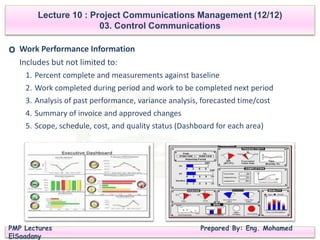
Lecture 10 focuses on Project Communications Management, detailing the planning, managing, and controlling of communications within projects. It emphasizes the importance of efficient and effective communication methods while identifying various communication types and technologies. The lecture outlines the processes required to create a communications management plan and monitor communication performance throughout the project lifecycle.