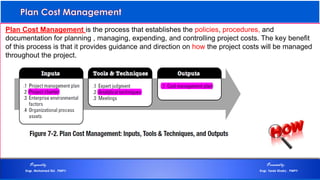
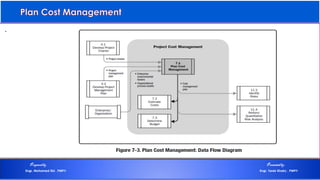
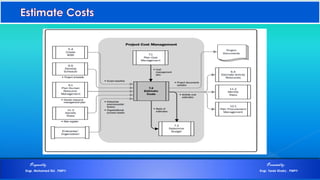
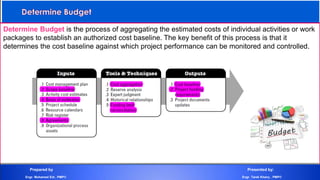
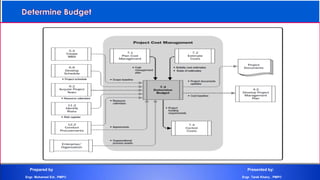
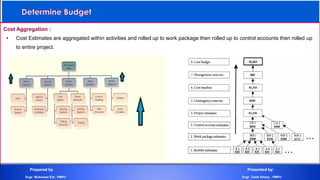
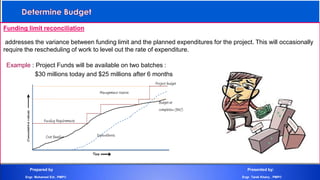
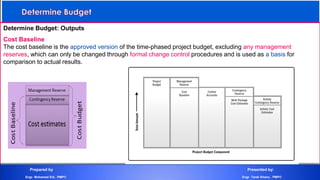
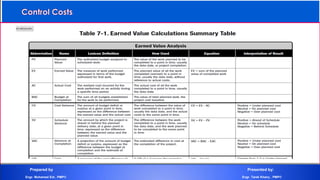
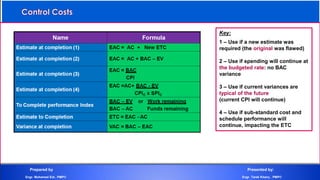
The document discusses project cost management and is presented by Engr. Mohamed Eid and Engr. Tarek Khairy. It covers key aspects of project cost management including estimating costs, developing budgets, and controlling costs. The presentation defines important cost management terms and outlines the processes and techniques used to estimate costs, determine budgets, and control costs over the lifetime of a project.