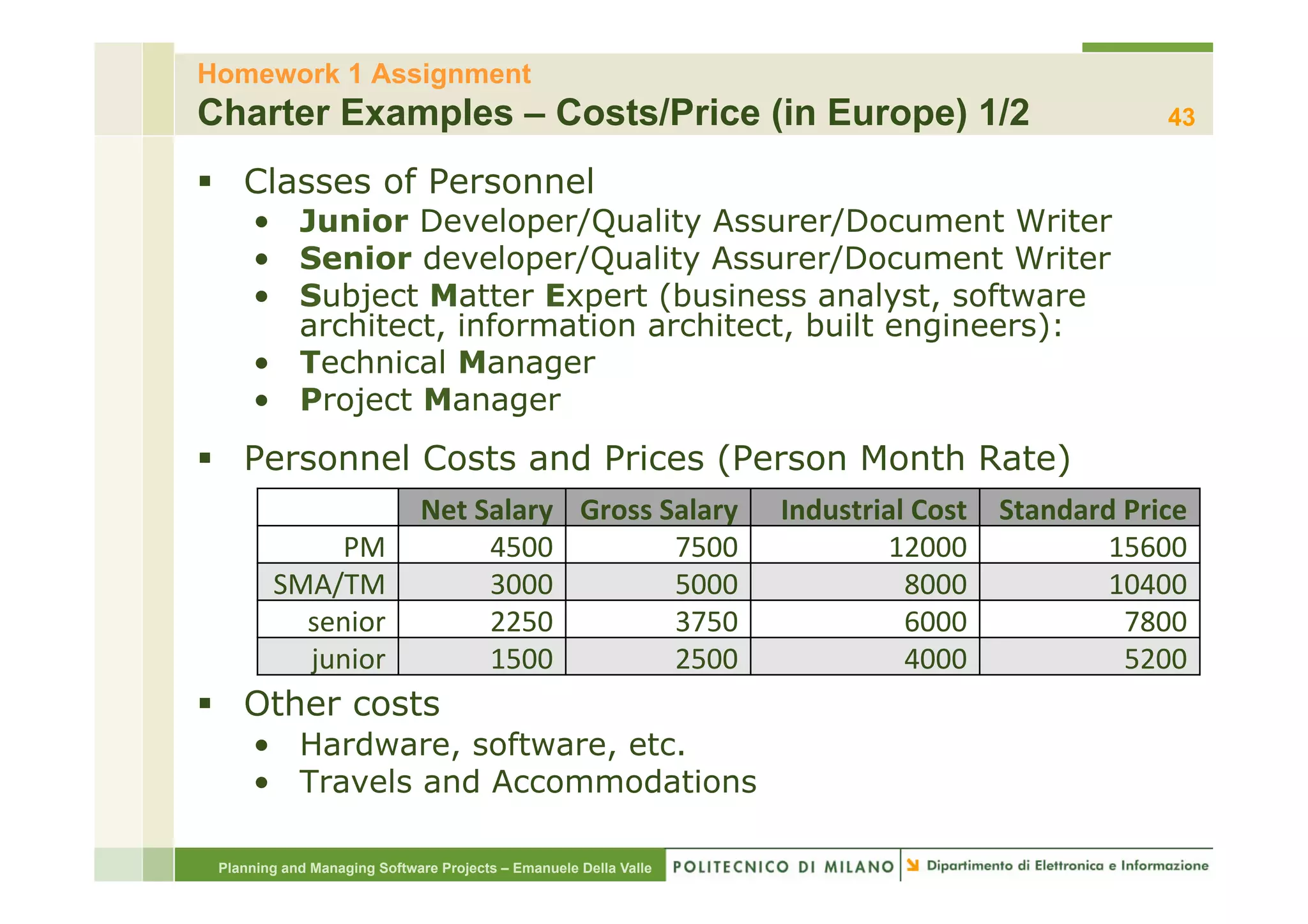
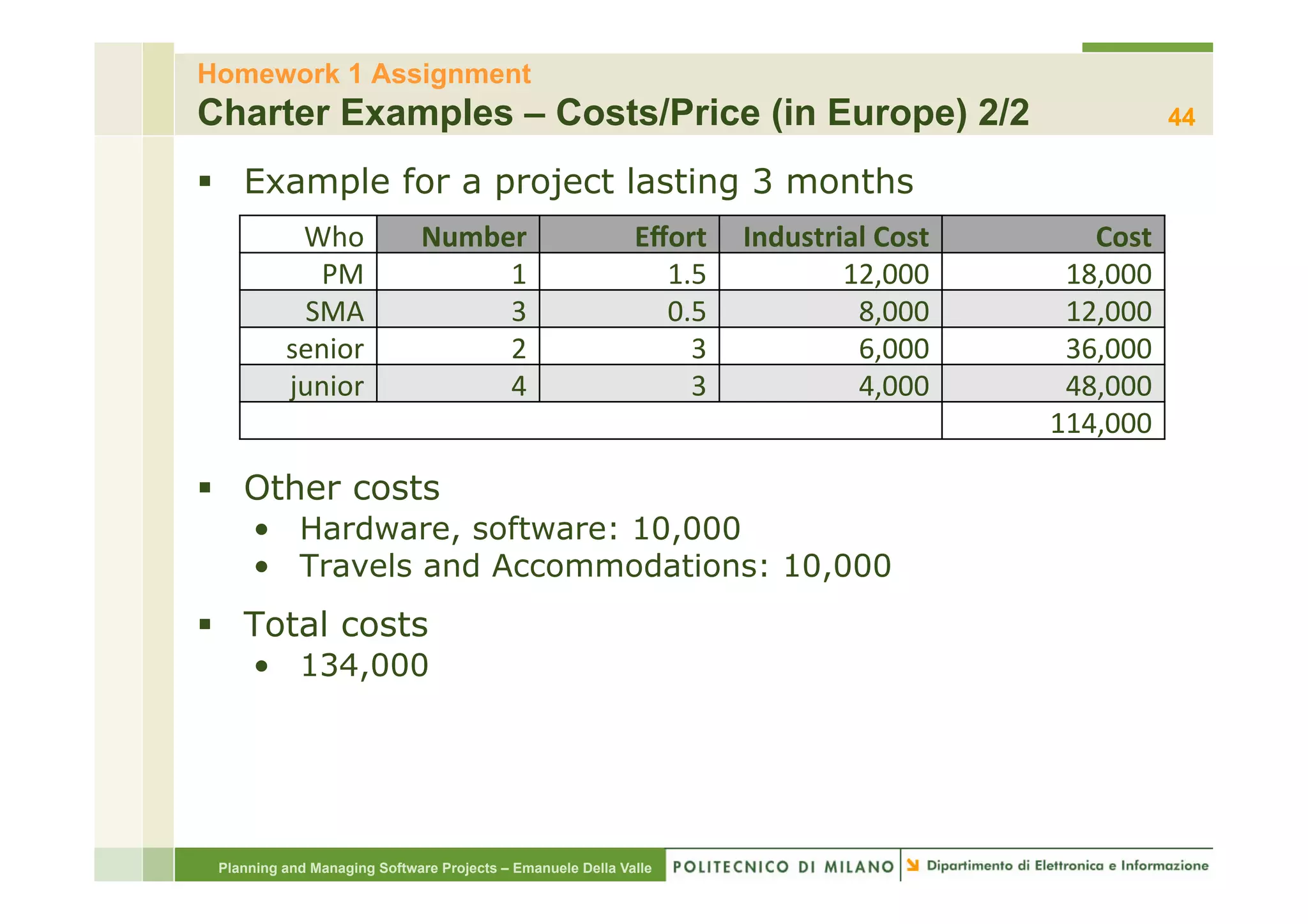
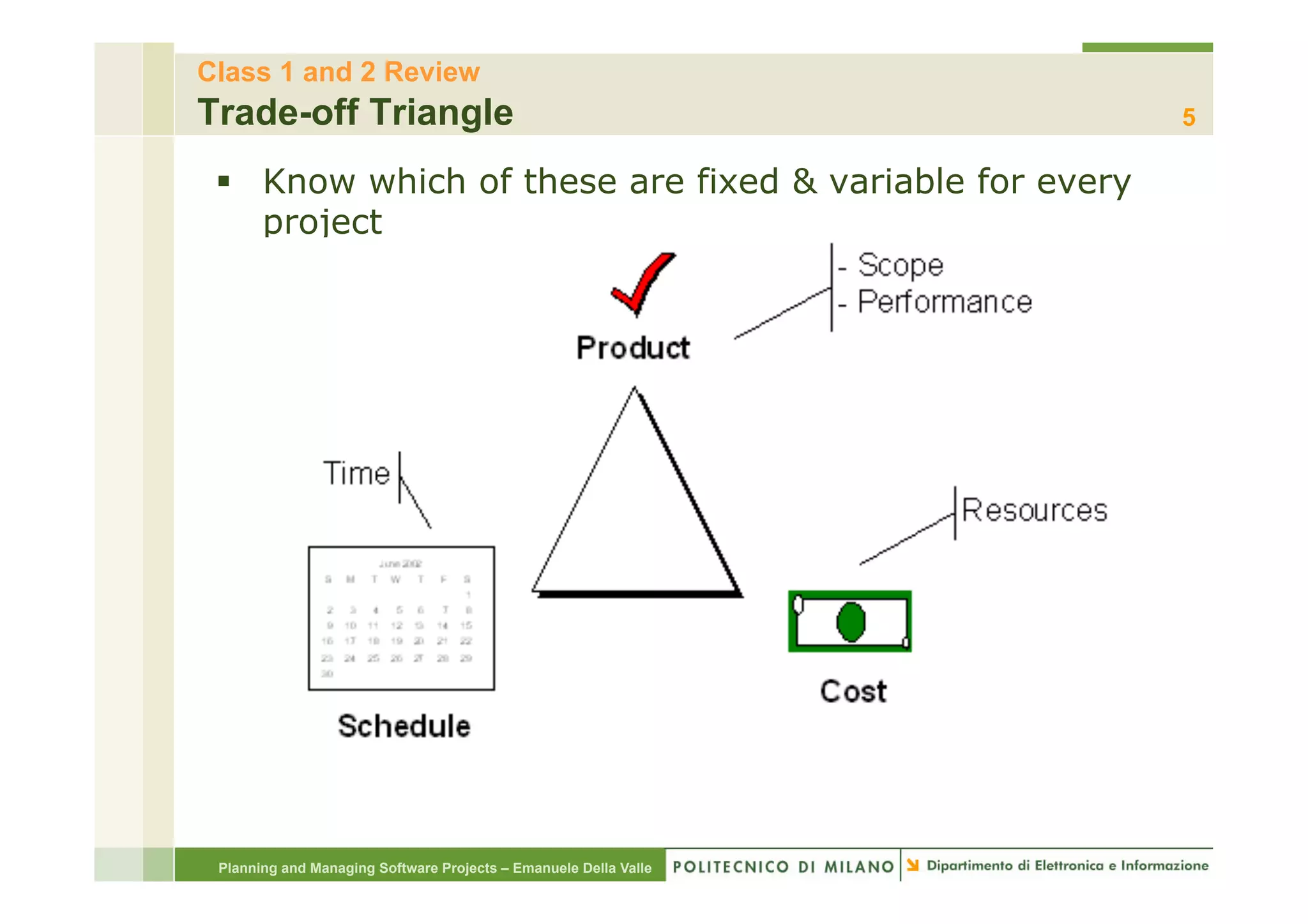
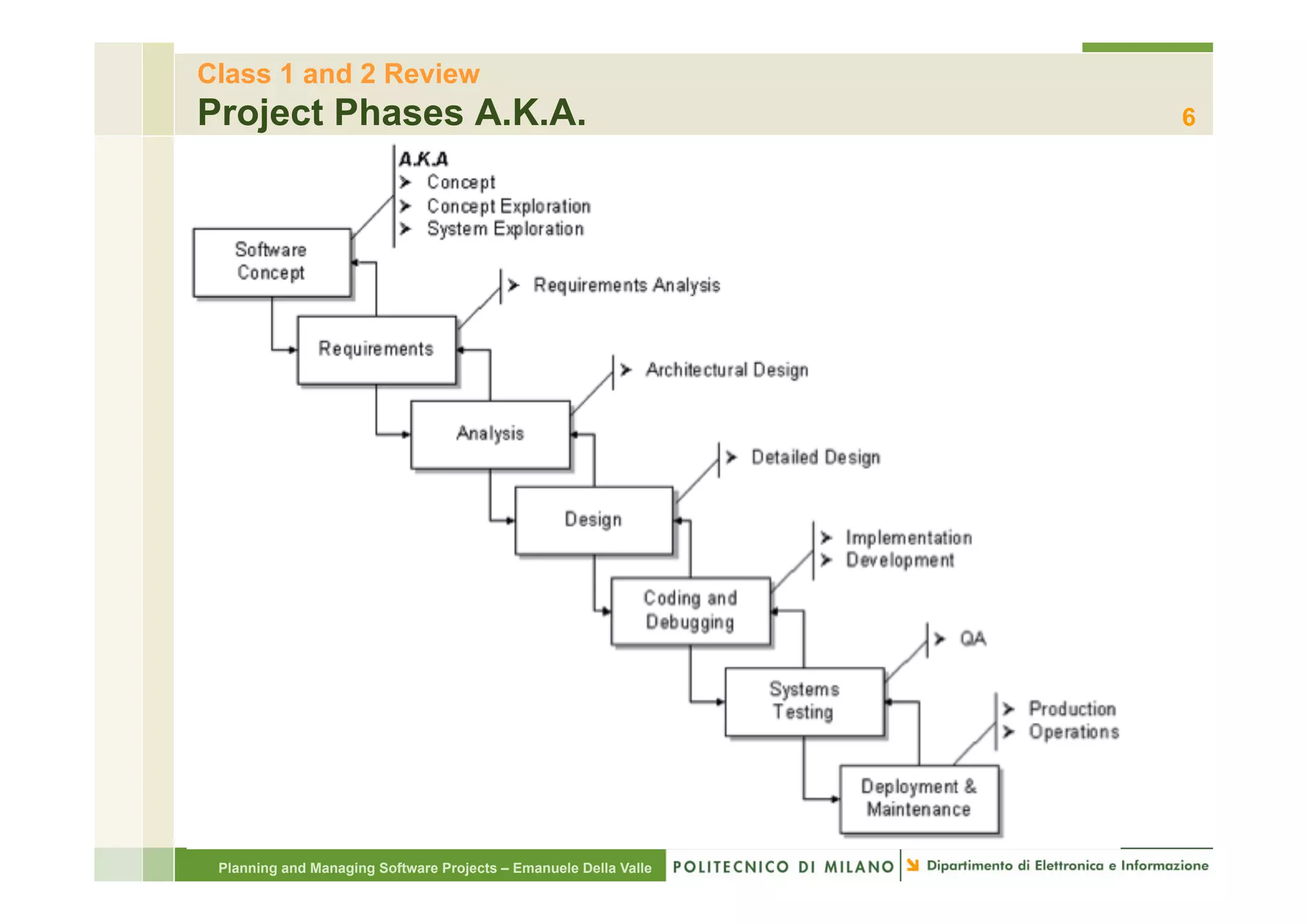
The document provides an overview of software project management principles as taught in a class. It covers project selection, initial documentation like the Statement of Work (SOW) and Project Charter, and factors contributing to project success. Additionally, it discusses the Project Management Institute (PMI) framework, including process groups and knowledge areas critical for managing software projects.







