The document outlines the principles of project cost management, including direct and indirect costs, fixed and variable costs, and the significance of life cycle cost and value analysis. It details the steps involved in planning cost management, estimating costs, determining budgets, and controlling costs, with a focus on various techniques such as earned value management and financial analysis methods. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of cost estimates, management reserves, and performance metrics to ensure effective financial oversight throughout a project's lifecycle.












![Lecture 07 : Project Cost Management (17/18)
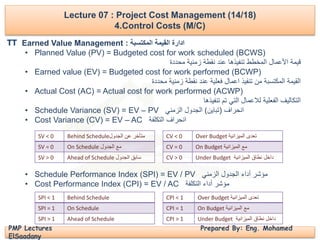
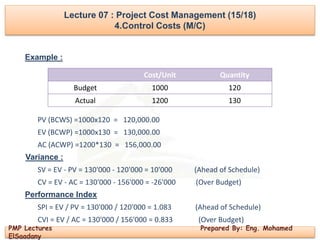
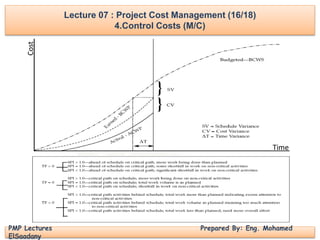
4.Control Costs (M/C)
PMP Lectures Prepared By: Eng. Mohamed
ElSaadany
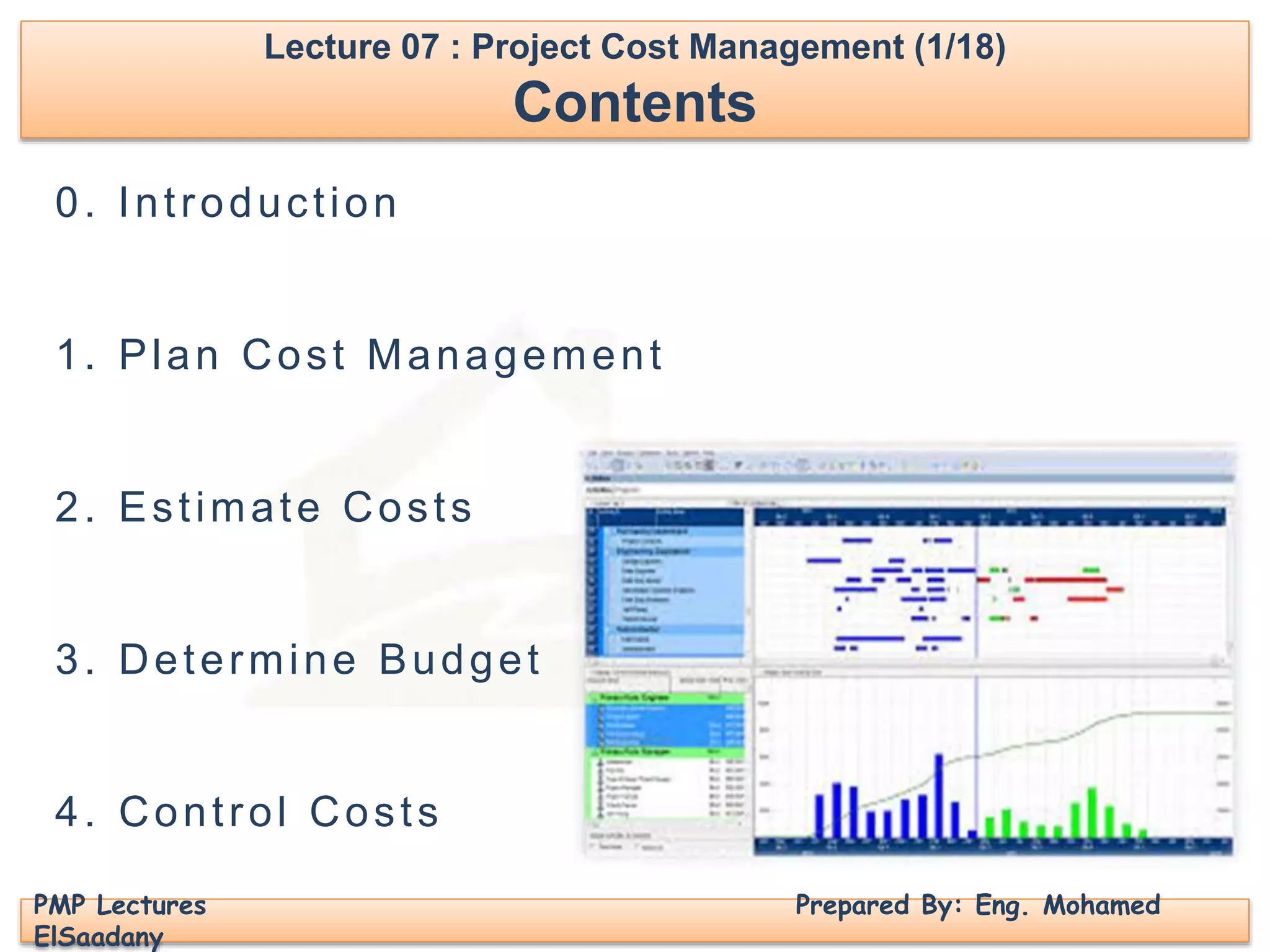
Forecasting : معايير خالل من التوقع
• Estimate at Completion (EAC) = Actual Cost+ Estimate to Complete (ETC).
المشروع نهاية في المتوقعة القيمة=اآلن حتى الفعلية القيمة+المشروع النهاء المتوقع
• There are various methods to calculate the Estimate to Complete (ETC)
المشروع النهاء المتوقعة القيمة لحساب طرق عدة يوجد
1- At the budgeted rate :
EAC = AC + (BAC – EV)
2- Considering CPI :
EAC = AC + [ (BAC – EV) / CPI ] = AC + BAC/CPI – EV/CPI
= AC + BAC/CPI – AC = BAC / CPI
3- Considering CPI and SPI :
EAC = AC + [ (BAC – EV) / (CPI x SPI) ]
TT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-cost-160117080633/85/PMP-Preparation-07-Cost-Management-17-320.jpg)