![Introduction to class 3 - Why Do Projects Succeed?
Stakeholder Triad 11
1. Function Representative
• The business person
• Or SME: Subject Matter Expert
2. Executive Sponsor
• Project s visionary & champion
• Also the General , Fall Guy [1], and Minesweeper
• Not the PM, Santa Claus , or the Tech Guy
3. Project Manager
• The Linchpin [2]
• Must be multi-lingual
[1] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fall_guy
[2] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linchpin
Planning and Managing Software Projects – Emanuele Della Valle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmsp201203understanding-software-project-management-120316091019-phpapp02/75/Understanding-Software-Project-Management-11-2048.jpg)
![Introduction to class 3
15 PM Job Functions 12
§ Define scope of project § Identify and evaluate
risks
§ Identify stakeholders,
decision-makers, and § Prepare contingency plan
escalation procedures
§ Identify
§ Develop detailed task list interdependencies
(work breakdown
structures) § Identify and track critical
milestones
§ Estimate time
requirements § Participate in project
phase review
§ Develop initial project
management flow chart § Secure needed resources
§ Identify required § Manage the change
resources and budget control process
§ Evaluate project § Report project status
requirements
[source: Northwest Center for Emerging Technologies, "Building a Foundation for
Tomorrow: Skills Standards for Information Technology,"Belleview, WA, 1999]
Planning and Managing Software Projects – Emanuele Della Valle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmsp201203understanding-software-project-management-120316091019-phpapp02/75/Understanding-Software-Project-Management-12-2048.jpg)